Assumptions are the backbone of every financial model, shaping projections and guiding decisions. Without clear documentation, these assumptions can lead to costly errors, misinterpretations, or even failed strategies.
Whether you’re forecasting revenue growth or estimating operational costs, the accuracy and transparency of your financial assumptions are critical. This blog explores the importance of documenting assumptions and provides actionable best practices to ensure your models remain reliable and insightful.
By the end of this article, you’ll gain a step-by-step guide to documenting assumptions effectively, minimizing risks, and enhancing decision-making confidence.
Sourcing Accurate Data for Financial Assumptions
Accurate data forms the backbone of reliable financial assumptions. Relying on guesswork can lead to flawed projections, making research-based inputs essential for sound decision-making. Examples of financial assumptions, such as revenue growth or marketing spend, should be informed by credible sources like industry benchmarks, competitor analysis, and public reports.
Industry averages provide a baseline for understanding market trends, while competitor insights offer a glimpse into strategies that have proven effective. Public reports, including financial statements and market studies, can further enhance the precision of your assumptions. For instance, startups often allocate significant budgets to marketing before generating revenue, as highlighted in the “Marketing Spend” insight from Startup Marketing.
Adjusting such assumptions to reflect pre-revenue spending patterns ensures they align with your business context. Adapting the data to your specific circumstances is equally important. Tailoring industry benchmarks or competitor data to your unique business model ensures assumptions remain relevant and actionable.
For example, if your SaaS startup targets enterprise clients, your customer acquisition cost (CAC) and sales cycle length will differ significantly from a B2C mobile app. Documenting these nuances in your financial assumptions examples will make your model more credible and investor-ready. For a comprehensive approach to aligning your assumptions with your business strategy, review your financial roadmap regularly to ensure all projections are grounded in current market realities.
Case Study: Dollar Cave Club Financial Assumptions Examples
Documenting financial assumptions is a cornerstone of effective business modeling. Dollar Cave Club offers man cave essentials as a subscription-based service. The company provides a practical example of outlining financial metrics to project revenue and growth.
For limited partner private equity, clear documentation demonstrates transparency and rigor to potential investors.
- Subscription Price:
- The club’s monthly subscription is set at $29.99.
- This figure directly informs revenue projections.
- For example, monthly revenue is calculated by multiplying the subscription price by the number of active subscribers. With 10,000 active subscribers, projected monthly revenue is $299,900.
- Churn Rate:
- The club has identified a 'Churn rate,' which refers to the percentage of customers who cancel subscriptions each month, of 4% per month, based on historical data and industry benchmarks from the Subscription Trade Association (SUBTA).
- This percentage represents the subscribers who cancel their memberships each month.
- Incorporating the churn rate into retention calculations refines long-term financial models, ensuring realistic forecasts. For instance, a 4% churn means the company must acquire at least 400 new subscribers monthly to maintain its base.
- Supplementary Revenue Streams:
- Besides subscriptions, the model includes revenue from advertising partnerships and product add-ons, which accounted for 18% of total revenue in 2024.
- Understanding these key metrics helps distinguish between known variables and unknown factors, allowing for more accurate scenario planning.
This case study shows how clear, actionable metrics like subscription price and churn rate can be used to document financial assumptions effectively. It serves as a sample financial assumptions template for businesses aiming to build robust financial models. The Dollar Cave Club example also demonstrates the importance of integrating supplementary revenue streams and using real market data to validate assumptions, a best practice increasingly adopted by high-growth startups in 2025.
Setting Up Revenue-Related Financial Assumptions Examples
Accurate revenue assumptions are essential for crafting reliable income statement forecasts. This process involves documenting key metrics like subscription prices, churn rates, and conversion percentages. By establishing clear financial assumptions, businesses can better predict income and identify growth opportunities.
For example, incorporating a 10% monthly organic SEO traffic growth rate into your projections can help forecast traffic increases effectively. This metric, detailed in the assumptions tab, provides a solid foundation for estimating revenue growth tied to improved visibility and engagement.
Metrics such as churn rate, which measures customer retention, and conversion rates, which track how many prospects become paying customers, are equally critical. Together, these figures form the backbone of financial modeling assumptions, ensuring projections remain grounded in measurable data.
For instance, Shopify’s 2025 investor presentation highlights a 3.5% monthly churn rate and a 4.2% conversion rate from free trial to paid subscription, both of which are used as financial assumptions examples in their forecasting models. Together, these figures form the backbone of financial modeling assumptions, ensuring projections remain grounded in measurable data.
By focusing on specific metrics, businesses can create a structured approach to revenue forecasting, paving the way for informed decision-making and sustainable growth. For a deeper understanding of how to structure your revenue assumptions, review the importance of financial forecasting in the context of your business model.
Documenting Cost Assumptions Precisely: Financial Assumptions Examples
Clear documentation of cost assumptions is essential for accurate financial planning. When projecting expenses like IT infrastructure, rent, legal fees, and other operational costs, basing these assumptions on realistic and sample financial assumptions ensures reliability. For example, using historical data or industry benchmarks can help align projections with actual market conditions.
Accurate cost assumptions prevent budgeting errors that could derail a project or business plan. Sample expense data serves as a foundation for realistic cost projections, reducing the risk of underestimating or overestimating expenses. Additionally, documenting these assumptions in a structured manner aids in overall financial analysis, making it easier to identify trends, allocate resources, and adjust strategies as needed.
By focusing on examples of financial assumptions grounded in real-world data, businesses can create a robust framework for decision-making. This approach not only enhances transparency but also builds confidence in the financial planning process.
For instance, Stripe’s 2025 financial model includes a 15% annual increase in customer support costs, reflecting both inflation and increased user volume. Additionally, documenting these assumptions in a structured manner aids in overall financial analysis, making it easier to identify trends, allocate resources, and adjust strategies as needed.
For startups preparing financial statements, referencing financial statements for startups can provide clarity on industry-standard cost categories and reporting practices.
Outlining Cash and Operations Assumptions: Financial Assumptions Examples
Effective cash flow management begins with clear financial assumptions. Starting with an opening cash balance of $1,000,000, businesses can establish a foundation for liquidity planning. This initial balance, as outlined in the financial model, plays a pivotal role in shaping projections and ensuring operational stability.
Fundraising plans also contribute significantly to liquidity. Whether through equity financing or debt, these strategies must align with operational needs to maintain cash flow consistency. Key metrics such as accounts receivable and payable days further influence liquidity. Shorter receivable cycles improve cash inflow, while optimized payable terms prevent cash shortages.
Documenting these assumptions is essential for monitoring financial health. By integrating metrics like the opening cash balance into the cash flow assumptions section of your model, businesses can proactively address liquidity challenges and enhance operational efficiency.
Importance of Descriptive Labels in Financial Models
Clear, descriptive labels are the backbone of effective financial modelling assumptions. They transform complex spreadsheets into user-friendly tools by replacing ambiguous cell references with meaningful identifiers. For example, using labels like “PagesPerVisit” instead of generic cell references enhances transparency and simplifies formula management. This approach not only reduces errors but also makes financial models easier to update and maintain.
Spreadsheet software like Excel is particularly useful for assigning labels and creating assumptions tabs. By defining assumptions clearly, such as “PagesPerVisit,” you can streamline updates and improve readability throughout your model. Descriptive labels are essential for ensuring accuracy and clarity in financial models.
Managing the Scope of Your Financial Assumptions List
A streamlined assumptions list is vital for maintaining clarity in your business plan. By focusing only on essential variables, you can reduce complexity and ensure your financial model remains adaptable. Prioritize key assumptions that directly impact forecasting accuracy, such as market growth rates or operational costs. Avoid including unnecessary details that may clutter the list and hinder decision-making.
A concise approach not only simplifies updates but also enhances the overall readability of your plan. For examples of financial assumptions, consider factors like revenue projections or pricing strategies—these are pivotal elements that shape the foundation of your business plan.
The Fundamentals of Financial Modeling: Financial Assumptions Examples
Financial modeling serves as a vital tool for analyzing and forecasting a business’s financial performance. It is a mathematical representation of a company’s financial situation, incorporating historical data, financial statements, and market trends to predict future outcomes. These models are essential for evaluating financial assumptions, such as revenue growth or cost projections, which help businesses make informed decisions.
Spreadsheet software like Microsoft Excel plays a central role in constructing these models. Excel allows users to input historical data and create projections, offering flexibility and precision in financial analysis. For example, it can be used to integrate past performance metrics with current market trends to simulate various scenarios.
Also hiring a financial modeling consultant helps if you are looking for a more nuanced approach. Financial modeling is not just about numbers, it’s about creating a roadmap for sustainable growth and strategic planning.
Key Components in Building Your Financial Model
Crafting a robust model requires a clear understanding of how to create a financial model for investors. Each component plays a vital role in ensuring the model’s accuracy and reliability, starting with historical data analysis. By examining past performance, businesses can identify trends and patterns that inform realistic assumptions. These assumptions, often derived from examples of financial assumptions, serve as the backbone of projections.
1. Historical Data and Assumption Development
Historical data provides the context needed to develop financial assumptions. For instance, trends in revenue growth or expense patterns can guide the creation of assumptions that align with market realities. A financial assumption example might include estimating a 5% annual growth rate based on prior performance.
2. Revenue Projections and Cost Forecasting
Revenue projections are central to any financial model, as they outline expected income streams. Pairing these projections with detailed cost and expense forecasting ensures a balanced approach. Accurate forecasting helps businesses anticipate operational costs and identify areas for optimization.
3. Cash Flow and Scenario Analysis
Cash flow analysis evaluates the inflow and outflow of funds, ensuring liquidity is maintained. Scenario analysis, on the other hand, quantifies risks by applying diverse assumptions to the model. This approach allows businesses to prepare for various outcomes, enhancing decision-making.
Step-by-Step Process for Building Your Financial Model
Creating a financial model requires a structured approach to ensure accuracy and usability. Below is an eight-step process to help you develop a robust model tailored to your needs.
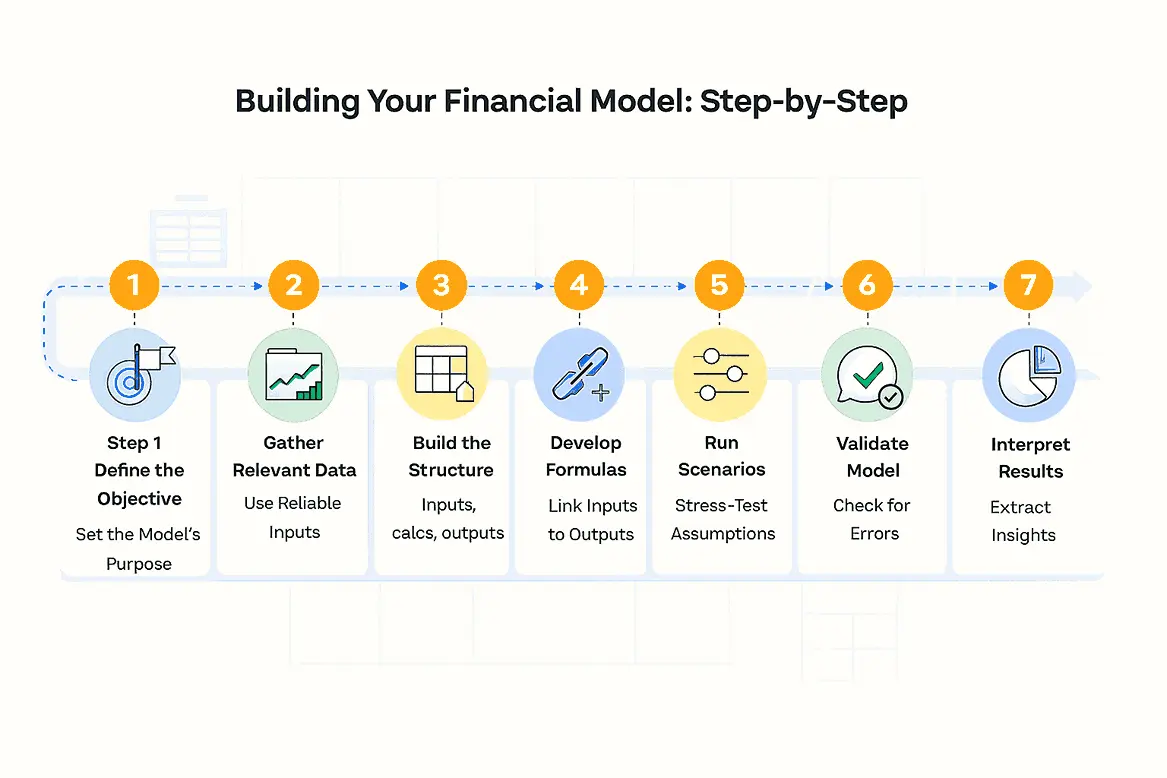
1. Define the Objective
Start by identifying the purpose of your financial model. Whether it’s for forecasting, valuation, or decision-making, a clear objective will guide the entire process. This step ensures the model aligns with your business goals and provides actionable insights.
2. Gather Relevant Data
Collect all necessary financial and operational data. This includes historical figures, market trends, and industry benchmarks. Reliable data forms the backbone of your model, ensuring its credibility.
3. Build the Structure
Design a logical framework for your model. Divide it into sections such as inputs, calculations, and outputs. A well-organized structure simplifies navigation and enhances usability.
4. Incorporate Financial Modelling Assumptions
Embed assumptions early in the process. These could include sample financial assumptions like growth rates, cost projections, or income statement assumptions. Clear assumptions improve the model’s reliability and adaptability to changing scenarios.
5. Develop Calculation Formulas
Use formulas to link inputs and assumptions to outputs. Ensure calculations are consistent and scalable. This step transforms raw data into meaningful projections.
6. Conduct Scenario Analysis
Test your model under various scenarios to evaluate its flexibility. Adjust assumptions to simulate best-case, worst-case, and most-likely outcomes. Scenario analysis is critical for validating the model’s integrity.
7. Validate the Model
Review the model for errors and inconsistencies. Cross-check calculations and ensure all assumptions are reasonable. Validation guarantees the model is both accurate and dependable.
8. Interpret the Results
Analyze the outputs to derive actionable insights. Focus on key metrics that align with your objectives. Proper interpretation transforms data into strategic decisions.
Best Practices for Reliable Financial Models
Creating dependable financial models requires a thoughtful approach to design and maintenance. Here are the key principles broken down, reflecting industry best practices:
- Simplicity:
- Keep models straightforward to reduce the likelihood of errors.
- Simple models are easier to use across teams and facilitate faster decision-making.
- Overcomplicated models can lead to confusion and inefficiencies, undermining their reliability. According to the Corporate Finance Institute’s 2025 survey, 68% of CFOs prefer models with fewer than 20 core assumptions.
- Documentation:
- Document assumptions thoroughly, including the source and rationale for each.
- Clear records of income statement assumptions and other financial assumptions ensure transparency.
- This transparency enables stakeholders to understand the rationale behind projections, fostering collaboration and minimizing miscommunication, especially when teams need to revisit or revise the model.
- Continuous Updates:
- Financial models must evolve as new data becomes available.
- Regularly reviewing and refining assumptions in the business plan ensures that the model remains relevant and accurate. In 2025, automated data feeds and scheduled model reviews are standard for high-growth companies.
By adhering to these principles- simplicity, documentation, and regular updates, you can create financial models that are both reliable and adaptable to changing circumstances. For further insights on how to present your financials to investors, reference investor-friendly financial reports for best-in-class reporting standards.
Conclusion
Assumptions aren’t just background notes in a financial model, they are the model. If they’re weak, undocumented, or based on guesswork, everything built on top of them becomes fragile. This article walked through how to ground assumptions in real data, use case studies like Dollar Cave Club to structure metrics, and define revenue, cost, cash flow, and operational drivers clearly.
It also covered the role of labels, scope control, and scenario analysis in keeping models usable instead of overwhelming. Finally, we looked at best practices: keep models simple, document every key input, and update them regularly as reality changes. Do that consistently, and your financial model stops being a static spreadsheet and becomes a living decision tool that investors, leaders, and teams can actually trust.
At Qubit Capital, we understand that a strong financial model is the foundation for successful fundraising and long-term growth, especially for limited partners VC evaluating new opportunities.
Explore our financial modeling services to build investor-ready models tailored to your startup's unique needs.
Key Takeaways
- Integrating real-life case studies, like Dollar Cave Club, provides practical insights and demonstrates how financial assumptions examples drive business outcomes.
- Clear documentation of financial assumptions is vital for model accuracy and limited partners' confidence.
- A dedicated assumptions tab centralizes data input and minimizes errors, a best practice in 2025 financial modeling.
- Descriptive labels enhance clarity and ease future updates, supporting collaboration across finance teams.
- A systematic, step-by-step process empowers reliable forecasting and supports strategic decision-making.
Frequently asked Questions
How do you choose credible sources for financial assumptions?
Use industry benchmarks, competitor analysis, and public reports for financial assumptions. These credible sources improve forecast accuracy and investor confidence.






