A robust financial model isn't just about attracting investors—it's a critical tool for steering your business toward success.
Investors rely on financial models to evaluate the viability and profitability of a startup. For founders, a good financial model showcases a deep understanding of their business. It has the power to convince investors of its potential.
Crafting such a model demands a nuanced grasp of what investors are truly seeking. The challenge intensifies when incorporating techniques like scenario analysis, stress testing, and integrating Key Performance Indicators (KPIs).
In this comprehensive guide, we'll delve deep into advanced financial modeling strategies and provide examples relevant to startup founders.
We'll explore investor psychology, advanced modeling techniques, and offer step-by-step guidance. This will help you craft a financial model that resonates with investors.
If you're new to financial modeling, start with our Beginner's Guide to Financial Modeling to build a solid foundation before diving into these advanced strategies.
Managing Investor Psychology and Expectations

Why do some startups effortlessly attract investor attention while others struggle to get noticed? The key often lies in understanding investor psychology and aligning your financial model with their expectations.
Investors evaluate more than just numbers; they're assessing the potential, risk, and growth trajectory your startup represents.
Why Financial Models Matter to Investors
Investors scrutinize financial models to:
- Assess Viability: Determine if your business can generate sustainable returns.
- Evaluate Risk: Understand potential challenges and your strategies to mitigate them.
- Gauge Growth Potential: See how your business can scale over time.
- Verify Assumptions: Ensure your projections are based on realistic and well-founded assumptions.
When you position your financial model with these priorities, you effectively address investor concerns and build confidence. Explore our article on What Investors Look For in Financial Models for deeper insights.
Tailoring Your Model to Different Investor Types
Different investors focus on varying aspects:
- Venture Capitalists (VCs): Look for rapid growth potential and a clear path to significant returns.
- Angel Investors: Seek innovative ideas with early traction and unique value propositions.
- Banks and Traditional Lenders: Prioritize cash flow stability and the ability to meet debt obligations.
Understand their perspectives to highlight relevant aspects of your financial model. Make it more compelling to each investor type.
Cultural Considerations in Investor Expectations
When engaging with international investors, cultural nuances can impact perceptions. Consider:
- Communication Styles: Adapt your presentation to align with cultural preferences.
- Regulatory Environments: Reflect different market conditions and compliance requirements.
- Business Etiquette: Show respect and understanding of local practices.
For strategies on building relationships across cultures, read our guide on International Networking Strategies for Startups.
Advanced Financial Modeling Techniques
To stand out in the startup arena, employing advanced financial modeling techniques is fundamental. These methods enhance the robustness of your financial model and provide deeper insights that can influence investor decisions.
Scenario Analysis and Stress Testing
Scenario analysis involves creating multiple financial projections based on varying assumptions to understand how different situations impact your business. This technique demonstrates the resilience and adaptability of your startup under various conditions.
Steps to Perform Scenario Analysis
- Identify Key Variables: Determine factors that significantly influence financial outcomes, such as sales volume, pricing strategies, or market growth rates.
- Develop Different Scenarios:
- Base Case: Your expected outcome based on current assumptions.
- Best Case: An optimistic scenario with favorable conditions.
- Worst Case: A pessimistic scenario accounting for potential setbacks.
- Model Each Scenario: Adjust your financial model for each scenario, changing only the relevant variables.
- Analyze and Compare Outcomes: Evaluate the financial statements and KPIs across scenarios to understand potential impacts.
Implementing Stress Testing
Stress testing examines the impact of extreme or unlikely events on your financial health, showcasing your preparedness for unexpected challenges.
Tools for Stress Testing
- Sensitivity Analysis: Change one variable at a time to assess its impact.
- Monte Carlo Simulations: Use statistical methods to model the probability of different outcomes.
- Financial Modeling Software: Utilize tools that handle complex simulations efficiently.
For a detailed exploration of these techniques, visit Advanced Financial Modeling Methods.
Sample Examples
Example 1: Market Expansion Scenario
A startup planning to enter a new market might model scenarios based on different market penetration rates. The best-case scenario assumes rapid adoption, while the worst-case accounts for slow growth due to competition.
Example 2: Cost Fluctuations
If your startup relies on commodities subject to price volatility, stress testing can assess the impact of sudden price increases on your cost of goods sold and profitability.
Demonstrating how your business would handle a 20% increase in raw material costs showcases risk awareness and management.
By incorporating these analyses, you provide investors with a transparent view of potential risks and your strategies to mitigate them.
Using AI-Powered Financial Modeling Tools
Integrating Artificial Intelligence (AI) into financial modeling transforms how startups forecast and analyze data. AI enhances accuracy and efficiency, providing predictive insights beyond traditional methods.
Utilizing AI and Automation
- AI Forecasting Platforms: Predict future trends using historical data and market indicators.
- Data Cleansing Tools: Automate data validation to ensure accuracy.
- Machine Learning Models: Improve predictions by learning from data inputs over time.
Enhancing Accuracy and Efficiency with AI
- Integrate with Existing Models: Use AI plugins with Excel or Google Sheets.
- Automate Routine Tasks: Reduce manual errors and focus on strategic analysis.
- Gain Predictive Insights: Uncover patterns not immediately apparent.
Sample Startup Stories with AI
Case Study: TechAdvantage
- Challenge: Needed accurate sales forecasting in a volatile market.
- Solution: Implemented AI tools to analyze customer behavior and market trends.
- Outcome: Increased forecasting accuracy by 25%, impressing investors and facilitating successful funding.
These examples illustrate how AI integration not only improves your financial model but also demonstrates your innovative approach.
Integrating Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
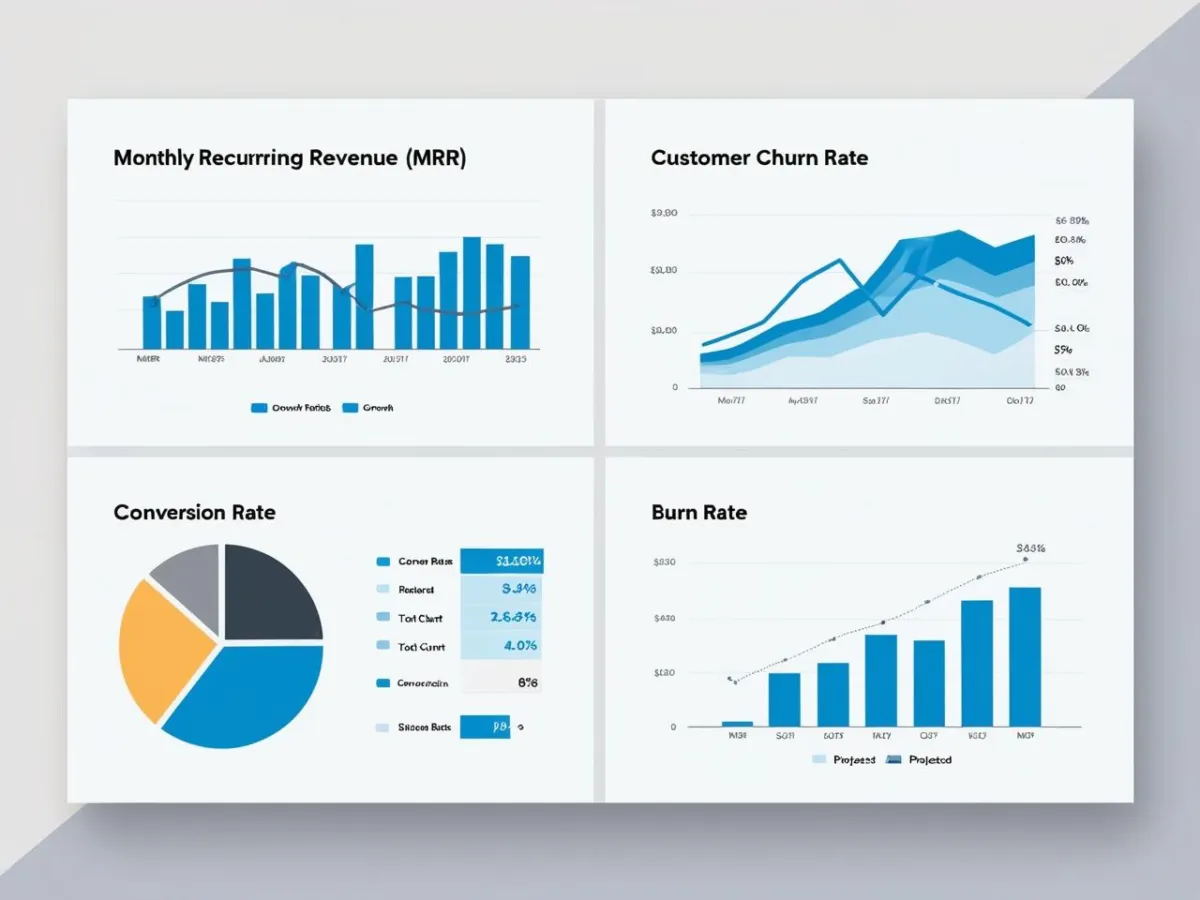
KPIs offer measurable evidence of your startup's performance and potential. Include them in your financial model to provide clear indicators of business health to the investors.
Choosing Relevant KPIs
Select KPIs that align with your industry:
- SaaS Companies:
- Monthly Recurring Revenue (MRR)
- Customer Churn Rate
- E-commerce Businesses:
- Conversion Rate
- Average Order Value (AOV)
- Manufacturing Firms:
- Production Efficiency
- Inventory Turnover Ratio
Integrating KPIs into Your Model
- Create Dashboards: Visualize KPIs with charts for quick interpretation.
- Benchmark Against Industry Standards: Provide context for your performance.
- Ensure Dynamic Updates: Link KPIs to real-time data sources.
Illustrative Examples of KPI Dashboards
- Sales Funnel Visualization: Shows conversion rates at each sales stage.
- Burn Rate Chart: Illustrates cash outflows over time, critical for understanding runway.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLV): Calculates the total revenue expected from a customer over their engagement period.
Effectively integrating KPIs communicates your startup's performance and strategic focus to investors.
Step-by-Step Guide to Building a Financial Model
You can create a financial model by breaking it down into structured steps. This makes the whole process manageable.
10 Steps to Building a Financial Model
1. Define Your Objective
Clarify whether the model is for fundraising, internal planning, or both. A clear objective guides the focus and complexity of your model.
2. Gather Historical Data
Collect accurate financial statements and ensure data integrity. Include past income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements.
3. Make Assumptions
Determine key assumptions like market growth rates, pricing strategies, and customer acquisition costs. Base these on research and industry benchmarks.
4. Choose the Right Tools
Select software that suits your needs, such as Excel for flexibility or specialized financial modeling software for advanced features.
5. Build the Income Statement
Project revenues and expenses, considering all revenue streams, cost of goods sold, operating expenses, and taxes.
6. Create the Balance Sheet
Project assets, liabilities, and equity. Include accounts receivable, inventory, fixed assets, debt, and equity financing.
7. Develop the Cash Flow Statement
Forecast cash inflows and outflows to assess liquidity and your ability to meet financial obligations.
8. Integrate KPIs
Include relevant KPIs to track performance over time. Use visual dashboards for easy interpretation.
9. Perform Scenario and Sensitivity Analysis
Test how changes in assumptions affect outcomes. This highlights potential risks and prepares you for investor inquiries.
10. Review and Update Regularly
Ensure accuracy by regularly reviewing and updating the model. Adjust assumptions as necessary to reflect current conditions.
Utilize these Financial Model Templates to streamline this process, offering structured formats and built-in formulas.
Sample Case Studies
Analyzing successful financial models provides practical insights.
Case Study 1:
Background
A mobile payment solutions startup, aimed to redefine traditional banking with innovative technology. They sought Series A funding to scale operations.
Key Elements of Their Financial Model
- Detailed Revenue Streams: Clear breakdowns of transaction fees, subscription models, and value-added services.
- Comprehensive KPIs: Metrics like customer acquisition cost, churn rate, and lifetime value.
- Sophisticated Scenario Analysis: Explored market adoption rates and regulatory impacts.
- Dynamic Financial Statements: Linked all statements for automatic updates when assumptions changed.
Investor Impact
Investors were impressed by the model's depth and realism, leading to a successful $10 million funding round.
Case Study 2:
Background
Another startup specialized in sustainable energy products and was looking to expand internationally. They needed capital to enter new markets.
Key Elements of Their Financial Model
- Customized for Investors: Adjusted the model to address specific concerns, including environmental impact metrics.
- AI Integration: Improved forecasting accuracy by analyzing energy market trends.
- International Adaptation: Incorporated different regulatory requirements and market conditions.
- Clear Growth Roadmap: Outlined detailed plans for scaling operations.
Investor Impact
By presenting a tailored and advanced financial model, the startup secured substantial venture capital, enabling international expansion.
Key Takeaways from the Case Studies
- Provide Clarity: Transparent projections build trust.
- Customize Your Model: Tailoring to investor interests demonstrates professionalism.
- Embrace Advanced Techniques: Sets you apart from competitors.
- Adopt a Global Perspective: Opens doors to a broader investor base.
Choosing the Right Financial Modeling Tools
To enhance your modeling process start by selecting appropriate tools.
Comparing Software Options
Microsoft Excel
- Pros:
- Highly flexible with extensive functionalities.
- Widely accepted in the finance industry.
- Supports advanced features like VBA scripting.
- Cons:
- Steeper learning curve for advanced features.
- Collaboration can be challenging without cloud integration.
Google Sheets
- Pros:
- Real-time collaboration capabilities.
- Cloud-based, accessible from anywhere.
- Easy sharing with customizable permissions.
- Cons:
- Limited advanced features compared to Excel.
- Performance issues with very large datasets.
Specialized Software
- Pros:
- Built-in financial modeling and forecasting functions.
- Industry-specific templates and reports.
- Advanced analytics and scenario planning features.
- Cons:
- Higher costs, which may not be feasible for early-stage startups.
- Learning curve associated with new software.
Recommendations Based on Startup Needs
- Early-Stage Startups: Google Sheets is suitable for basic modeling and collaboration when resources are limited.
- Growth-Stage Startups: Excel offers advanced features necessary for complex models.
- Complex Financial Needs: Specialized software is ideal when advanced forecasting and reporting are required.
For guidance on managing budgets and cash flows using these tools, see Effective Financial Tools for Startups.
Advanced Tool Features
Excel Power Query and Power Pivot
- Purpose: Manage large datasets efficiently.
- Benefits: Simplify data preparation and enhance data analysis capabilities.
Macro Programming with VBA
- Purpose: Automate repetitive tasks and complex calculations.
- Benefits: Save time, reduce errors, and improve model consistency.
Google Sheets Add-ons
- Purpose: Extend functionality with third-party tools for analytics and automation.
- Benefits: Enhance collaboration features and streamline workflows.
Including visuals like screenshots and tutorials can greatly enhance understanding and facilitate learning.
Overcoming Common Challenges
Financial modeling comes with challenges, but proactive strategies can strengthen your model.
Potential Pitfalls
Overcomplicating the Model
- Issue: Complex models with unnecessary details can confuse investors.
- Solution: Focus on clarity and include only essential information that adds value.
Inconsistent Data
- Issue: Using outdated or inconsistent data leads to inaccurate projections.
- Solution: Establish a single source of truth for data inputs and regularly verify data integrity.
Unrealistic Assumptions
- Issue: Overly optimistic or unfounded assumptions undermine credibility.
- Solution: Base assumptions on market research, historical data, and industry benchmarks.
Lack of Flexibility
- Issue: Models that cannot accommodate changes limit analysis.
- Solution: Design models with adjustable parameters and utilize scenario planning tools.
Addressing Errors
- Implement Error Checks: Use validation rules and error alerts within your model.
- Peer Reviews: Have financial experts or team members review the model.
- Test with Extreme Values: Input outlier values to verify model responsiveness.
Maintaining Accuracy
- Document Methodologies: Keep detailed notes on assumptions and data sources.
- Version Control: Use software to track changes and maintain previous versions.
- Regular Updates: Schedule periodic reviews to update data and assumptions.
When challenges arise, consider Consulting Financial Modeling Experts who can provide expertise and fresh perspectives.
Adapting to Cultural Differences
With international investors, you must be extra conscious of the cultural differences.
Adapting Your Model
- Regulatory Compliance: Incorporate local financial regulations and reporting standards.
- Currency Adjustments: Present financials in both your local currency and that of the investor's country.
- Language and Terminology: Use region-specific financial terminology and translate key parts if necessary.
Understanding Market Differences
- Accounting Standards: Adjust your model for IFRS or GAAP as applicable.
- Market Dynamics: Consider differences in consumer behavior and economic conditions.
- Tax Implications: Factor in varying tax rates and compliance requirements.
Strategies for International Operations
- Local Partnerships: Collaborate with local firms to gain insights.
- Cultural Sensitivity: Be aware of norms that may influence investor perceptions.
- Tailored Communication: Adjust your pitch to align with cultural expectations.
For strategies on navigating financial planning across different markets, read our guide on Financial Planning for Global Expansion.
Maintaining and Updating Your Financial Model
A financial model is a living document. Regular updates and maintenance are indispensable to keep it relevant and accurate.
Importance of Regular Updates
- Reflect Business Changes: Ensure your model mirrors operational realities.
- Respond to Market Shifts: Incorporate new market data and economic indicators.
- Build Investor Confidence: Demonstrate diligence and adaptability.
Setting Up Maintenance Processes
- Scheduled Reviews: Establish regular intervals for model updates.
- Designated Ownership: Assign team members responsible for maintenance.
- Change Logs: Document all updates for transparency.
Automating Updates
- Data Integration: Connect your model to accounting software for real-time data.
- Automated Reports: Generate reports automatically at specified intervals.
- Notifications: Set alerts for anomalies or when certain thresholds are met.
Invest time in regular updates. This will make sure your financial model remains a powerful tool for decision-making and investor communications.
What’s Next
A financial model that secures funding requires a blend of technical skills and strategic thinking. It also demands an understanding of investor expectations.
By employing advanced techniques, you position your startup for success. Remember to integrate relevant KPIs for maintaining your model diligently,
We've explored how to understand investor psychology, leverage advanced tools, and apply practical steps in building your model. With actionable insights and access to valuable resources, you can now craft a financial model that tells a compelling story.
For more, explore our resources or contact Qubit Capital and get personalized support tailored to your needs.
For comprehensive guidance, read our Ultimate Guide to Financial Modeling.
Key Takeaways
- Align with Investor Expectations: Tailor your model to demonstrate viability, risk mitigation, and growth potential.
- Employ Advanced Techniques: Use scenario analysis, stress testing, and AI tools to enhance your model's credibility.
- Integrate Relevant KPIs: Provide measurable evidence of performance and growth potential.
- Follow a Structured Approach: Breaking down the process into steps facilitates efficiency and thoroughness.
- Select Suitable Tools: Choose software that matches your needs and complexity.
- Adapt for Cultural Differences: Tailor your model for international investors by considering regional nuances.
- Maintain Your Model: Regular updates keep your model accurate and build investor confidence.
Frequently asked Questions
What are the three basic financial models?
The three basic financial models commonly used are:
- Three-Statement Model: Integrates the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement into one dynamic model, providing a comprehensive view of financial performance.
- Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) Model: Projects future cash flows and discounts them to present value to estimate the company’s intrinsic value, essential for valuation analysis.
- Budget Model: Used for planning and monitoring finances over a specific period, helping in resource allocation and performance evaluation.
For foundational knowledge, see our Introduction to Financial Modeling.


 Back
Back