Operating profit is essential for evaluating a company’s financial health. This metric reveals how efficiently a business generates income from its core operations, excluding external factors like taxes or interest. Whether you’re a business owner or an investor, mastering operating profit calculation can provide valuable insights into profitability and operational efficiency.
Exploring operating profit concepts dovetails with the broader discussion found in how to create a financial model for investors, where you can appreciate how financial metrics support funding strategies.
This cheat sheet simplifies the process, offering actionable steps and real-world examples to help you calculate operating profit with ease. Let’s dive into the essentials and uncover how this metric can transform your financial decision-making.
What You Need to Know About Operating Profit and Why It Matters
Operating profit is a critical financial metric that highlights the income generated from a company’s core business operations, excluding non-operating factors like interest and taxes. Unlike gross profit, which only accounts for revenue minus the cost of goods sold, operating profit provides a deeper insight into the efficiency of a company’s day-to-day operations.
This metric plays a pivotal role in financial analysis by offering a clear picture of how effectively a business is managing its operational expenses relative to its revenue. Investors and stakeholders often rely on operating profit to benchmark a company’s performance against competitors and industry standards. It serves as a reliable indicator of operational efficiency, helping businesses identify areas for improvement and make informed strategic decisions.
Understanding operating profit also complements the importance of financial forecasting for startups, as accurate projections can help businesses anticipate operational challenges and optimize their financial planning. For example, analyzing operating profit alongside forecasting insights can reveal how well a company is positioned to sustain growth or weather economic fluctuations.
By focusing on operating profit, businesses can ensure they are maximizing their core operational potential while minimizing unnecessary costs. This makes it an indispensable tool for evaluating the health and sustainability of a company’s operations.
How to Calculate Operating Profit with Formulas and Simple Steps
Understanding operating profit is essential for evaluating a business's financial health. This section simplifies the calculation process by breaking down the formula and guiding you through each step.
The Operating Profit Formula
The formula for calculating operating profit is straightforward:
Operating Profit = Gross Profit - Operating Expenses - Depreciation - Amortization
To begin, you need to calculate Gross Profit, which is derived from:
Gross Profit = Revenue - Cost of Goods Sold (COGS)
Once you have the gross profit, subtract operating expenses, depreciation, and amortization to arrive at the operating profit. Each component plays a critical role in accurately determining this figure.
Step-by-Step Guide to Calculate Operating Profit
Determine Revenue and COGS
Start by identifying your total revenue and the cost of goods sold. Revenue represents the total income generated from sales, while COGS includes direct costs such as materials and labor. For example, if your revenue is $500,000 and COGS is $200,000, your gross profit would be:
Gross Profit = $500,000 - $200,000 = $300,000Identify Operating Expenses
Operating expenses include costs such as rent, utilities, salaries, and marketing. Suppose these expenses total $100,000.Account for Depreciation and Amortization
Depreciation refers to the reduction in value of tangible assets like equipment, while amortization applies to intangible assets such as patents. If depreciation is $20,000 and amortization is $10,000, these amounts must be subtracted.Calculate Operating Profit
Using the formula, subtract operating expenses, depreciation, and amortization from gross profit:
Operating Profit = $300,000 - $100,000 - $20,000 - $10,000 = $170,000
This systematic approach ensures accuracy and avoids errors in categorizing expenses.
Why Accurate Categorization Matters
Misclassifying expenses can distort your operating profit and lead to incorrect financial conclusions. For instance, including non-operating costs like interest payments or taxes in operating expenses can skew the results.
Key Factors to Keep in Mind When Calculating Operating Profit
Understanding the nuances of operating profit calculations is essential for accurate financial analysis. One critical consideration is excluding revenues from non-core activities, such as occasional asset sales or interest income, unless these are integral to the business's operations. Including such irregular income streams can distort the true picture of operational efficiency.
Depreciation methods also play a pivotal role in shaping operating profit margins. For instance, a company using an accelerated depreciation method may report lower operating profits in the short term compared to one using straight-line depreciation. This difference arises because accelerated methods allocate higher depreciation expenses earlier in an asset's life, directly impacting reported profits. Similarly, the disposal of assets can lead to one-time gains or losses that should be excluded from operating profit unless they are part of the core business model.
Connecting operating profit metrics to strategic planning is mirrored in how to develop a financial roadmap for a startup, providing you with a perspective on aligning financial data with long-term goals. By focusing on these factors, businesses can ensure their operating profit reflects true operational performance, enabling better decision-making and financial planning.
How Operating Profit Compares to Other Financial Metrics
While gross profit, EBITDA, and net profit each provide valuable insights, operating profit narrows the focus to core business operations.
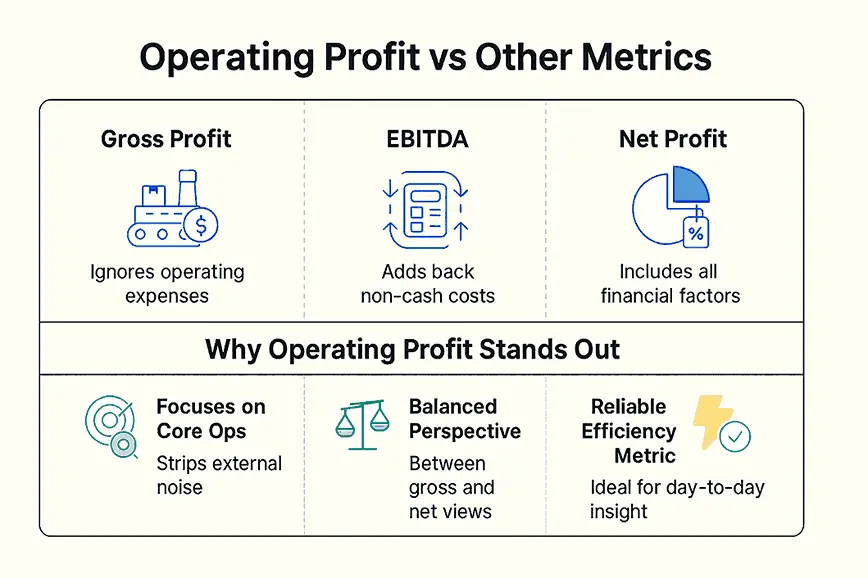
Gross Profit vs. Operating Profit
Gross profit represents the revenue remaining after subtracting production costs, such as materials and labor. However, it doesn’t account for operating expenses like rent, salaries, or utilities. Operating profit, on the other hand, goes a step further by factoring in these costs, offering a clearer picture of profitability from day-to-day operations.
EBITDA vs. Operating Profit
EBITDA (Earnings Before Interest, Taxes, Depreciation, and Amortization) adds back non-cash expenses like depreciation and amortization to operating profit. While EBITDA is often used to assess cash flow potential, operating profit provides a more grounded view by including these non-cash costs, which can significantly impact long-term financial planning.
Net Profit vs. Operating Profit
Net profit encompasses all expenses, including taxes, interest, and one-time charges, making it the most comprehensive metric. However, it can be influenced by external factors unrelated to core operations. Operating profit isolates the performance of the business itself, making it a more reliable indicator for operational efficiency.
Reviewing operating profit considerations enhances your understanding of financial control practices, which is further elaborated in finance management best practices for startups.
Learn from Walmart: A Real-World Operating Profit Analysis
Walmart’s financial performance offers a compelling example of how operating profit calculations translate theoretical concepts into actionable insights. With an operating income of $27.01 billion and total revenues of $648.12 billion for fiscal year 2024, Walmart demonstrates the delicate balance between revenue generation and cost efficiency.
Operating profit, also known as operating income, is a critical metric for assessing a company’s profitability from its core operations. Walmart’s figures highlight how businesses can achieve substantial profitability while managing extensive operational costs. The company’s ability to maintain a robust operating income amidst its massive revenue stream underscores the importance of strategic cost management and operational efficiency.
For a deeper dive into Walmart’s quarterly performance, refer to Walmart Q4. Additionally, Walmart’s Form 10-K provides comprehensive financial statements and footnotes for further analysis.
Walmart’s financial data serves as a practical case study for businesses aiming to optimize profitability while scaling operations.
How to Improve Efficiency with Operating Profit Margin Calculations
Operating profit margin is a metric, expressed as a percentage of total revenue, highlights how effectively a business controls costs and manages operations. A higher margin often signals superior efficiency, but it’s crucial to compare results against industry benchmarks for meaningful insights.
Calculating Operating Profit Margin
The formula for operating profit margin is straightforward:
Operating Profit Margin (%) = (Operating Profit ÷ Total Revenue) × 100
Operating profit represents earnings before interest and taxes (EBIT), while Total Revenue reflects the overall sales generated. Use Total Revenue to understand how overall sales factor into margin calculations, ensuring accuracy in your analysis.
Tools for Enhanced Analysis
Visual aids like Excel templates can simplify margin calculations. By automating formulas, these tools reduce errors and save time, making them ideal for businesses aiming to streamline financial assessments. Additionally, integrating these templates with broader financial modeling concepts can provide deeper insights.
Limitations to Consider
While operating profit margin is a valuable indicator, it’s not without limitations. Factors such as seasonal fluctuations, one-time expenses, and industry-specific cost structures can skew results. Always interpret this metric alongside other financial indicators for a comprehensive understanding.
By mastering operating profit margin calculations, businesses can uncover opportunities to improve efficiency and drive profitability.
Additional Resources to Deepen Your Knowledge
Expanding your understanding of operating profit requires access to reliable tools and learning materials. To support your journey, explore financial tools like profit margin calculators and tutorials that break down complex concepts into actionable insights. External resources such as industry-specific blogs and financial analysis guides can also provide valuable perspectives.
For a deeper dive, consider reviewing case studies that illustrate the strategic application of operating profit in real-world scenarios. These resources not only enhance your knowledge but also equip you to apply these principles effectively in your business decisions.
Boost Your Expertise with the FMVA® Analyst Certification
The FMVA® certification is a transformative program designed to elevate financial analysis skills to a professional level. Its curriculum covers essential topics such as financial modeling, valuation techniques, and advanced Excel applications, ensuring participants gain a robust understanding of financial analysis.
Professionals pursuing the FMVA certification benefit from enhanced analytical capabilities, making them more competitive in the finance industry. This certification is particularly valuable for those aiming to refine their expertise in analyst training and achieve career growth.
Conclusion
A clear and methodical approach to calculating operating profit is essential for businesses aiming to make informed financial decisions. Throughout this blog, we’ve emphasized the importance of understanding key strategies, such as analyzing revenue streams, managing expenses effectively, and utilizing accurate financial metrics. These insights not only help in optimizing profitability but also provide a solid foundation for strategic planning.
As you refine your financial presentations and aim to impress investors, consider how professional tools and expertise can elevate your efforts. At Qubit Capital, we specialize in creating compelling pitch decks that showcase your operating profit metrics with precision and impact.
👉 Explore our Pitch Deck Creation service today and let us help you present your financial story with confidence.
Key Takeaways
- Operating profit is key to measuring core operational efficiency
- Accurate calculation requires a clear formula and structured approach
- Comparing it with other metrics offers richer financial insights
- Examples like Walmart show how these principles work in practice
- Margin analysis supports strategic decisions and financial discipline
Frequently asked Questions
What is operating profit and how is it calculated?
Operating profit represents the earnings generated from a company’s primary business activities. It is calculated by subtracting operating expenses, depreciation, and amortization from gross profit. This metric is essential for evaluating operational efficiency without the influence of non-operational factors.






