Getting early-stage funding in the aerospace industry is highly challenging for startups, yet the sector continues to attract significant investment interest. The aerospace sector is preparing for its most significant transformation since the jet age, driven by the need to achieve Net Zero in aviation by 2050, creating unprecedented opportunities for innovative companies that can navigate the complex partnership landscape.
Recent trends highlight unparalleled investment momentum. In 2024, annual capital deployment in the aerospace partnership market is projected to exceed $3 billion. This scale positions the sector to accelerate both technological progress and sustainability targets. For startups, it underscores readiness for ambitious partnership-driven growth.
This comprehensive guide explores how aerospace companies can leverage prime partnerships to raise capital, scale operations, and achieve sustainable growth in one of the world's most demanding industries.
Understanding Aerospace Prime Partnerships for Capital Raising
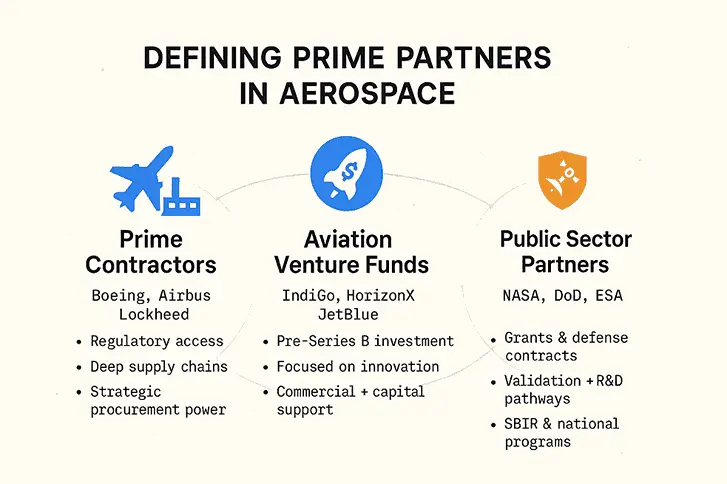
Aerospace prime partnerships are alliances between emerging companies and industry leaders, such as OEMs, defense contractors, airlines, and government agencies.
Defining Prime Partners in Aerospace
- Prime contractors in aerospace typically include major manufacturers like Boeing, Airbus, Lockheed Martin, Northrop Grumman, and Raytheon, along with their extensive supplier networks. These companies possess the financial resources, regulatory expertise, and market access that smaller aerospace companies need to scale effectively.
- Corporate venture capital arms have emerged as significant players in aerospace partnerships. IndiGo Ventures is focused on investing in early-stage startups driving innovation in aviation and allied sectors, targeting companies at the pre-Series A to Series B stages. Similarly, established funds like Boeing HorizonX Ventures, Airbus Ventures, and JetBlue Technology Ventures actively seek partnership opportunities with innovative aerospace startups.
- Government entities including NASA, the Department of Defense, and international space agencies serve as crucial prime partners, offering both funding and validation through programs like NASA's Small Business Innovation Research (SBIR) program and various defense contracting opportunities.
While looking at aerospace prime partnerships, you may notice that the article on fundraising strategies deep tech startups offers additional insights into diverse funding avenues that complement the strategies discussed here.
Strategic Value Beyond Capital
Aerospace prime partnerships provide strategic advantages that traditional venture capital cannot offer. Partnering with investors brings you more than just funding, including access to established supply chains, regulatory expertise, customer relationships, and technical knowledge accumulated over decades of aerospace operations.
These partnerships also provide market validation that independent fundraising cannot achieve. When a major aerospace prime partners with an emerging company, it signals confidence in the technology and business model to other potential investors, customers, and regulatory bodies.
Types of Prime Partnerships for Capital Raising
Aerospace companies can pursue various aerospace prime partnerships depending on their stage of development, technology focus, and capital requirements.
1. Direct Investment Partnerships
Direct equity investments from aerospace primes represent the most straightforward partnership model. AE Industrial Partners is a private investment firm with $5.6 billion AUM specializing in aerospace and industrial sectors. This demonstrates significant capital availability among specialized aerospace investors.
The scale of direct investment is rapidly increasing. In 2025, equity commitments to aerospace partnership initiatives reached $2 billion. This capital injection demonstrates investor confidence and accelerates growth for new entrants.
These partnerships typically involve minority equity stakes that provide capital while preserving management control for the emerging company. The prime partner gains strategic access to new technologies and potential supply chain partners while the startup receives both funding and industry expertise.
2. Joint Venture Structures
Aerospace & Defense Cross-Border Joint Ventures have become increasingly common as companies seek to access international markets and share development costs. These structures allow emerging companies to partner with established players to develop new technologies or enter new markets while sharing both risks and rewards.
Joint ventures particularly benefit companies developing expensive technologies like advanced materials, propulsion systems, or avionics, where development costs exceed the resources of individual companies but market opportunities justify shared investment.
3. Technology Licensing and Development Agreements
Many aerospace partnerships begin with technology licensing or development agreements that can evolve into equity relationships. These arrangements allow primes to evaluate emerging technologies before making larger investment commitments while providing startups with revenue and validation.
AURA AERO announces major orders, strategic partnerships including a $200 US funding deal, demonstrating how initial commercial relationships can evolve into significant capital partnerships.
4. Supply Chain Integration Partnerships
Supply chain partnerships offer emerging companies access to established distribution networks and customer relationships while providing capital through advance payments, inventory financing, or equity investments. With strong industry tailwinds, aero-parts and component manufacturing is emerging as one more segment in India's manufacturing outsourcing story.
These partnerships particularly benefit companies with proven manufacturing capabilities seeking to scale production capacity or enter new geographic markets.
Corporate Venture Capital in Aerospace
Corporate venture capital has become a dominant force in aerospace partnerships, offering specialized expertise and strategic alignment that traditional financial investors cannot provide. By 2027, industry revenues are forecast to surpass $3 billion, over 2.5× higher than 2023 levels. This amplifies the role of strategic investors and positions corporate ventures as key growth catalysts.
Major Corporate Venture Players
IndiGo Ventures launched in August with approval from SEBI to raise Rs 600 crore, representing the growing trend of airline and aerospace companies establishing dedicated venture arms. Other significant players include Boeing HorizonX Ventures, Airbus Ventures, Lux Capital, SpaceFund, Space Capital, and Acorn Growth Companies.
These corporate venture arms bring industry-specific knowledge, regulatory expertise, and customer access that generic venture capital firms cannot offer. They understand aerospace development timelines, certification requirements, and market dynamics that influence investment decisions.
Investment Focus Areas
Corporate venture capital in aerospace typically focuses on technologies that align with parent company strategic objectives. The Clean Aviation Joint Undertaking (JU) focusses on developing disruptive new aircraft technologies to achieve climate neutrality by 2050, with the EU committing funding of €1.7 bn to 2031.
Key investment areas include:
- Propulsion technologies including electric, hybrid, and sustainable aviation fuels
- Advanced materials for weight reduction and performance improvement
- Digital technologies including AI, IoT, and predictive maintenance
- Manufacturing innovations including additive manufacturing and automation
- Urban air mobility and unmanned systems
An examination of space launch startup venture capital presents alternative financing perspectives that broaden your view beyond the specific methods outlined in this guide.
Strategic Partnership Benefits
Corporate venture partnerships provide several advantages over traditional venture capital. Jeh Aerospace combines deep sectoral expertise with sharp operational execution, delivering 100,000 flight-critical aeroengine components and securing $100 million in long-term contracts with global aerospace companies.
These partnerships offer:
- Regulatory guidance for navigating complex certification processes
- Customer introductions to established aerospace customers
- Technical validation through prime contractor expertise
- Supply chain access to established vendor networks
- International expansion support through global operations
Digital Transformation as a Partnership Advantage
Expanding on these benefits, integrating digital technologies such as artificial intelligence, augmented reality, and blockchain can further strengthen aerospace partnerships. These tools optimize manufacturing processes, enhance predictive maintenance, and improve supply chain transparency. Digital transformation also enables partners to address complex technical challenges collaboratively, increasing operational efficiency and competitive differentiation.
Strategic Partnerships with OEMs
Original Equipment Manufacturers represent some of the most valuable potential partners for emerging aerospace companies, offering both capital and market access through established customer relationships.
Partnership Development Strategies
Successful OEM partnerships typically begin with smaller engagements that demonstrate value before evolving into larger strategic relationships. Founded by industry veterans Vishal Sanghavi and Venkatesh Mudragalla – alumni of Tata's aerospace joint ventures with Boeing, Lockheed Martin, and Sikorsky – Jeh Aerospace combines deep sectoral expertise with sharp operational execution.
The most effective approach involves:
- Technology demonstration through pilot programs or proof-of-concept projects
- Regulatory compliance demonstration through certifications and quality standards
- Supply chain integration through smaller initial contracts
- Performance validation through measurable improvements in cost, quality, or capability
Value Proposition Development
OEMs evaluate potential partners based on their ability to solve specific problems or enhance competitive positioning. AURA AERO is the first aerospace project to be selected for the EU's Innovation Fund program, which will allocate a total of €95 million to 85 decarbonization projects.
Compelling value propositions typically include:
- Cost reduction through innovative manufacturing or design approaches
- Performance improvement in areas like fuel efficiency, weight reduction, or reliability
- Risk mitigation through supply chain diversification or technological advancement
- Market differentiation through unique capabilities or customer experiences
Long-term Relationship Building
Successful OEM partnerships require long-term relationship building that extends beyond individual transactions. This partnership will propel use of next-generation technology in the aerospace and aviation sector, strengthens the Indo-US aerospace ties, advances make-in-India and accelerates innovation.
Key relationship building strategies include:
- Executive engagement at multiple organizational levels
- Technical collaboration through joint development programs
- Strategic planning alignment with OEM long-term objectives
- Performance excellence in all contracted activities
Government and Defense Partnerships for Aerospace Funding and Validation
Government partnerships offer unique advantages for aerospace companies, including non-dilutive funding, regulatory validation, and access to defense markets that private partnerships cannot provide.
Federal Funding Programs
NASA's Small Business Innovation Research (SBIR) program supports technological innovation in several industries and aerospace is one of them. The SBIR program provides structured funding progression from Phase I feasibility studies through Phase III commercialization.
Other significant programs include:
- FAA's Aviation Workforce Development (AWD) program offering capital for projects promoting aerospace education
- Department of Transportation's Airport Improvement Program (AIP) providing grants for airport infrastructure improvements
- Defense Innovation Unit (DIU) accelerating commercial technology adoption by the Department of Defense
- Air Force AFWERX supporting dual-use technology development
Academic-Industry Collaboration for R&D Funding
Building on government partnership opportunities, academic-industry collaborations offer aerospace startups access to specialized R&D funding and technical expertise. These partnerships enable companies to co-develop applied research projects with universities, strengthening grant proposals and facilitating technology transition. Engaging with academic partners can improve eligibility for programs targeting technology readiness and innovation. This approach also fosters long-term relationships that support workforce development and future commercialization.
International Government Partnerships
AURA AERO has already built a 10,000 square foot hangar within the Embry-Riddle University Research Park in Daytona Beach, Florida, supported by a $3.4 million investment from Space Florida. This demonstrates how state and local government partnerships can provide significant capital and infrastructure support.
International opportunities include:
- European Space Agency (ESA) programs for space technology development
- UK's Aerospace Technology Institute (ATI) funding for sustainable aviation technologies
- Canada's Strategic Innovation Fund supporting aerospace innovation
- Australia's Cooperative Research Centres (CRC) program for aerospace research
Defense Contractor Integration
Defense contractor partnerships offer access to substantial government contracting opportunities while providing technical expertise and regulatory guidance. The private equity opportunity in aerospace & defense demonstrates significant investor interest in this sector.
Successful defense partnerships typically involve:
- Subcontracting relationships that provide revenue while building capabilities
- Technology development agreements for specific defense applications
- Joint bidding arrangements for larger government contracts
- Supply chain integration for established defense programs
Detailed information on satellite startup government grants deepens your understanding of public funding models that support small-satellite ventures alongside crowdfunding approaches.
International Partnership Models
Global aerospace partnerships offer access to international markets, manufacturing capabilities, and funding sources that domestic partnerships alone cannot provide.
Cross-Border Investment Structures
Prime Capital has more than USD 1 billion in financing volume across more than 200 aircraft, becoming one of the leading German investment managers in the aviation financing market. This demonstrates the significant international capital available for aerospace partnerships.
International partnership models include:
- Cross-border joint ventures for technology development and market access
- Foreign direct investment through international aerospace companies
- Sovereign wealth fund investments in strategic aerospace technologies
- Export credit agency financing for international expansion
Regional Partnership Opportunities
Despite India being one of the world's fastest-growing aviation markets, the country is still a small player in the global aerospace manufacturing industry, highlighting opportunities for international partnerships in emerging markets.
Key regional opportunities include:
- Asian manufacturing partnerships for cost-effective production
- European technology partnerships for advanced aerospace technologies
- Middle Eastern partnerships for aviation services and maintenance
- Latin American partnerships for regional market access
Cultural and Regulatory Considerations in International Partnerships
International partnerships require careful attention to cultural differences, regulatory requirements, and business practices that vary significantly across regions. Aerospace companies must undergo extensive auditing to get certifications ensuring safety, high performance, reliability, and top-notch quality controls.
Success factors include:
- Local expertise through regional partners or advisors
- Regulatory compliance with multiple jurisdiction requirements
- Cultural sensitivity in business relationship development
- Risk management for currency, political, and operational risks
Mitigating Cultural and Regulatory Partnership Risks
- Conduct thorough due diligence on local regulations and business practices before formalizing international partnerships.
- Engage cross-cultural advisors to facilitate communication and resolve misunderstandings between global teams.
- Develop flexible contract structures that accommodate jurisdictional differences and evolving regulatory requirements.
Case Studies in Successful Aerospace Partnerships
Real-world examples demonstrate how aerospace companies have successfully leveraged prime partnerships to raise capital and scale operations.
Case Study 1: Jeh Aerospace's Multi-Partner Strategy
Jeh Aerospace raised $2.75 million in seed funding through a strategic partnership with leading global VC firm General Catalyst, followed by additional investment from IndiGo Ventures. This multi-partner approach demonstrates how aerospace companies can build diverse funding sources.
Key Success Factors:
- Industry veteran leadership with experience at Tata's aerospace joint ventures
- Proven execution delivering 100,000 flight-critical components within first year
- Strategic positioning addressing global supply chain constraints
- Multiple partnership types combining venture capital and strategic corporate investment
Results Achieved:
- $100 million in long-term contracts secured with global aerospace companies
- 100-member specialized team of engineers and technicians
- AS9100 standards compliance for quality certification
- Dual geography presence in USA and India for market access
Case Study 2: AURA AERO's Government-Private Partnership Model
AURA AERO is making the Sunshine State its US base, with backing of Space Florida, combined with selection for the EU's Innovation Fund program. This demonstrates how companies can combine government support with private partnerships.
Partnership Structure:
- EU Innovation Fund providing €95 million across 85 projects
- Space Florida investment of $3.4 million for facility development
- $200 million private funding for US expansion
- Strategic location partnerships for manufacturing and assembly
Strategic Benefits:
- Regulatory validation through government program selection
- Infrastructure support through state agency partnerships
- Market access through established aerospace hubs
- International expansion capabilities through dual-continent presence
Value Proposition Development
Prime partners evaluate potential partnerships based on strategic value rather than purely financial returns. Seek private investors, venture capitalists, or angel investors who are interested in aerospace innovation with solid business plan and compelling pitch.
Strategic Value Drivers:
- Problem-solving capability addressing specific partner pain points
- Competitive differentiation providing unique market advantages
- Risk mitigation through supply chain diversification or technology advancement
- Growth acceleration enabling partner expansion into new markets or capabilities
Relationship Development Process
Successful aerospace partnerships require patient relationship building that may span multiple years before resulting in formal agreements.
Engagement Phases:
- Initial contact through industry events, introductions, or direct outreach
- Technical validation through pilot programs or proof-of-concept projects
- Commercial evaluation demonstrating economic value and market potential
- Strategic alignment confirming long-term partnership compatibility
- Legal structuring negotiating terms that balance risk and reward appropriately
Benefits and Challenges of Prime Partnerships
Understanding both the advantages and potential drawbacks of aerospace prime partnerships enables aerospace companies to make informed decisions about their capital-raising strategies.
Strategic Benefits
- Market Validation and Credibility: Prime partnerships provide immediate market validation that independent companies cannot achieve. When established aerospace companies partner with emerging firms, it signals confidence in technology and business model to other stakeholders.
- Accelerated Market Access: Corporate partnerships with established aerospace companies provide collaboration opportunities on research and development projects or investments in startups with promising ideas. This access can reduce customer acquisition timelines from years to months.
- Technical and Regulatory Expertise: Prime partners bring decades of experience navigating complex regulatory requirements, quality standards, and certification processes that emerging companies must master for success.
- Supply Chain Integration: Established partners provide access to vetted supplier networks, manufacturing capabilities, and distribution channels that would take years to develop independently.
- Risk Mitigation: Partnership with established players reduces market, technical, and financial risks through shared resources, expertise, and market knowledge.
Potential Challenges
- Control and Independence: Prime partnerships may limit strategic flexibility and decision-making autonomy as partners seek influence over business direction and key decisions.
- Competitive Concerns: Partnering with industry incumbents may create conflicts of interest or limit opportunities to work with competitors or enter certain market segments.
- Cultural Integration: Large aerospace companies often have different cultures, decision-making processes, and timelines than entrepreneurial ventures, creating potential friction.
- Intellectual Property Risks: Partnerships may require sharing proprietary technology or giving partners access to competitive advantages that could be difficult to protect.
- Dependency Risks: Over-reliance on single partners for capital, customers, or market access can create vulnerabilities if partnerships end or partner priorities change.
Risk Mitigation Strategies
- Diversified Partnership Portfolio: Developing relationships with multiple partners reduces dependency risks while providing access to different capabilities and markets.
- Clear Legal Frameworks: Comprehensive partnership agreements that define roles, responsibilities, intellectual property rights, and exit provisions protect all parties' interests.
- Milestone-Based Progression: Structuring partnerships with performance milestones allows both parties to validate value before making larger commitments.
- Independent Capability Development: Maintaining some independent capabilities in critical areas prevents complete dependence on partners for essential business functions.
Conclusion
Aerospace prime partnerships offer emerging companies access to resources, expertise, and market validation that independent fundraising cannot provide.
The success stories of companies like Jeh Aerospace, AURA AERO, and JJG Aero demonstrate that well-structured prime partnerships can accelerate growth, reduce risks, and create sustainable competitive advantages. These partnerships combine financial capital with strategic assets including regulatory expertise, customer relationships, technical knowledge, and supply chain access that are essential for aerospace success.
For aerospace entrepreneurs willing to invest the time and resources required to develop prime partnerships, the rewards extend far beyond capital access. Stop waiting for the stars to align, discover our Startup Matchmaking service and meet your next breakout partnership.
Key Takeaways
- Prime partnerships in aerospace provide access to specialized capital, regulatory expertise, and market validation that traditional venture capital cannot offer
- Corporate venture capital arms from major aerospace companies are increasingly active, with funds like IndiGo Ventures raising Rs 600 crore specifically for aerospace investments
- Government partnerships through programs like NASA SBIR and international funding initiatives provide non-dilutive capital and regulatory validation
- Successful partnerships require proven technical capabilities, regulatory compliance, and alignment with prime partner strategic objectives
- Case studies demonstrate that multi-partner strategies combining venture capital, corporate investment, and government support create the strongest foundation for growth
- International partnerships offer access to global markets and manufacturing capabilities but require careful attention to cultural and regulatory differences
Frequently asked Questions
How can aerospace startups attract OEM partnerships for raising capital?
Aerospace startups should demonstrate technical expertise, regulatory compliance, and a compelling value proposition to attract OEM partnerships for capital raising.






