Powerful fintech innovations are redefining how businesses and consumers transact, invest, and interact with money.
Qubit Capital stands at the forefront of this dynamic environment, using its expertise to bridge capital and technology. We empower startups, entrepreneurs, and investors worldwide to thrive in both emerging and established markets.
In this comprehensive guide, you’ll discover how innovation in fintech—including artificial intelligence (AI), blockchain, and embedded finance—shapes industry growth globally.
You’ll also learn about the roles of RegTech, investor psychology, and regional trends in Latin America, MENA, Southeast Asia, and Europe.
Explore the Future of Fintech Funding to uncover additional insights into shifting capital opportunities for forward-thinking investors and entrepreneurs.
Understanding the FinTech Growth Sector
Overview of FinTech Industry Growth
The fintech industry growth has surged over the past decade, driven by disruptive fintech technologies and changing consumer expectations.
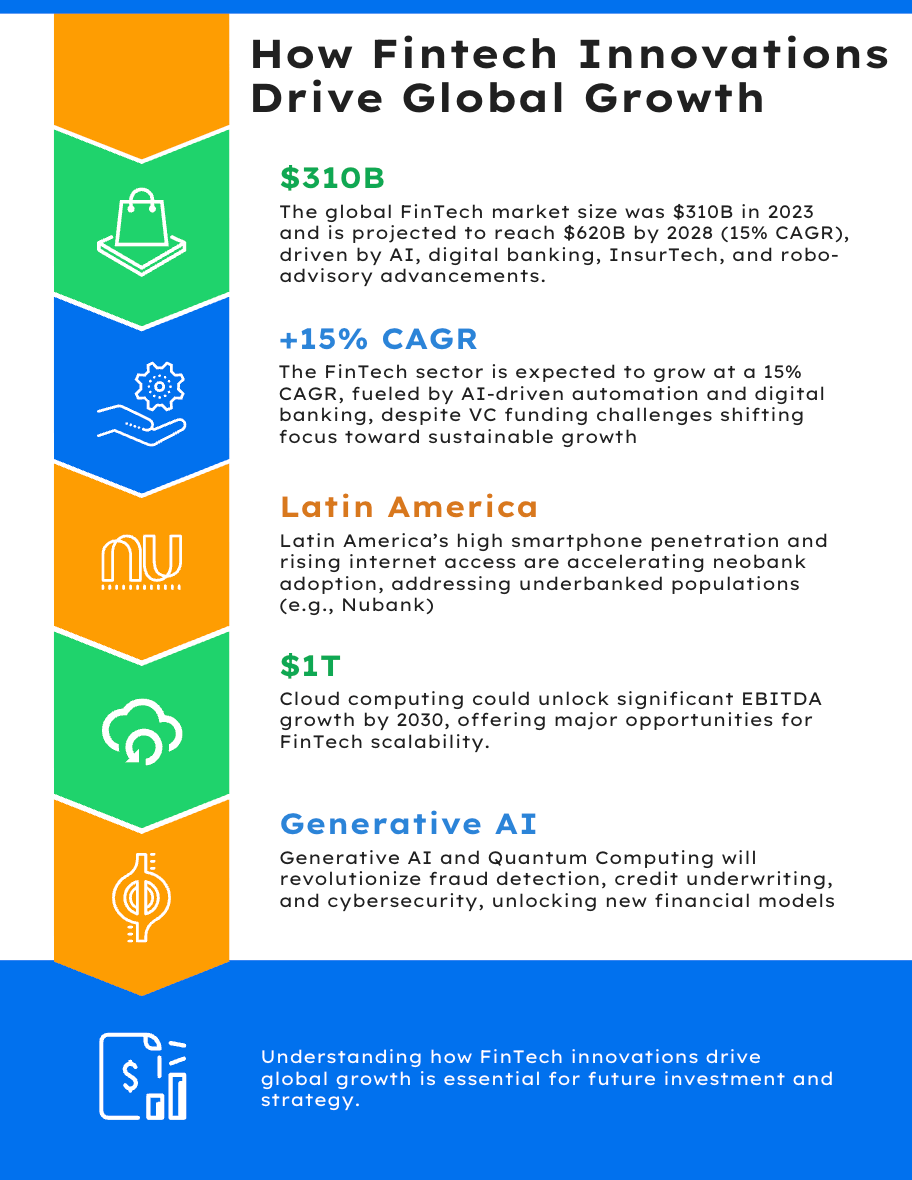
Global market valuations reached around $310 billion in 2023, with projections indicating a leap to $620 billion by 2028. This expansion, estimated at a CAGR of roughly 15%, stems from innovations in digital banking, payment processing, InsurTech, and robo-advisory services.
Healthy profitability emerges from streamlined onboarding, AI-powered credit scoring, and advanced analytics, which cut operational costs and boost customer retention. Digital-only banks (neobanks) attract users by offering convenient, user-friendly platforms without the overhead of physical branches.
Yet the FinTech ecosystem also faces headwinds. A slowdown in global venture capital (VC) funding has compelled many startups to prioritize sustainable growth over rapid scaling, proving that clear value propositions and competitive advantages matter more than ever.
Emerging Markets Spotlight
While North America and parts of Europe have dominated for years, newer regions—particularly Latin America and MENA—are becoming FinTech epicenters. These markets provide untapped potential to address underbanked populations and introduce novel financial solutions.
Latin America
Rapid smartphone penetration and rising internet usage have fueled growth in fintech across Latin America. Many residents remain unbanked or underbanked, creating strong demand for digital banking, peer-to-peer lending, and payment solutions.
Companies like Nubank in Brazil illustrate how offering user-centric services—free credit cards, straightforward digital experiences, and minimal fees—can spark incredible user growth.
Middle East and North Africa (MENA)
MENA countries like the United Arab Emirates (UAE) and Saudi Arabia have launched FinTech sandboxes, allowing innovative businesses to experiment under regulatory supervision.
Peer-to-peer lending service Beehive and buy-now-pay-later (BNPL) provider Tamara exemplify the region’s appetite for frictionless, technology-driven finance. This focus on innovation, combined with supportive policies, fosters a thriving ecosystem positioned for ongoing momentum.
Southeast Asia and Europe
Southeast Asia showcases embedded finance within super-apps, such as Grab and Gojek, blending ride-hailing, food delivery, and fintech capabilities in one ecosystem.
Europe’s Payment Services Directive 2 (PSD2) encourages open banking, sparking an array of startups that compete with traditional financial providers by offering real-time payments, cross-border transfers, and enhanced digital services.
For strategic forecasts on up-and-coming markets, Explore Fintech Funding Trends for 2025. This resource compares how rising economies may outpace global slowdowns, providing deeper insights into venture capital’s shifting priorities in Latin America, MENA, and beyond.
Technological Innovations in FinTech
Three transformative innovations in fintech stand out as catalysts for industry-wide change: AI, blockchain, and embedded finance. Each addresses pressing industry challenges and shapes new business opportunities.
AI in Financial Services
Artificial intelligence underpins modern fintech technologies, delivering efficiency, security, and personalized experiences at scale.
Operational Efficiency
AI-driven automation slashes manual processes across back-end operations. Chatbots, for example, resolve customer queries swiftly and reduce wait times.
Machine learning models also improve credit scoring by analyzing unconventional data sources—like social media and behavioral patterns—to offer more accurate approvals and quicker turnaround.
Fraud Detection and Security
AI excels at recognizing anomalies in payment and transaction data. Real-time alerts help businesses halt fraudulent behavior before severe damage occurs. Additionally, biometric security—like facial recognition or fingerprint scanning—heightens digital protection and grants customers peace of mind.
Stripe is a leading example of real-time fraud prevention, investigating patterns to differentiate suspicious activity from legitimate transactions. With adaptive machine learning, these platforms become increasingly precise, thereby curbing fraudulent incidents and enhancing trust in digital finance.
Personalized Banking
AI elevates user experiences by tailoring financial products to individual lifestyles. Algorithms can recommend personalized investment portfolios, budget insights, or specialized loan offers. This deep understanding of customer behavior cultivates loyalty, especially when combined with user-friendly apps.
To dive deeper, Learn more about AI in financial services and explore how AI transforms credit underwriting and risk mitigation strategies.
Blockchain and Distributed Ledger Technologies
Blockchain disrupts traditional finance by establishing decentralized, tamper-resistant systems. Its transparent nature, coupled with robust security features, has the potential to reinvent payments, remittances, supply-chain finance, and more.
Enhancing Transparency and Security
Because each transaction is securely logged and verifiable, blockchain cuts down on fraudulent activities and eliminates the need for multiple intermediaries. Solutions like Ripple handle cross-border payments affordably and within seconds, bypassing the sluggish procedures of legacy systems.
Major financial institutions, such as JPMorgan Chase, are also launching proprietary blockchain frameworks to optimize internal transactions.
Smart Contracts and DeFi Solutions
Smart contracts—self-executing agreements recorded on the blockchain—minimize the chance for disputes by ensuring that terms are automatically enforced.
Meanwhile, decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms like Aave and Compound challenge traditional banking by offering lending and borrowing without central oversight.
In several emerging markets, blockchain-powered remittance services reduce transaction times from days to minutes, effectively reaching underserved groups. This highlights blockchain’s power in boosting financial inclusion.
Embedded Finance
Embedded finance integrates financial tools directly into non-financial ecosystem platforms, enabling users to manage money, borrowing, and insurance without leaving a familiar interface.
Redefining Customer Journeys
Imagine an e-commerce site offering instant credit within its checkout process or a ride-hailing app granting microloans to drivers. These scenarios exemplify embedded finance.
Shopify, for instance, streamlines merchant payments with Shopify Payments, sidestepping third-party solutions. By embedding financial tools, businesses expand service offerings, create new revenue streams, and exemplify user-centric design.
Expanding Access for Small Businesses
Embedded finance especially benefits small enterprises with limited capital or manpower. Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) vendors embed invoicing, short-term credit, and payment solutions into products that help owners track cash flow and secure funding more easily.
Through partnerships with established finance providers, these SaaS companies keep compliance overhead low while delivering convenience.
Market Trends and Growth Opportunities
The FinTech world isn’t static. Emerging regulations, consumer tastes, and investor preferences shape market evolution. Staying aligned with these trends helps entrepreneurs and investors position themselves for success.
Regional Analysis (Deep Dive)
A closer look at regional ecosystems reveals how cultural norms and policy environments guide fintech innovation.
• Latin America has seen a boom in neobanks catering to millennials and underbanked populations.
• MENA focuses on experimentation inside regulated sandboxes, boosting solutions in payments and lending.
• Southeast Asia thrives on super-apps, merging all-in-one financial and lifestyle services.
• Europe promotes open banking and cross-border interoperability, encouraging highly competitive digital finance offerings.
For data that outlines how these continents stack up, Explore global market trends. This reference uncovers potential hot spots for FinTech expansion and explains each region’s unique regulatory climate, helping investors gauge risks and opportunities accurately.
Funding and Investment Outlook
Despite global VC funding fluctuations, regional hubs remain robust, proving that localized demand can sustain FinTech growth—even when aggregate funding dips.
Global VC Trends
Fewer mega-rounds suggest a pivot to sensible valuations and business models oriented toward profitability. Startups that balance innovation with clear paths to revenue stand out. Risk-averse investors now scrutinize leadership teams, regulatory compliance, and user adoption before committing capital.
Regional Resilience
Various markets in Asia-Pacific and parts of Africa continue to attract attention for solutions addressing financial inclusion. Investors see not only profit potential but also social impact, forging a dynamic landscape where innovative startups can thrive.
Investor Psychology and Cultural Considerations
Investment decisions often hinge on local risk tolerance and consumer sentiment. For example, Southeast Asia’s appetite for novel payment apps contrasts with Europe’s more cautious approach, which stresses data security and compliance. Understanding these nuances is essential.
Cross-border expansions demand cultural awareness and strategic partnerships to mitigate friction from differing regulations or consumer expectations.
Regulatory and Compliance Innovations
Innovation transforms finance, but it also brings fresh regulatory challenges. As financial services modernize, they need advanced solutions to safeguard user data, comply with rules, and maintain public trust.
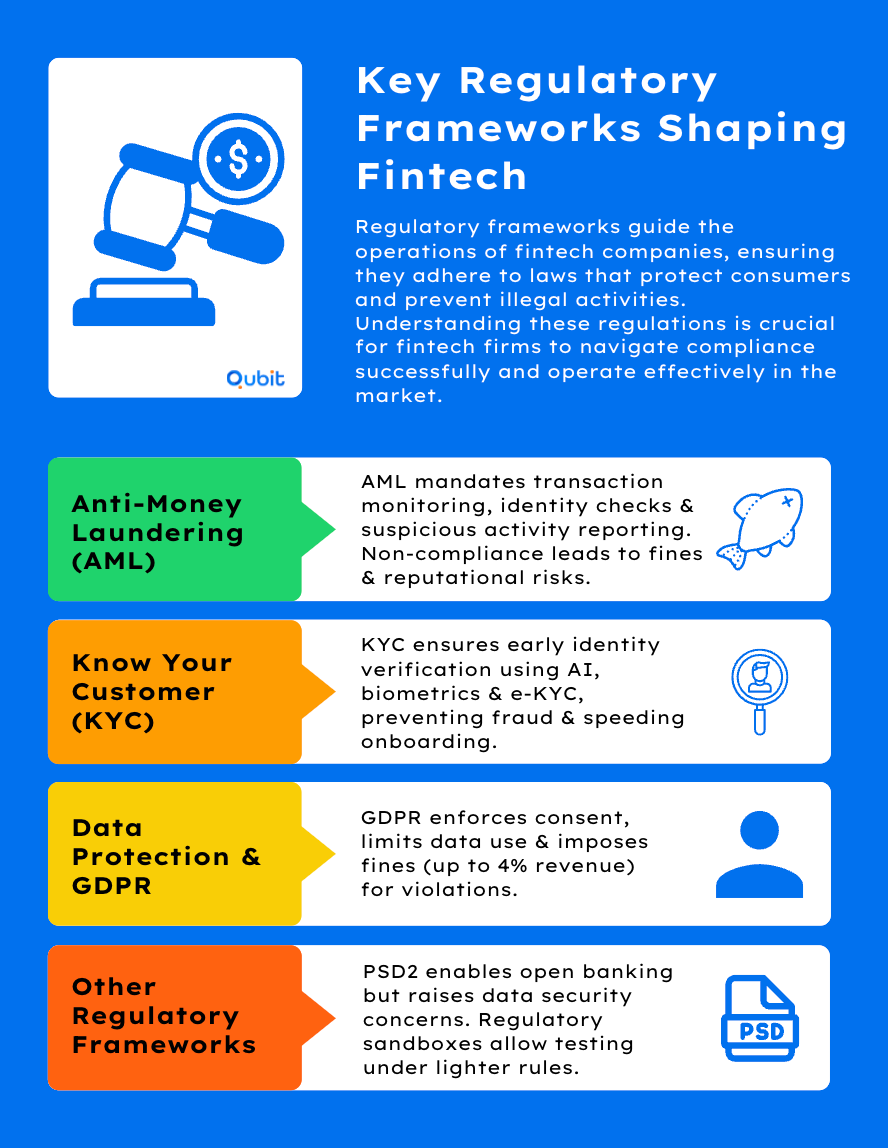
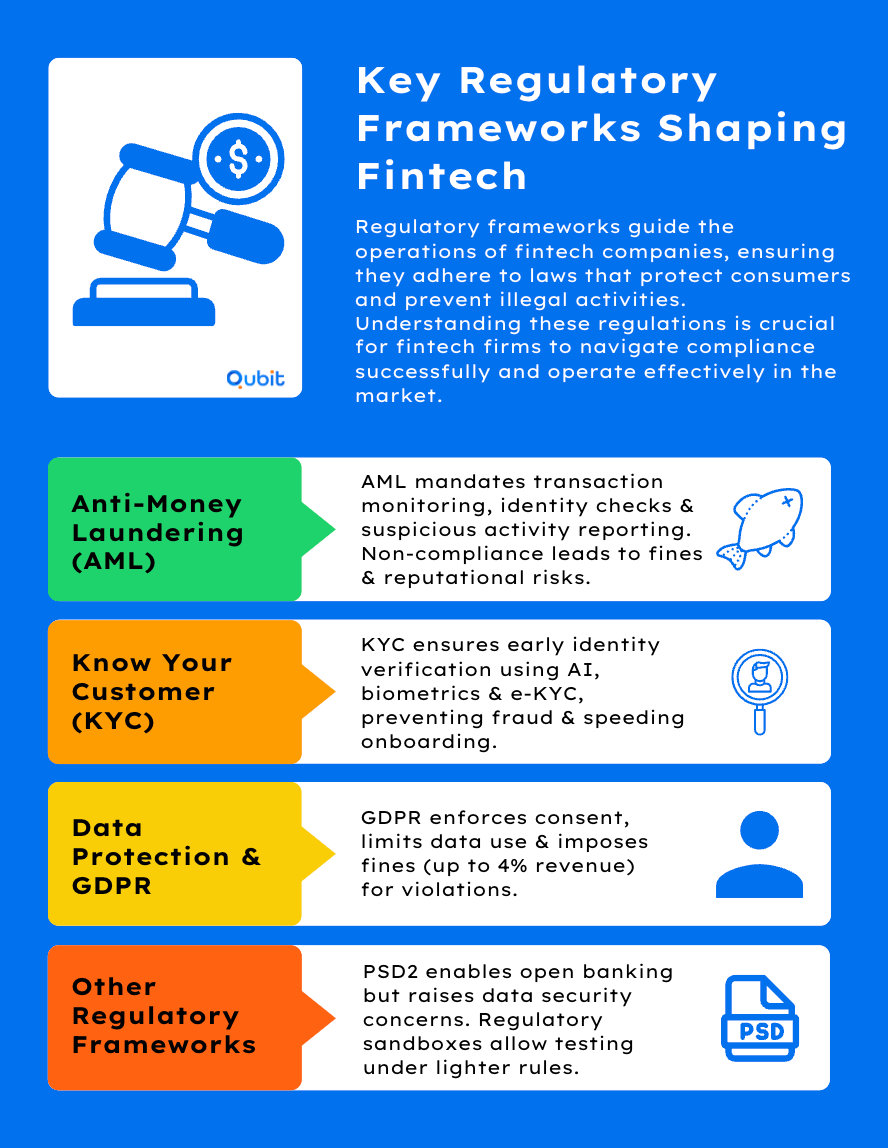
The Rise of RegTech
Regulatory technology (RegTech) automates and streamlines compliance, enabling FinTechs to focus on innovation rather than endless paperwork.
Automating Compliance Processes
AI- and blockchain-based tools handle identification checks, transaction monitoring, and Anti-Money Laundering (AML) tasks.
Companies such as Fenergo offer integrated solutions for Know Your Customer (KYC) and client lifecycle management, ensuring better adherence to industry mandates. By reducing human error, these platforms expedite compliance checks and free up resources for product development.
Reducing Costs and Enhancing Accuracy
Manual compliance procedures are notoriously expensive and prone to mistakes. RegTech simplifies and verifies tasks in real time while keeping historical records readily available for audits. For more on how these cutting-edge tools power regulation at scale, Explore RegTech advancements. This resource details emerging technologies that streamline compliance for both startups and big financial institutions.
Enhancing Transparency and Trust
RegTech solutions offer real-time oversight, creating transparent frameworks that bolster investor and consumer confidence. The improved accuracy of automated regulatory reporting means fewer penalties, better relationships with authorities, and an overall boost in brand credibility.
Balancing Innovation with Compliance
Sector growth doesn’t excuse companies from meeting rigorous standards. Successful FinTech organizations strike a balance: they harness fresh ideas while adhering to legal requirements across multiple jurisdictions.
Best Practices for Compliance
FinTechs that embed compliance into their business strategies earn investors’ trust and maintain stable user growth. Adopting robust data encryption, agile governance, and ongoing staff training fosters a culture prepared for regulatory shifts. Startups should integrate compliance into their product development to reduce costly retrofits later.
Multi-Jurisdictional Compliance
Operations spanning various nations encounter distinct consumer data and financial regulations. Tools that centralize compliance tasks—like global KYC platforms—reduce fragmentation and confusion. Collaborating with experienced local counsel also prevents inadvertent rule violations that can otherwise derail expansion.
Proactive Regulatory Engagement
Forward-thinking companies communicate regularly with regulators, voicing concerns and clarifying novel business models. This collaboration can shape practical policy guidelines that encourage responsible innovation rather than stifling creativity. It also equips FinTechs with early insights into pending legal changes, allowing them to pivot quickly.
Case Studies
Case Study A: Cloud-Powered Microloans in Latin America
A Chilean FinTech startup specialized in microloans for farmers who lacked the collateral demanded by conventional banks. By using AI on a cloud platform, the company analyzed alternate data sets—like crop yields and weather—to assess creditworthiness.
• Challenges Faced: Limited digital literacy among rural populations and initial distrust of digital financial services made adoption difficult.
• Solutions Implemented: The FinTech partnered with agricultural cooperatives, provided user-friendly mobile apps, and held workshops to build familiarity.
• Results Achieved: Default rates declined by 40%, and loan approvals rose 60% within a year. This success injected vitality into rural economies, enabling farmers to invest in better crop management and infrastructure.
Case Study B: Embedded Finance for E-commerce Growth
An Indonesian e-commerce platform introduced a buy-now-pay-later (BNPL) feature at checkout to bolster sales and user loyalty.
• Challenges Faced: Concerns about high default rates among first-time credit users and technical difficulties integrating the BNPL module.
• Solutions Implemented: The platform formed a partnership with a local risk analytics firm to refine credit scoring algorithms, swiftly identifying viable borrowers. The checkout interface remained seamless, prioritizing user experience.
• Results Achieved: The BNPL feature drove a 25% rise in total sales and saw a 10% jump in repeat customers over three months. Positive word-of-mouth and repeat purchasing propelled both income and brand loyalty.
Lessons Learned & Key Strategies
Effective innovations in fintech often share common threads:
- Local Customization: Tailor solutions to specific populations and regulatory climates.
- Strategic Partnerships: Collaborate with domain experts and community groups to build trust.
- Technology Integration: Embrace AI and cloud computing to automate workflows and scale faster.
- User-Centric Design: Refine interfaces for intuitive onboarding and reduce friction in daily use.
- Agile Mindset: Adapt continuously as user feedback, regulations, or market conditions evolve.
Overcoming Challenges in FinTech Innovations
In a rapidly shifting market, even the most groundbreaking concepts can stall if unprepared for regulatory hurdles, security risks, and tough competitors.
Common Challenges
Q: What are the challenges faced by fintech innovations?
A: Several obstacles can hamper fintech innovations, including:
• Regulatory complexities in multi-jurisdictional markets
• Cyber threats demanding advanced security measures
• Building consumer trust amid skepticism toward digital finance
• Fierce competition from both established players and emerging startups
• Maintaining scale without losing service quality or compliance
Q: How are fintech startups contributing to market growth?
A: FinTech startups spur industry expansion by:
• Reaching underserved segments (unbanked, underbanked, or niche verticals) with targeted solutions
• Driving novel, tech-driven business models and cost efficiencies
• Enhancing financial inclusion by delivering user-friendly mobile platforms
• Pressuring incumbents to innovate, ultimately benefiting consumers
Solutions and Mitigation Strategies
• Risk Management: Layered security mechanisms and AI-based fraud detection halt illicit activity.
• Regulatory Awareness: Automated compliance monitoring plus local legal counsel helps maintain alignment with shifting laws.
• Scalable Development: Test new features with small pilot groups before mass rollout.
• Partnership-Building: Partner with established banks or complementary startups to proliferate services while sharing costs.
• Continuous Improvement: Maintain feedback loops and iterative product updates to remain competitive.
• Education Initiatives: Inform users about privacy and fraud prevention, easing adoption barriers.
Qubit Capital consistently advises its investees to balance innovation, compliance, and capital efficiency. Those who master this trifecta can stand out even in crowded or tightly regulated environments.
The Future Outlook
As technology advances, fintech innovation will continue pushing boundaries worldwide. Cloud computing, generative AI, and even quantum computing promise breakthroughs that will transform the fundamental nature of finance.
Cloud Computing & Beyond 2030
Experts predict that widespread cloud adoption might unlock over $1 trillion in EBITDA across top global firms by 2030. That seismic shift stems from advantages like on-demand scalability, lower infrastructure costs, and automated compliance features built into modern cloud platforms.
Scalability and Flexibility
Cloud-hosted services allow FinTechs to scale quickly in response to demand spikes. Startups can test new features, pilot them in select markets, and expand swiftly when results prove promising.
Cost Efficiency
Rather than sinking capital into hardware, companies adopt pay-as-you-go cloud services. Freed-up funds can then be channeled into research and marketing, accelerating company growth. Tighter collaboration between data scientists and developers also speeds up innovation cycles.
Enhancing Security and Compliance
Leading cloud providers offer enterprise-grade security protocols, advanced encryption, and automated backups. Through integrated compliance features, FinTechs operating in multiple regions more easily align with local regulatory standards.
Generative AI and Quantum Computing
Technologies like generative AI and quantum computing could radically expand what FinTech can accomplish.
Generative AI
Beyond chatbots, generative AI helps build custom investment strategies, automates complex insurance underwriting, and analyzes massive sets of consumer data. The result is deeper personalization for users and more accurate risk modeling for financial firms.
Quantum Computing
Quantum computing’s unparalleled processing power will transform high-end tasks such as big data analytics, instantaneous fraud detection, and cryptography. Though still in its infancy, quantum breakthroughs may extend FinTech’s capabilities, from super-fast transaction verifications to nearly unbreakable encryption methods.
Investor & Entrepreneur Action Plan
To capitalize on these imminent shifts in fintech industry growth, strategic planning is crucial:
- Identify Promising Markets: Seek regions with supportive regulatory frameworks and surging consumer appetite for digital finance.
- Localize the Service Stack: Adapt products to each market’s cultural, linguistic, and regulatory needs.
- Adopt an Agile Roadmap: Regularly iterate offerings based on feedback and pivot swiftly to keep pace with market demands.
- Refine Your Pitch: Master Advanced Storytelling Techniques in Fintech to highlight clear benefits for investors and end users, helping your solution stand out.
This approach fosters growth exactly where demand is strongest.
Going Forward
Modern fintech innovations are reshaping finance through AI-driven personalization, blockchain-based trust, and seamless embedded finance solutions. Simultaneously, RegTech ensures compliance and global security, while cloud computing and generative AI unlock the next chapter of expansion.
Efforts in Latin America, MENA, Southeast Asia, and Europe illustrate how local culture, regulation, and consumer needs drive unique yet globalfintech innovation stories.
As a leader in aligning capital with technology, Qubit Capital champions solutions that improve access, drive scale, and adhere to regulatory standards.
Whether you’re an entrepreneur tackling microloans or an investor eyeing cross-border expansions, the opportunities to innovate in FinTech have never been greater.
If you’re ready to capitalize on advanced industry strategies, Contact Qubit Capital Today for bespoke guidance. You can also explore future-focused resources like Discover Next-Gen Payment Solutions to stay ahead in tomorrow’s finance ecosystem.
Key Takeaways
• Use AI for efficiency and personalization, especially in credit scoring and fraud detection.
• Incorporate blockchain to boost transparency and security, cutting back costly intermediaries.
• Embed financial services in existing platforms to elevate customer engagement and generate new revenue.
• Tap into emerging regions to reach underbanked populations and benefit from supportive regulators.
• Combine innovation with robust compliance practices to win investor trust and ensure long-term stability.
• Keep a keen eye on cloud computing and emerging tech (like quantum computing) for future scalability.
• Maintain adaptability, partner wisely, and refine user-focused designs to stay competitive in a crowded FinTech arena.