Understanding which startup metrics matter most to investors is essential for any founder aiming to secure funding. These metrics not only reflect a company’s performance but also provide insights into its potential for growth and scalability. Investors rely on key performance indicators (KPIs) to assess the health of a startup, from revenue growth to customer acquisition costs.
Your analysis of performance metrics gains additional depth when you connect these insights with startup scouting strategies, which offer a nuanced view of early-stage investment tactics.
This article explores the essential metrics that guide investor decisions and why they’re critical for startups. Did you know that startups on Carta raised 18.4% more capital in 2024 than in 2023? Let’s jump right in.
The Crucial Importance of Tracking Startup Metrics
Understanding the pulse of a startup begins with tracking its performance indicators. These metrics are not just numbers; they are the foundation for evaluating a company’s growth potential, operational efficiency, and overall health. For startups, the ability to measure and analyze data-driven metrics can mean the difference between scaling successfully or stalling prematurely.
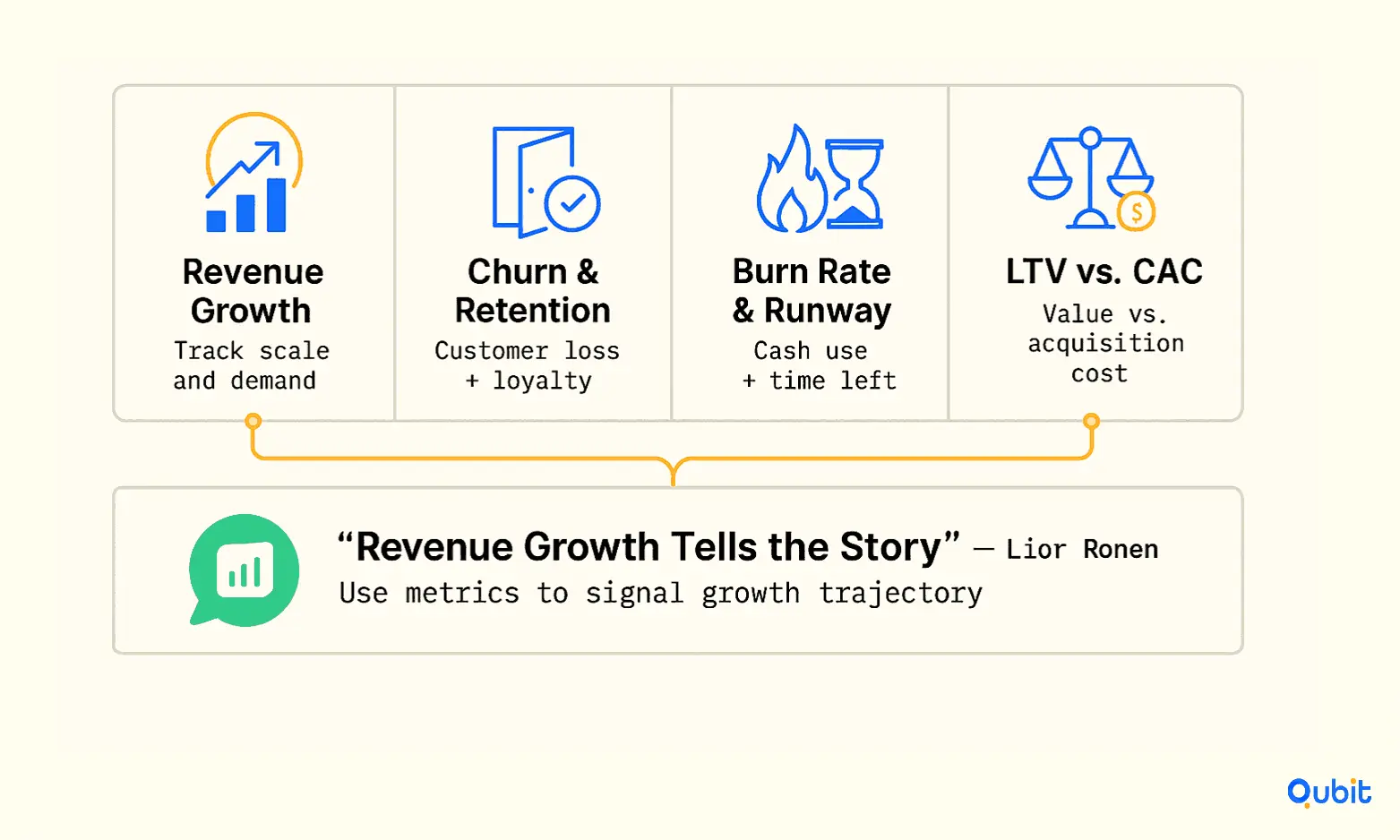
Why Startup Metrics Matter
Startup performance indicators provide a clear lens into how a business is functioning and where it’s headed. Metrics like revenue growth, customer acquisition cost (CAC), and operational margins reveal whether a company is on a sustainable path. For instance, revenue growth is often seen as a direct reflection of market demand and scalability. As Lior Ronen from Finro Financial Consulting aptly puts it, “Revenue growth tells investors where a company is today and where it’s headed.” This insight is invaluable for both founders and stakeholders.
Moreover, investors rely heavily on these data points to make informed decisions. A report from the Carta State of Private Markets Q4 2024 highlights an 18.4% increase in capital raises for late-stage startups, underscoring the importance of demonstrating strong financial metrics to attract funding. Such trends emphasize that startups with a solid grasp of their metrics are better positioned to secure investor confidence.
The Role of Metrics in Strategic Decision-Making
Metrics are not just about tracking progress; they are instrumental in shaping a startup’s strategy. Key performance indicators (KPIs) like churn rate, lifetime value (LTV), and gross margins help founders identify areas of improvement and allocate resources effectively. For example, understanding startup churn rate benchmarks can refine your evaluation of performance risks and sustainability. High churn rates might signal product dissatisfaction or misaligned customer targeting, both of which require immediate attention.
Additionally, operational metrics such as burn rate and runway provide clarity on financial health, enabling startups to plan for the long term. Without these insights, decision-making becomes reactive rather than proactive, leaving businesses vulnerable to unforeseen challenges.
Data-Driven Metrics: A Competitive Advantage
Startups that prioritize data-driven metrics gain a significant edge in their industries. By consistently tracking and analyzing performance indicators, they can identify trends, predict outcomes, and adapt strategies to stay ahead of competitors. This approach fosters a culture of accountability and continuous improvement, which is essential for long-term success.
Assessing Startup Valuation: Key Financial Metrics to Monitor
Determining the value of a startup is a critical step for investors seeking to make informed decisions. Valuation metrics serve as the foundation for understanding a startup’s market worth, offering insights into its financial health and growth trajectory. By analyzing specific financial indicators, investors can gauge sustainability, profitability, and long-term potential.
Growth Prospects: A Predictor of Future Value
A startup’s growth potential often acts as a key determinant of its valuation. Metrics such as revenue growth rate and customer acquisition trends provide a snapshot of how effectively the business is scaling. For instance, consistent double-digit revenue growth signals strong demand and operational efficiency. However, growth must be balanced with scalability, rapid expansion without a sustainable model can lead to financial instability.
Gross Margin: Measuring Profitability
Gross margin is another essential metric that highlights the profitability of a startup’s core operations. This figure represents the percentage of revenue remaining after deducting the cost of goods sold (COGS). A higher gross margin indicates efficient cost management and a strong ability to generate profit. For startups in competitive industries, maintaining a healthy gross margin is crucial for long-term survival.
ROI: Evaluating Investment Efficiency
Return on Investment (ROI) is a critical metric for assessing how effectively a startup utilizes its resources to generate returns. Investors often examine ROI to determine whether the startup’s strategies align with its financial goals. A high ROI suggests that the business is maximizing its resources, while a low ROI may indicate inefficiencies or misaligned priorities.
Historical Valuation Challenges and Future Projections
Challenges such as fluctuating market conditions or operational setbacks often shape the valuation trajectory. Combining this historical data with future projections—such as anticipated revenue streams or market expansion plans, offers a comprehensive view of the startup’s potential.
Your examination of key performance indicators becomes more comprehensive when you consider financial metrics to evaluate startups, blending quantitative data with practical financial assessments.
Essential Metrics for Investor Reports: Performance, KPIs, and More
Investor reports are the cornerstone of transparent communication between startups and their stakeholders. By presenting a balanced mix of operational and financial metrics, these reports provide a clear snapshot of a company’s performance and future potential. Selecting the right combination of metrics is not just about showcasing growth; it’s about aligning with strategic goals and ensuring clarity for decision-making.
The Importance of a Diverse Metric Set
A comprehensive investor report goes beyond revenue figures. It integrates operational metrics like customer satisfaction and retention with financial indicators such as burn rate and profitability. This holistic approach ensures that investors gain a full understanding of the business’s health and trajectory. For instance, growth analysis metrics help highlight scalability, while metrics like product-market fit demonstrate the startup’s alignment with customer needs.
One example of operational success is the case of Startup Delta, which prioritized customer success to improve its Net Promoter Score (NPS). By gathering feedback and enhancing support through a dedicated team, the company increased its NPS to 50 and doubled customer referrals. This demonstrates how focusing on customer-centric metrics can significantly impact overall performance. Learn more about Startup Delta’s NPS improvement.
Key Financial Metrics to Include
Financial metrics are the backbone of investor reports. They provide insights into the company’s fiscal health and operational efficiency. Among the most critical are:
Burn Multiple: This metric evaluates how efficiently a startup uses its funding to generate revenue. For instance, AI-native startups have been leading the way in cost efficiency, achieving sub-1.0× burn multiples compared to traditional SaaS companies, which average around 1.6×. This stark contrast highlights the transformative potential of AI in optimizing operational costs.
CAC Payback Period: The Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) payback period is another essential metric. It measures the time required to recover the cost of acquiring a customer. A shorter CAC payback period indicates a more sustainable growth model.
Operational Metrics That Matter
Operational metrics provide a lens into the day-to-day performance of a startup. Metrics like user engagement, churn rate, and customer lifetime value (CLV) are indispensable for understanding how well the product or service resonates with its target audience. Your exploration of startup performance is enriched by integrating user growth metrics for startups, which provide a focused look into engagement and scalability factors.
Streamlining the Reporting Process
Creating investor reports can be a time-intensive process, but tools like Rundit’s Investor Reporting Tool simplify the task. This platform offers templates that combine metric updates with narrative summaries, ensuring that reports are both comprehensive and easy to digest. By streamlining updates for each metric, startups can focus more on strategy and less on administrative tasks.
Effective Investor Reporting and Fundraising Strategies for Startups
Transparent communication with investors is a cornerstone of startup success. Investor reporting, when done efficiently, not only builds trust but also provides a clear picture of a company’s financial health. This clarity becomes even more critical during volatile market conditions, where uncertainty can erode confidence. By adopting organized reporting processes and showcasing strong leadership, startups can significantly enhance their fundraising outcomes.
1. Prioritize Transparent Financial Reporting
Investors value transparency, especially when it comes to financial reporting. Providing accurate and timely updates on revenue, expenses, and cash flow ensures stakeholders remain informed about the company’s financial position. This transparency fosters trust and reduces the likelihood of misunderstandings.
To streamline reporting:
- Automate financial tracking: Use tools that consolidate data for easy analysis and presentation.
- Focus on key metrics: Highlight performance indicators that align with investor expectations, such as growth rates, customer acquisition costs, and profitability trends.
- Maintain consistency: Deliver reports on a regular schedule to establish reliability.
Your review of startup metrics is complemented by an analysis of metrics for deal sourcing success, which links scouting effectiveness with broader performance outcomes.
2. Demonstrate Strong Leadership
A capable leadership team can make or break investor confidence. Investors are not only funding ideas but also the people behind them. Demonstrating strategic decision-making, adaptability, and a clear vision reassures stakeholders that their investment is in capable hands.
Key leadership practices include:
- Proactive communication: Address challenges openly and outline actionable solutions.
- Team alignment: Ensure all members of the leadership team share a unified vision and can articulate it effectively.
- Resilience under pressure: Showcase the ability to navigate uncertainties while maintaining focus on long-term goals.
3. Optimize Fundraising Strategies
Organized reporting processes directly impact fundraising success. When startups present clear, data-driven insights, they position themselves as reliable and professional. This approach not only attracts investors but also simplifies due diligence processes.
Effective fundraising strategies include:
- Tailored pitches: Customize presentations to align with the interests of specific investors.
- Highlight growth potential: Use financial reports to demonstrate scalability and market opportunities.
- Build relationships: Engage with investors beyond formal meetings to establish rapport and trust.
By combining transparent reporting with strong leadership and strategic fundraising, startups can create a compelling narrative that resonates with investors.
Decoding Unit Economics for Sustainable Growth
Understanding the profitability of individual operations is essential for startups aiming to scale effectively. Unit economics, which focuses on the financial performance of a single unit of product or service, provides the granular insights needed to assess sustainability. By analyzing metrics like Lifetime Value (LTV) and Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC), businesses can refine their strategies and ensure long-term growth.
Why Unit Economics Matter
Unit economics serves as the foundation for evaluating whether a business model is viable. It breaks down profitability at the per-unit level, offering clarity on how much value each customer or transaction generates. For startups, this analysis is critical to avoid scaling prematurely or investing in unprofitable channels.
Key Ratios: LTV and CAC
Two pivotal metrics in unit economics are Lifetime Value (LTV) and Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC).
- Lifetime Value (LTV): This metric calculates the total revenue a customer generates over their relationship with the business. A higher LTV indicates strong customer retention and recurring revenue streams.
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): CAC measures the cost of acquiring a new customer, including marketing and sales expenses. Keeping CAC low while maintaining a high LTV is the hallmark of a sustainable business model.
The ratio between LTV and CAC is particularly insightful. A healthy LTV-to-CAC ratio—typically above 3:1—signals that a business is generating sufficient profit from its customers relative to acquisition costs.
Optimizing Unit Economics
Improving unit economics often involves enhancing customer retention, reducing acquisition costs, or increasing the average transaction value. For instance, investing in customer experience can boost LTV, while refining marketing strategies can lower CAC. These adjustments not only improve profitability but also position the business for sustainable growth.
Unit economics isn’t just a financial metric; it’s a strategic tool. By understanding these numbers, startups can make informed decisions about scaling, pricing, and resource allocation.
Robust Financial Projections: Planning Future Success
Creating reliable financial projections is a cornerstone of effective business planning. These projections not only guide strategic decisions but also serve as a critical tool for attracting investors. By combining historical data with well-informed assumptions, businesses can craft financial forecasts that inspire confidence and demonstrate potential for growth.
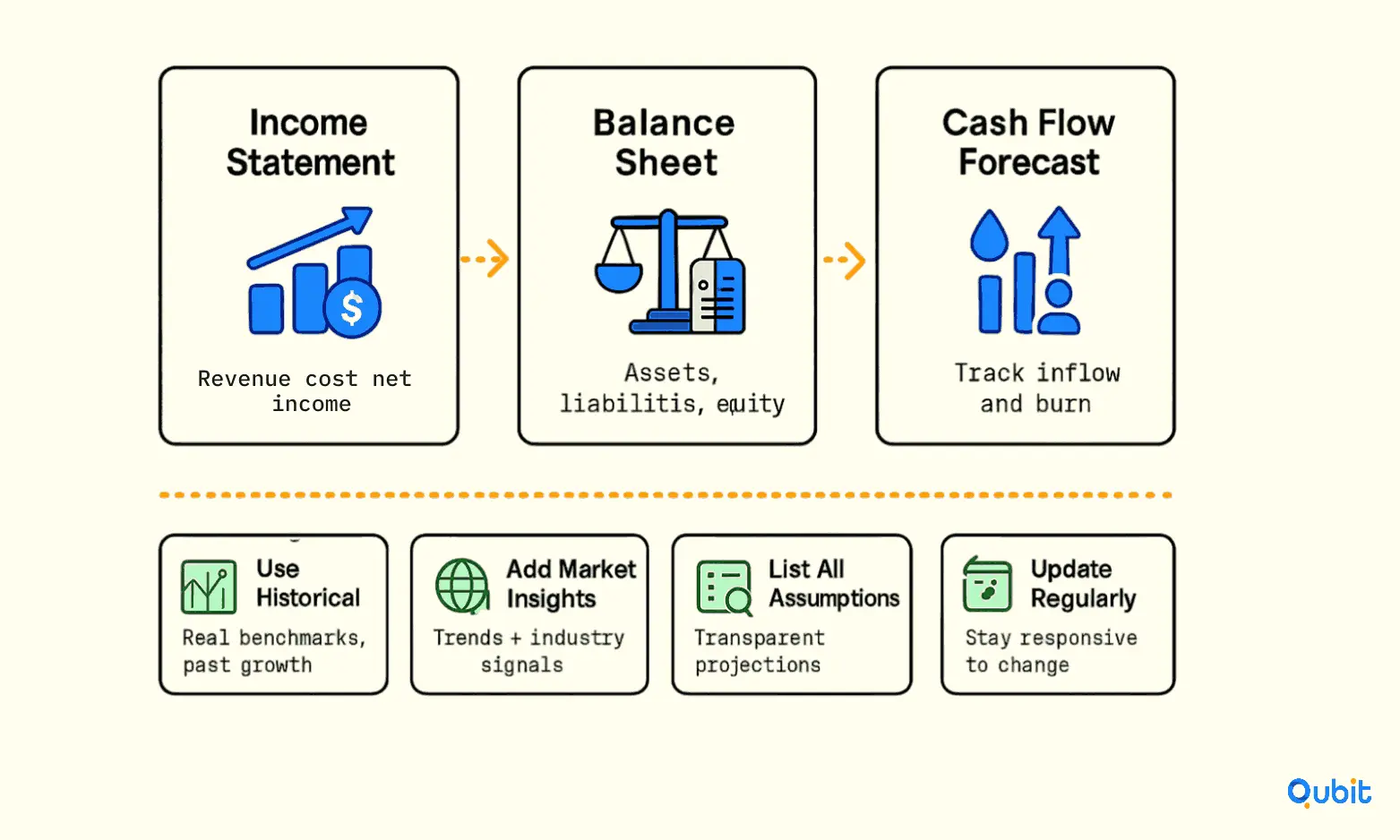
Building Accurate Financial Statements
The foundation of any robust financial projection lies in standardized financial statements. Start by creating detailed income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow forecasts. These documents provide a clear snapshot of your company’s financial health and serve as a baseline for future predictions.
- Income Statement: This outlines revenue, expenses, and net income over a specific period. By analyzing historical trends, you can estimate future revenue streams and identify areas for cost optimization.
- Balance Sheet: A balance sheet highlights assets, liabilities, and equity, offering a comprehensive view of your company’s financial position. Accurate projections here help in assessing long-term stability.
- Cash Flow Forecast: Predicting cash inflows and outflows ensures you can manage liquidity effectively. A well-prepared cash flow forecast also helps mitigate risks associated with unexpected financial shortfalls.
Best Practices for Credible Projections
Use Historical Data as a Benchmark
Historical financial data is invaluable for identifying trends and setting realistic benchmarks. For instance, analyzing past revenue growth rates can help you project future sales with greater accuracy.Incorporate Market Insights
External factors, such as industry trends and economic conditions, should inform your assumptions. This ensures your projections remain grounded in reality while accounting for potential market shifts.Be Transparent with Assumptions
Clearly document the assumptions underlying your projections. Whether it’s expected customer growth or anticipated cost reductions, transparency builds trust with stakeholders and investors.Regularly Update Projections
Financial projections are not static. Regularly revisiting and adjusting them based on new data or changing circumstances ensures they remain relevant and actionable.
Why Investors Value Clear Projections
Investors rely on financial projections to evaluate a company’s potential for growth and profitability. Well-structured projections demonstrate that you’ve thoroughly analyzed your business model and market opportunities. They also highlight your ability to anticipate challenges and plan accordingly.
By presenting clear and realistic forecasts, you help investors visualize the trajectory of your business. This not only boosts their confidence but also positions your company as a reliable and forward-thinking investment opportunity.
Conclusion
Building a successful startup requires a strategic approach to financial planning and investor relations. From tracking essential startup metrics and valuing companies through comprehensive financial indicators to crafting detailed investor reports and utilizing unit economics alongside robust financial projections, each step plays a critical role in shaping your business's future. Equally important is presenting a clear, narrative-driven pitch deck that instills confidence in potential investors.
If you’re ready to secure the right capital, we at Qubit Capital are here to help with our Fundraising Assistance service.
Key Takeaways
- Startup metrics provide a holistic view of a company’s growth, efficiency, and market potential.
- Valuation and financial metrics are essential for assessing a startup’s worth and sustainability.
- Detailed investor reporting, incorporating tools and real-world data, enhances transparency.
- Strong unit economics, reflected by metrics such as CAC and LTV, underpin profitability.
- Robust financial projections build investor confidence and help secure funding.
Frequently asked Questions
What are the Key Financial Metrics for Startups?
Key financial metrics include cash balance, gross burn rate, EBITDA, and ROI. These provide insights into a startup’s financial health and operational efficiency.


 Back
Back