Did you know that space-tech venture capital investments reached $3.3 billion across 166 deals in just the first half of 2025? This staggering figure reflects the unprecedented momentum building in the launch and orbital services sector, where venture capital is reshaping how space ventures access critical funding.
This comprehensive exploration of the venture capital landscape for launch and orbital services provides actionable strategies and data-driven insights specifically tailored for aerospace startups navigating today's complex funding environment. From analyzing investment trends to examining alternative financing paths, we'll uncover the strategies that successful space ventures use to secure capital in an increasingly competitive market.
A detailed look at satellite startup government grants illuminates how public funding channels can integrate with the technical and regulatory dimensions of satellite ventures, enriching your funding perspective.
Let's jump right in.
In-Depth Analysis of Venture Capitalist for Launch and Orbital Services
Market Overview and Background
The launch and orbital services sector has undergone a fundamental transformation over the past decade, evolving from a government-dominated domain to a thriving commercial ecosystem. This shift has created unprecedented opportunities for venture capital investment, with private investors increasingly recognizing the sector's potential for substantial returns.
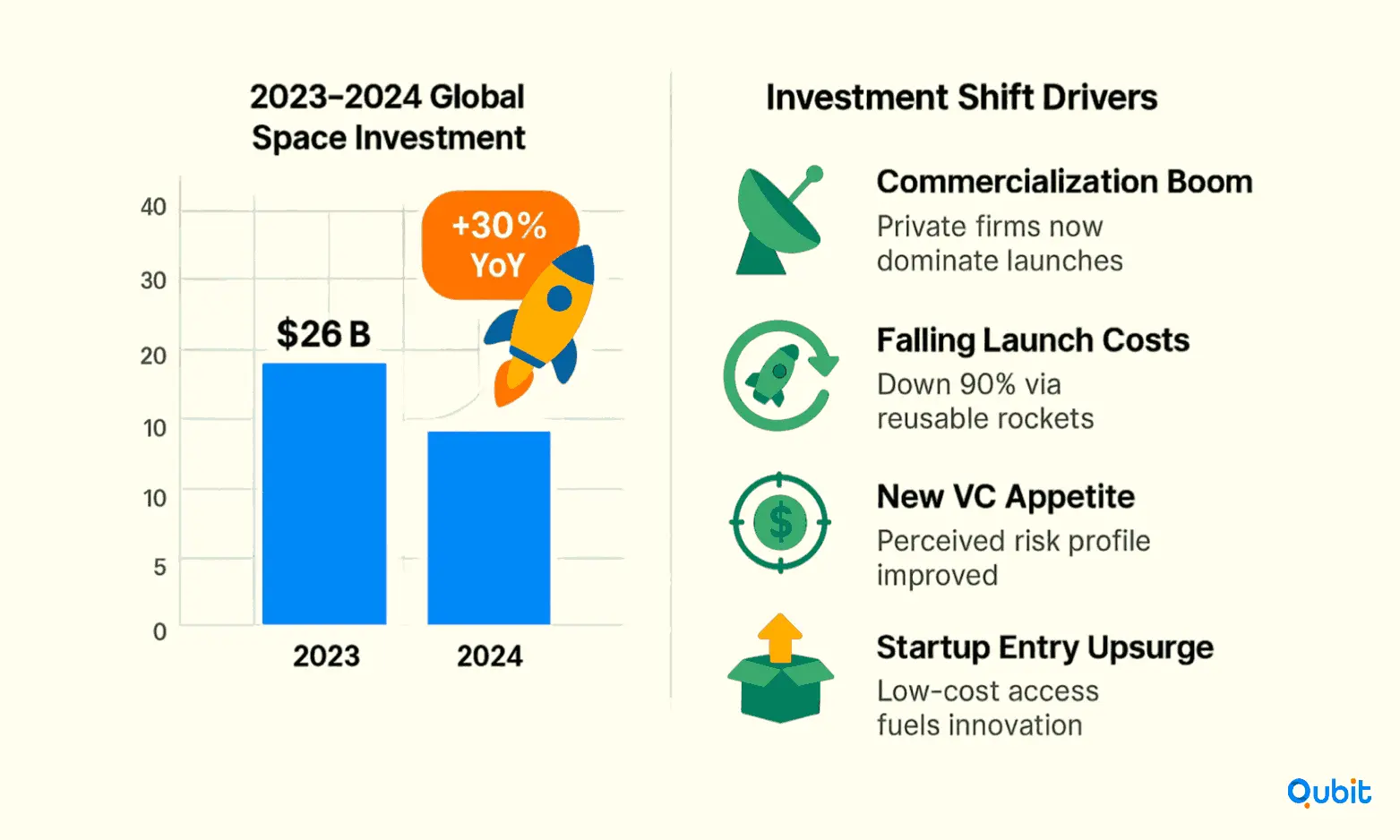
Market Size and Growth Trajectory
The space economy has experienced remarkable expansion, with total space investments reaching $26 billion in 2024, marking a 30% increase year-over-year. This growth represents more than just numerical increases, it signals a fundamental shift in how investors perceive the risk-reward profile of space ventures.
The democratization of space access has been a key driver of this growth. Where launch costs once prohibited all but the most well-funded government programs, technological innovations have dramatically reduced barriers to entry. Launch costs have decreased by 90% due to reusable rockets, enabling new business models and lowering the barrier to entry for innovative startups.
Sector Composition and Opportunities
The launch and orbital services market encompasses several distinct segments, each presenting unique investment opportunities:
- Launch service providers focusing on small satellite deployment, rideshare missions, and dedicated launch solutions
- Orbital infrastructure companies developing space-based manufacturing, satellite servicing, and orbital logistics
- Ground support services including mission planning, satellite operations, and data analytics platforms
- Enabling technologies such as propulsion systems, satellite components, and space-qualified hardware
This diversity creates multiple entry points for investors with varying risk tolerances and sector expertise. Early-stage ventures can focus on component-level innovations, while larger funds target integrated service providers with proven commercial traction.
Regulatory Environment Evolution
The regulatory landscape has become increasingly supportive of commercial space activities. The FAA has streamlined launch licensure processes, achieving 98% on-time approvals and reducing administrative burdens that previously hindered rapid startup deployment. This regulatory efficiency directly impacts startup valuations by reducing time-to-market risks and operational uncertainties.
International regulatory harmonization efforts are also creating opportunities for global expansion, allowing successful domestic ventures to scale internationally with reduced regulatory friction. This trend particularly benefits startups with proprietary technologies that can be deployed across multiple jurisdictions.
Competitive Dynamics
The sector's competitive landscape features a mix of established aerospace primes, well-funded unicorns, and emerging startups pursuing disruptive technologies. This environment creates both challenges and opportunities for new entrants:
Traditional aerospace companies bring manufacturing expertise and customer relationships but often lack the agility to pursue rapidly evolving market opportunities. Venture-backed startups can capitalize on this agility advantage while leveraging partnerships with established players for manufacturing scale and market access.
The emergence of mega-constellations has created substantial demand for launch services, orbital infrastructure, and support systems. This demand surge provides multiple monetization opportunities for startups across the value chain.
Detailed Investment Trends & Analysis
Current Funding Landscape
The venture capital environment for launch and orbital services has reached unprecedented levels of activity and sophistication. VC space tech funding reached $5.9 billion worldwide by June 2025, demonstrating sustained investor confidence in the sector's commercial potential.
Investment patterns reveal several key trends reshaping how capital flows into space ventures:
Late-Stage Funding Dominance
A significant shift toward later-stage investments characterizes the current market, with 41% of space funding now targeting late-stage deals—the highest percentage in a decade. This trend reflects growing investor confidence in established space tech companies that have demonstrated commercial viability and scalable business models.
This late-stage focus creates both opportunities and challenges for early-stage ventures. While competition for seed and Series A funding has intensified, successful early-stage companies can expect more substantial follow-on rounds as they mature.
Alternative Financing Strategies
Traditional equity financing represents just one component of today's diverse funding landscape. Attention to aerospace partnership funding for space startups sheds light on how strategic industry collaborations contribute to scalable investment models within the emerging space sector, aligning with broader capital trends.
Debt financing has emerged as a viable alternative for companies with tangible assets and predictable revenue streams. Astra's success in securing $13.4 million in debt financing demonstrates how struggling space firms can leverage creative funding solutions, using assets as collateral to maintain operations while pursuing strategic pivots.
Revenue-based financing and equipment financing options are becoming increasingly available as lenders develop expertise in evaluating space industry assets and cash flows. These alternatives can provide capital without the dilution associated with equity rounds, particularly valuable for companies approaching profitability.
Crowdfunding and Community Capital
Community-driven funding approaches have proven particularly effective for missions with clear public interest or educational components. This strategy not only provides capital but also builds customer bases and generates market validation data valuable for institutional funding rounds.
An examination of crowdfunding smallsat missions provides a nuanced view of alternative financing paths that balance grassroots support with technological innovation, complementing conventional funding methods.
Sector-Specific Investment Patterns
Launch service providers typically require substantial upfront capital for manufacturing, testing, and regulatory compliance. Investors in this segment focus on companies with differentiated propulsion technologies, innovative manufacturing approaches, or unique market positioning.
Orbital services companies often present more asset-light business models focused on software, data analytics, or specialized mission planning. These ventures can achieve earlier profitability with lower capital requirements, making them attractive to investors seeking faster returns.
Geographic Investment Distribution
Investment activity remains concentrated in traditional aerospace hubs, with California, Texas, and Washington leading in both deal volume and funding amounts. However, emerging clusters in Colorado, Virginia, and international markets are attracting increasing attention as talent and infrastructure develop.
Prospective Future Outlook & Projections
Market Expansion Drivers
Several fundamental trends are positioned to drive continued expansion in venture capital investment for launch and orbital services over the coming years. The convergence of technological advancement, regulatory support, and market demand creates a compelling environment for sustained growth.
Technology-Driven Cost Reductions
The dramatic reduction in launch costs represents just the beginning of a broader technology-driven transformation. Advanced manufacturing techniques, including 3D printing and automated assembly, are reducing production costs across the supply chain. These improvements directly impact startup economics by lowering capital requirements and improving unit margins.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning applications are streamlining mission planning, optimizing orbital mechanics, and enhancing predictive maintenance capabilities. Companies integrating these technologies demonstrate superior operational efficiency and scalability, making them particularly attractive to growth-stage investors.
Expanding Market Applications
The addressable market for launch and orbital services continues expanding as new applications emerge. Earth observation, communications, and scientific research represent established sectors, but emerging opportunities in orbital manufacturing, space tourism, and asteroid mining suggest substantial long-term growth potential.
Recent BryceTech data suggests that VC remains the primary engine for space startup capital, accounting for 92% of $7.8 billion in 2024 funding. This dominance indicates that venture capital will continue playing a central role in sector development rather than being displaced by other funding sources.
Regulatory Momentum
Continued regulatory streamlining enhances the investment attractiveness of space ventures by reducing operational risks and accelerating time-to-market. The FAA's streamlined launch licensure approach demonstrates how evolving regulations could bolster the market for space launch ventures, creating a more predictable environment for investor planning.
International cooperation agreements and standardized regulatory frameworks are expanding accessible markets for successful domestic ventures. This regulatory harmonization reduces expansion risks and increases potential returns on successful investments.
Investment Strategy Evolution
Investor strategies are becoming increasingly sophisticated as the sector matures. Early-stage investors are developing specialized expertise in evaluating technical risks, regulatory compliance, and market positioning. This specialization improves capital allocation efficiency and increases the likelihood of successful outcomes.
Corporate venture capital activity is accelerating as established aerospace companies, telecommunications providers, and technology giants recognize strategic value in space capabilities. These strategic investors offer not just capital but also market access, technical expertise, and operational scale.
Emerging Financing Models
Revenue-based financing and hybrid funding structures are gaining traction as alternatives to traditional equity financing. These approaches can provide growth capital while preserving founder control and reducing dilution, particularly attractive for companies with predictable revenue streams.
Government-backed investment programs and public-private partnerships are creating additional funding pathways. These programs often focus on strategic national priorities while providing commercial returns, creating win-win scenarios for investors and startups.
Long-term Market Projections
The long-term outlook for venture capital investment in launch and orbital services remains exceptionally positive. Market size projections suggest continued double-digit growth rates as space applications become increasingly integrated into terrestrial business models.
The emergence of space-based supply chains, orbital manufacturing capabilities, and interplanetary commerce opportunities represents transformational growth potential. While these applications remain nascent, early investments in enabling technologies and infrastructure could generate substantial returns as these markets develop.
Risk factors including regulatory changes, technological challenges, and market competition require careful evaluation, but the fundamental drivers of sector growth appear robust and sustainable. Your exploration of fundraising strategies for deep-tech startups connects broad financial models with practical market insights, offering you a framework that complements the overall venture capital landscape.
Conclusion
The analysis of investment trends in the launch and orbital services sector highlights a dynamic and rapidly evolving industry. From identifying emerging opportunities to understanding the challenges, this blog has explored the strategies that can help startups thrive in a competitive environment. A data-driven approach remains essential for decoding the complexities of the venture capital ecosystem and making informed decisions.
At Qubit Capital, we specialize in helping startups secure the funding they need to scale and succeed. If you're ready to take the next step in your fundraising journey, reach out to us today. Our Fundraising Assistance service is designed to guide you through every stage of securing seed capital or series funding. Let us help you turn your vision into reality.
Key Takeaways
- Investment in space startups is gaining momentum with significant VC activity in launch and orbital services.
- The blog provides a detailed analysis of market trends and investment strategies in this niche sector.
- Data-backed insights and case studies, such as Astra's debt financing, highlight alternative funding paths.
- Regulatory innovations and reduced launch costs are key factors influencing industry growth.
Frequently asked Questions
What are the top venture capital firms investing in space startups?
Leading venture capital firms in the space sector often focus on technology and aerospace innovation. These firms prioritize startups with groundbreaking ideas and significant growth potential, ensuring they align with the industry’s unique demands.






