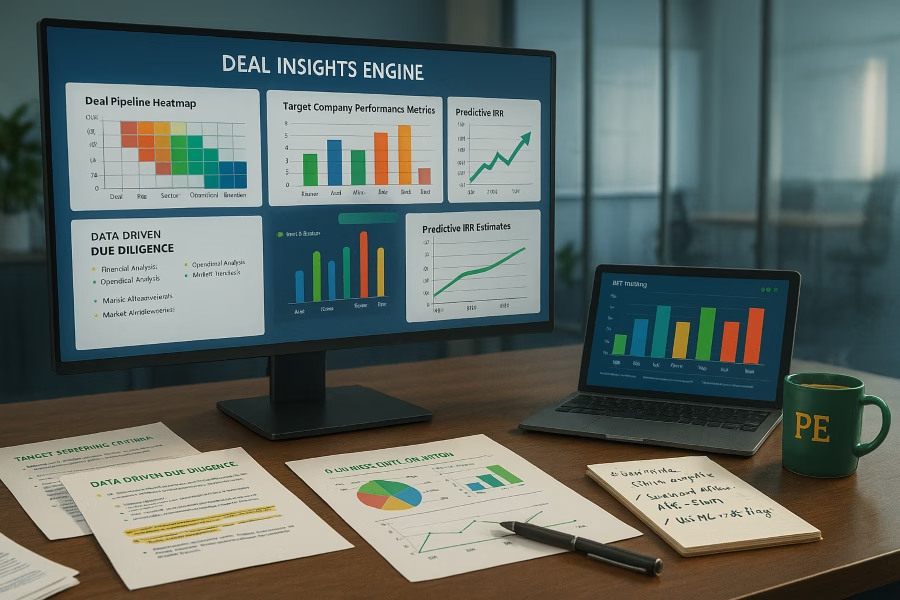
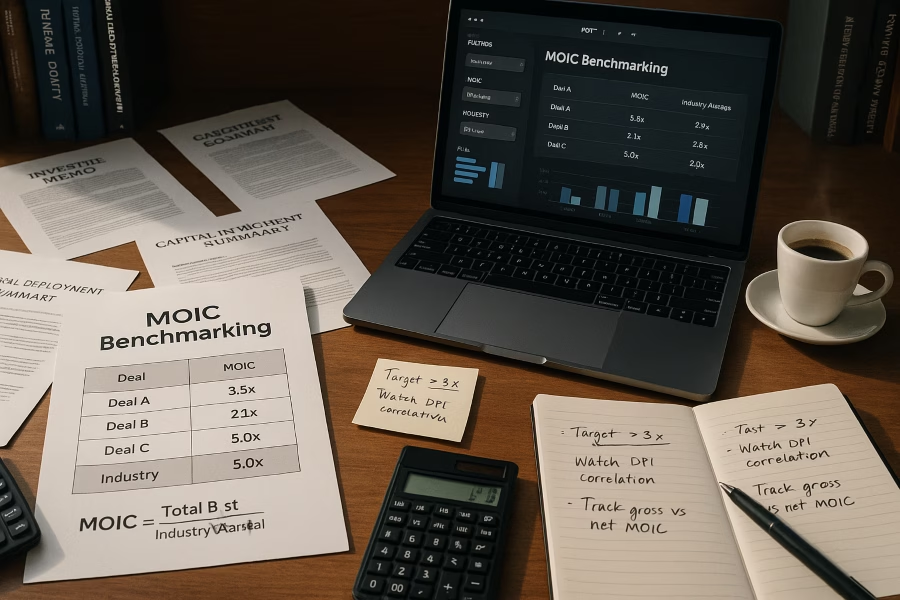
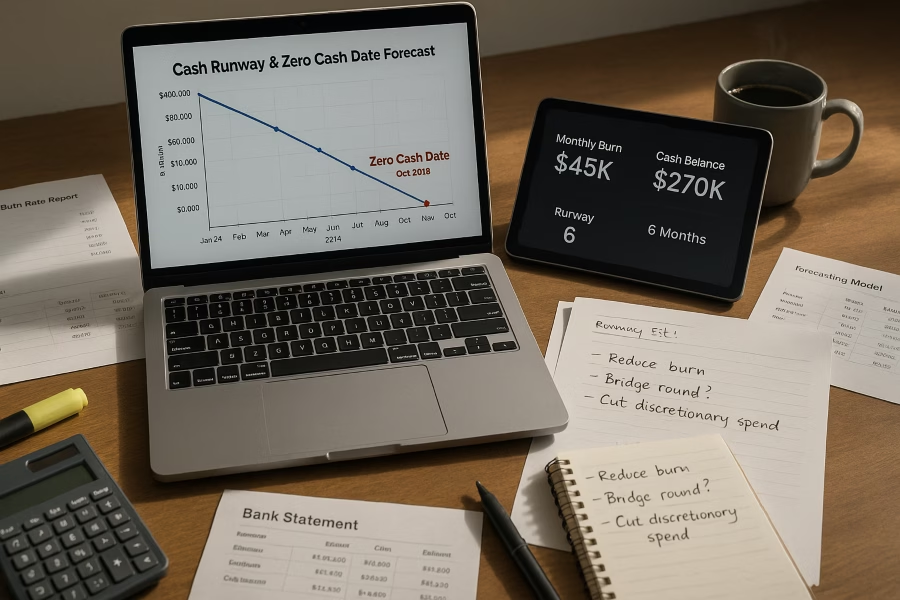
Private equity thrives on precision, and business intelligence (BI) has become the cornerstone of informed decision-making in this competitive field. By harnessing data-driven insights, firms can uncover hidden opportunities, mitigate risks, and optimize deal strategies. Whether it’s evaluating market trends or forecasting financial outcomes, BI tools empower investors to make confident, evidence-based choices.
Your evaluation of forecasting methods is complemented by perspectives on the best financial forecasting software for startups, detailing various software options to aid in accurate predictions.
This article explores how private equity professionals can use BI to gain a competitive edge, offering strategies, case studies, and actionable tips. Let’s jump right in to discover how data transforms decision-making in private equity.
Build Your Data Foundation with Business Intelligence in Private Equity
Business intelligence (BI) is transforming how private equity firms operate, offering a structured approach to collecting, storing, and analyzing data for smarter decision-making. By harnessing BI, firms can uncover actionable insights that enhance deal sourcing and portfolio management, ultimately driving stronger returns.
In private equity, the ability to process data quickly and visualize it effectively is critical. Interactive dashboards, powered by advanced BI tools, enable firms to monitor key performance indicators (KPIs) across their portfolio in real time. This ensures timely decisions that align with market trends and investment goals.
The global private equity market, valued at $787 billion in 2024, is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 8.73% through 2033. This growth underscores the importance of adopting robust BI solutions to capitalize on emerging opportunities. For example, AI-driven BI tools are revolutionizing the industry by enabling faster data processing and improving deal sourcing efficiency.
To stay ahead, private equity firms can also explore sector-specific innovations. In retail-focused portfolio companies, consider examples like Retail Tech, which highlights market disruptors that can inform investment strategies.
How Business Intelligence Boosts Your Competitive Edge and Efficiency
Business Intelligence (BI) tools are transforming decision-making processes for private equity firms, enabling them to thrive in a data-driven environment. By harnessing reliable, data-backed insights, these tools empower firms to make informed choices that drive operational efficiency and sharpen their competitive edge.
Real-Time Insights for Smarter Decisions
BI tools provide private equity firms with access to real-time metrics, allowing them to track performance and identify opportunities as they arise. This capability is particularly crucial in an industry forecasted to grow from $460 billion in 2024 to $765 billion by 2027, as highlighted in the U.S. PE Market Forecast. Such projections underscore the expanding scope of BI-driven opportunities, making timely data analysis indispensable for staying ahead.
Enhanced Efficiency Through Deep Data Analysis
Operational efficiency is another key benefit of BI frameworks. By analyzing vast amounts of data, firms can streamline processes, reduce redundancies, and allocate resources more effectively. This focus on efficiency not only improves day-to-day operations but also enhances long-term profitability.
Governance and Metrics Tracking
Robust governance is supported by BI frameworks, which ensure that firms adhere to compliance standards while maintaining transparency. Additionally, these tools simplify the tracking of key performance metrics, a trend increasingly embraced by private equity firms. As noted in the PE Trend, adopting dashboard technologies has become essential for pinpointing critical data points and optimizing strategies.
By integrating BI tools into their operations, private equity firms can achieve unparalleled efficiency and gain a competitive edge in a rapidly evolving market.
Create a Winning Business Intelligence Strategy for Data-Driven Results
A successful Business Intelligence (BI) strategy in private equity hinges on the seamless integration of high-quality data and scalable systems. By focusing on master data management, data governance, and efficient ETL processes, firms can unlock actionable insights that drive strategic decision-making and operational efficiency.
1. Establishing Master Data Management for Consistency
Master Data Management (MDM) is the cornerstone of any effective BI strategy. It ensures a single source of truth across portfolio companies, eliminating discrepancies and enabling consistent reporting. For private equity firms managing diverse investments, MDM simplifies the consolidation of financial, operational, and transactional data. This unified approach not only enhances data accuracy but also accelerates decision-making processes.
2. Implementing Robust Data Governance
Data governance is essential for maintaining the integrity and security of sensitive information. A well-defined governance framework establishes clear protocols for data access, usage, and compliance. For example, when addressing ESG-related compliance, the collaboration between Deloitte, Informatica, and Workiva serves as a model for aligning governance practices with regulatory requirements. Deloitte ESG demonstrates how thoughtful governance can simplify complex data management challenges.
3. Optimizing ETL Processes for Efficiency
Efficient ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) processes are vital for converting raw data into actionable insights. By automating data extraction and transformation, private equity firms can reduce manual errors and improve scalability. Streamlined ETL workflows also enable faster integration of new portfolio companies, ensuring that decision-makers have access to timely and accurate data.
4. Leveraging Real-Time Data Stores
Real-time operational data stores empower firms to make informed decisions based on up-to-the-minute information. These systems provide immediate visibility into key performance indicators, enabling proactive responses to market changes. For instance, transactional data analysis and vendor renegotiations led to $850K recovered in less than an hour for a Capstone Partners client. This case study highlights the rapid ROI achievable through a well-executed BI strategy.
5. Connecting BI to Broader Financial Modeling
A robust BI strategy complements broader financial modeling practices, such as scenario analysis and investor-focused projections. Additionally, insights from how to create a financial model for investors provide foundational knowledge for constructing projections that attract stakeholders.
Business Intelligence (BI) tools have evolved far beyond the limitations of traditional spreadsheets, offering businesses the ability to uncover deeper insights and make data-driven decisions with precision. While spreadsheets remain a staple for basic data organization, they often fail to meet the demands of modern BI, such as real-time analytics and dynamic visualization.
Advanced BI tools now integrate machine learning (ML) capabilities, enabling streamlined data processing and predictive analytics. These ML-driven solutions empower businesses to identify patterns and trends that might otherwise go unnoticed, providing actionable insights to stay ahead in competitive markets.
Interactive dashboards are another standout feature of modern BI tools. Unlike static reports, these dashboards allow users to explore data in real time, customizing views and drilling down into specifics. This functionality ensures that decision-makers have access to the most relevant information at any given moment.
For businesses in private equity or finance, incorporating AI-driven tools can further enhance analytics capabilities. A technical overview of ai financial modeling tools illustrates how these innovations can streamline and optimize your projection processes, offering unparalleled accuracy and efficiency.
By embracing advanced BI tools, businesses can transform raw data into meaningful insights, fostering smarter strategies and improved outcomes. Whether through ML-driven solutions or interactive dashboards, these tools are redefining how organizations approach analytics and decision-making.
What’s Next for Business Intelligence in Private Equity Analytics?
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are reshaping the future of BI, offering private equity firms unparalleled tools for data-driven decision-making. These technologies enable deeper insights by automating complex data analysis, identifying patterns, and predicting trends with remarkable accuracy. As a result, firms can make more informed investment decisions, optimize portfolio performance, and uncover opportunities that might otherwise go unnoticed.
Real-time analytics is another game-changer, empowering firms to adapt their strategies dynamically in response to market fluctuations. With access to up-to-the-minute data, decision-makers can evaluate risks, seize emerging opportunities, and refine their approaches without delay. This agility is particularly critical in the fast-paced private equity landscape, where timing can significantly impact outcomes.
Moreover, integrating real-time BI into operational workflows enhances ongoing stress testing and scenario planning. For example, a review of model robustness incorporates examples from how to stress test financial models, offering insights into the methods used for evaluating resilience under varying conditions. This ensures that firms remain prepared for both anticipated and unforeseen challenges.
As AI in Business Intelligence continues to evolve, private equity firms must stay ahead by adopting these cutting-edge tools. The ability to harness AI, ML, and real-time analytics will not only streamline operations but also provide a competitive edge in an increasingly data-driven industry.
How Allvue Systems Offers Custom BI Solutions for Private Equity
Private equity firms often face unique challenges in managing data and tracking performance across their portfolios. Allvue Systems addresses these complexities by delivering tailored BI software solutions designed specifically for private equity needs.
With Allvue’s BI solutions, firms gain access to customized dashboards that simplify decision-making. These dashboards integrate analytics and visualization tools, allowing users to track portfolio performance and monitor deal sourcing with precision. The software’s user-friendly interface ensures that even complex data is presented in an intuitive format, enabling teams to focus on strategic insights rather than data interpretation.
By offering tailored visualization and performance tracking, Allvue Systems empowers private equity firms to streamline operations and enhance oversight.
Fragmented data can be a silent obstacle for private equity firms aiming to optimize their investment strategies. Relying on traditional spreadsheets often results in isolated data silos, making it difficult to perform comprehensive performance analysis across portfolios. These silos not only slow decision-making but also hinder the ability to identify opportunities and risks effectively.
Conclusion
Business Intelligence (BI) solutions offer a transformative approach by consolidating data into unified, real-time dashboards. With cross-portfolio analytics, firms can access actionable insights that drive faster and smarter investment decisions. Breaking down fragmented data is no longer optional—it’s essential for developing competitive strategies in a rapidly evolving market.
If you’re looking to secure the right investors, we at Qubit Capital can help with our Investor Outreach service. Enhance your investor relations with data-driven insights that align with your firm’s goals.
Key Takeaways
- Strong business intelligence is crucial for informed decision-making in private equity
- Master data management and data governance reduce data silos and improve consistency
- Actionable BI strategies enhance deal sourcing and boost portfolio performance
- Advanced tools and real-time analytics provide a competitive edge
- Effective BI integration strengthens investor relations and operational efficiency