Key performance indicators (KPIs) are the backbone of effective financial modeling, offering clarity and direction in a sea of complex data. Without the right KPIs, even the most sophisticated financial models can fail to deliver actionable insights.
Developing expertise in advanced financial modeling techniques leads to more accurate KPI alignment. It also provides deeper insights into key performance metrics.
This blog aims to provide a comprehensive guide on integrating KPIs into your financial model—highlighting KPI in finance best practices—to ensure you measure what truly matters to your business. Let’s get started.
Grasping KPI Fundamentals in Financial Models
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) serve as the backbone of financial models, offering measurable insights into the effectiveness of strategies and the overall health of a business. Understanding KPIs in finance is essential for creating models that accurately reflect performance and guide decision-making.
What Are KPIs?
KPIs are quantifiable metrics used to evaluate the success of specific objectives. In financial models, they act as benchmarks for assessing operational efficiency, profitability, and strategic alignment. For example, metrics like Gross Profit Margin provide a snapshot of profitability by calculating the percentage of revenue remaining after deducting the cost of goods sold (COGS).
Why Are KPIs Critical in Financial Models?
KPIs are indispensable for tracking financial performance metrics and aligning them with business goals. They provide clarity, enabling businesses to identify strengths, weaknesses, and areas for improvement. For instance, integrating KPIs into financial models ensures that projections resonate with stakeholders and illustrate potential growth. To support this integration, tools like NetSuite Financial Management Software automate KPI calculations and offer real-time dashboards for streamlined tracking.
Additionally, KPIs help businesses adapt to evolving trends. Incorporating insights from trends ensures that models remain relevant and reflective of current market dynamics.
Categorizing KPIs
KPIs can be grouped into three main categories:
- Operational KPIs
These metrics focus on day-to-day efficiency and productivity. Examples include inventory turnover rates and customer acquisition costs, which help businesses optimize operations and reduce inefficiencies. - Financial KPIs
Financial metrics, such as Gross Profit Margin and return on investment (ROI), evaluate profitability and fiscal health. They are pivotal in measuring the success of financial strategies and ensuring sustainable growth. - Strategic KPIs
These indicators align with long-term business objectives, such as market share growth or brand equity. Strategic KPIs ensure that financial models reflect broader organizational goals and provide a roadmap for achieving them.
Here is a rundown:
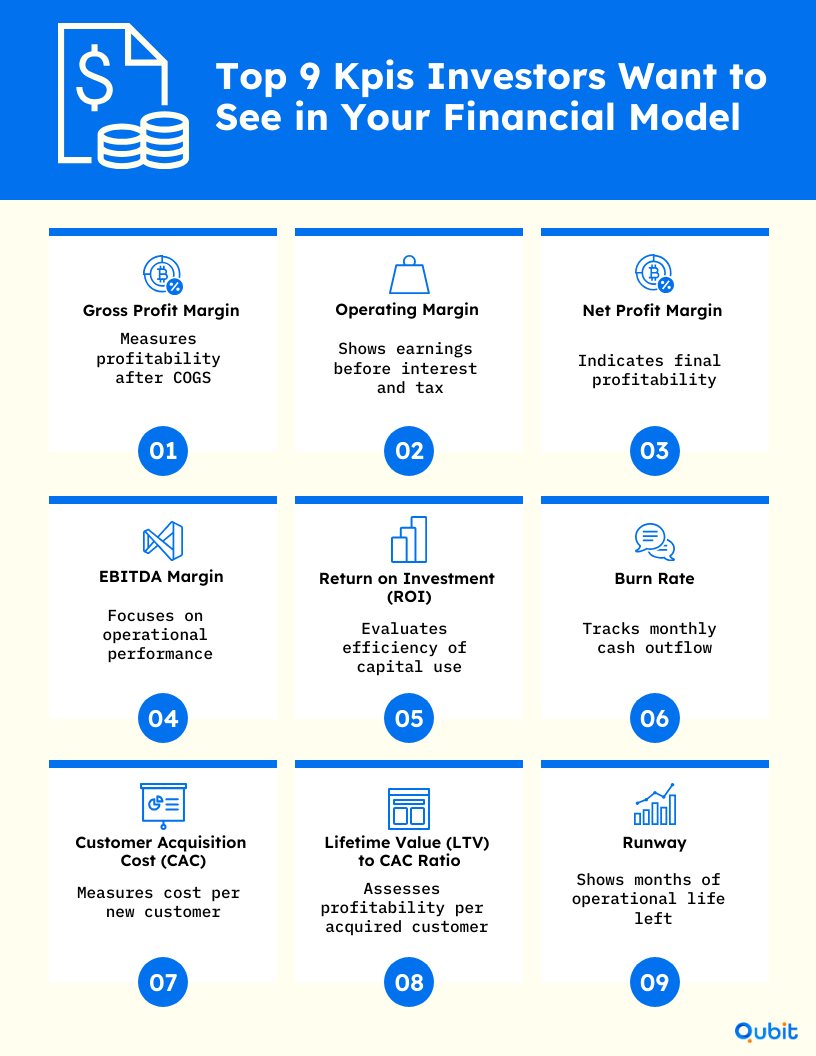
- Gross Profit Margin
This metric offers a snapshot of profitability by showing the percentage of revenue remaining after deducting the cost of goods sold (COGS). It gives investors a clear picture of how efficiently your startup turns sales into profit.
Formula:
(Net Sales−COGS)/Net Sales×100%(text{Net Sales} - text{COGS}) / text{Net Sales} times 100% - Operating Margin
Operating margin evaluates the percentage of revenue left after paying for operating expenses, reflecting how well the core business operations perform before accounting for interest and taxes.
Formula:
(Operating Income/Net Sales)×100%(text{Operating Income} / text{Net Sales}) times 100% - Net Profit Margin
This KPI demonstrates overall profitability by indicating what portion of revenue converts into net profit after all expenses.
Formula:
(Net Profit/Net Sales)×100%(text{Net Profit} / text{Net Sales}) times 100% - EBITDA Margin
Focusing on operational performance, the EBITDA margin compares earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization to net sales, showing the efficiency of your business operations.
Formula:
(EBITDA/Net Sales)×100%(text{EBITDA} / text{Net Sales}) times 100% - Return on Investment (ROI)
ROI measures the efficiency of capital deployment by calculating the return relative to the investment cost—a key indicator for investors assessing financial performance.
Formula:
(Net Profit/Investment Cost)×100%(text{Net Profit} / text{Investment Cost}) times 100% - Burn Rate
This indicator tracks how quickly a startup is consuming its cash reserves on a monthly basis, which is critical for understanding how long the business can operate before needing additional funds.
Formula:
Burn Rate=Monthly Operating Expensestext{Burn Rate} = text{Monthly Operating Expenses}
Note: Burn rate is generally expressed in currency per month. - Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC)
CAC measures the average expense incurred to acquire a new customer, highlighting the efficiency of your marketing and sales strategies.
Formula:
CAC=Total Marketing and Sales Expenses/Number of New Customerstext{CAC} = text{Total Marketing and Sales Expenses} / text{Number of New Customers} - Lifetime Value (LTV) to CAC Ratio
This ratio compares the total revenue expected from a customer over their lifetime to the cost of acquiring that customer, ensuring that customer acquisition efforts are financially sustainable.
Formula:
LTV to CAC Ratio=Customer Lifetime Value (LTV)/CACtext{LTV to CAC Ratio} = text{Customer Lifetime Value (LTV)} / text{CAC} - Runway
Runway estimates the number of months your startup can continue operating using its current cash reserves, which is essential for planning future funding rounds.
Formula:
Runway (months)=Available Cash/Monthly Burn Ratetext{Runway (months)} = text{Available Cash} / text{Monthly Burn Rate}
Tools for Effective KPI Integration
To maximize the impact of KPIs, businesses must use the right tools. For instance, the best financial forecasting software for startups simplifies KPI integration into models, enhancing accuracy in projections. Similarly, courses like CFI’s KPI Dashboard Course teach professionals how to design dashboards that track and visualize KPIs effectively.
Aligning KPIs with strong financial projections helps businesses track performance. It also enhances investor appeal—an essential part of how to create a financial model for investors.
KPIs are more than just numbers—they are actionable insights that drive informed decision-making, ensuring that financial models remain relevant, accurate, and impactful.
Implementing KPI Strategies in Your Financial Models
Integrating KPIs into financial models requires a thoughtful approach to ensure alignment with business objectives and measurable outcomes. By focusing on the right metrics and utilizing advanced tools, businesses can create models that drive informed decision-making and sustained growth.
1. Identify the Right Metrics
The foundation of effective KPI integration lies in selecting metrics that truly reflect your company’s performance and priorities. Start by analyzing your business goals—are you aiming to improve profitability, enhance operational efficiency, or expand market share? Once you’ve clarified your objectives, identify KPIs that directly correlate with these goals.
For example, financial KPIs such as gross profit margin or return on investment (ROI) are ideal for evaluating profitability. Operational metrics like inventory turnover or customer acquisition cost can help measure efficiency. To ensure relevance, avoid generic KPIs and focus on metrics tailored to your industry and business model.
2. Map KPIs to Financial Goals
After pinpointing the right metrics, the next step is to integrate them into your financial models. This involves mapping KPIs to specific financial goals, ensuring each metric contributes to a broader strategic objective.
For instance, if your goal is to increase revenue, KPIs like average revenue per user (ARPU) or sales growth rate can be embedded into your forecasting models. Similarly, if cost reduction is a priority, metrics such as operating expense ratio or cost per unit produced should be tracked.
To enhance accuracy, use historical data and industry benchmarks to set realistic targets for each KPI. This ensures your financial models remain grounded in achievable outcomes while offering a clear roadmap for performance improvement.
3. Utilize Advanced Tools for Real-Time Monitoring
Modern tools and software have revolutionized how businesses monitor KPIs within financial models. Platforms equipped with real-time dashboards and predictive analytics allow you to track performance metrics dynamically, making adjustments as needed.
For example, tools like Tableau or Power BI enable businesses to visualize financial KPIs and identify trends or anomalies quickly. Real-time monitoring ensures that your models remain responsive to changing market conditions, helping you stay ahead of potential risks.
Additionally, automation tools can streamline data collection and analysis, reducing manual errors and freeing up resources for strategic planning. By integrating these technologies, businesses can optimize their financial models for precision and adaptability.
Qubit Capital’s Expertise
At Qubit Capital, we specialize in creating financial models that incorporate tailored KPIs to drive business success. Whether you need help identifying impactful metrics or integrating advanced monitoring tools, our team is here to assist. Learn more about our Financial Model Creation services today.
Real-Life Examples of KPI Impact in Financial Operations
Key performance indicators (KPIs) are more than just numbers—they are essential tools for driving efficiency and innovation in financial operations. Through real-world examples, this section explores how integrating KPIs into financial models can transform operational performance and strategic decision-making.
Peel Police – Restructuring for Efficiency and Innovation
Peel Regional Police demonstrated the power of KPIs by restructuring their operations to align with technology advancements, innovation, and community-focused policing. By implementing a "fit for purpose" strategy, they identified key metrics to evaluate the effectiveness of their initiatives.
This approach allowed them to streamline processes, improve resource allocation, and foster stronger community relationships. Their success underscores how a well-integrated KPI system can redefine operational efficiency in public safety.
SGTraDex – Revolutionizing Supply Chain Data Sharing
Singapore’s SGTraDex initiative highlights the role of KPIs in digital transformation. By creating a "digital highway" for secure and streamlined supply chain data sharing, SGTraDex utilized KPIs to measure the impact of their innovations. These metrics helped them safeguard sensitive information while improving operational transparency and efficiency across multiple stakeholders. The result was a more resilient and collaborative supply chain ecosystem.
Strategic Insights: Scenario Analysis and KPI Resilience
Scenario analysis plays a crucial role in keeping KPIs relevant under fluctuating conditions. Understanding how to perform scenario analysis in financial modeling equips businesses with the tools to evaluate financial resilience and make proactive adjustments.
These examples illustrate that integrating KPIs into financial models is not just about tracking numbers—it’s about driving innovation, improving efficiency, and enabling strategic execution. Whether optimizing law enforcement operations or revolutionizing supply chain management, KPIs provide the foundation for measurable success.
Future-Proofing KPI Integration with Emerging Trends
The evolution of financial key performance indicators (KPIs) is being shaped by groundbreaking technologies and global compliance demands. As AI-powered analytics redefine how businesses measure success, organizations must adapt their KPI strategies to remain competitive and compliant.
AI-Powered Analytics: Transforming KPI Tracking
Artificial intelligence is revolutionizing the way financial performance metrics are analyzed and integrated. AI-driven tools not only streamline data collection but also uncover actionable insights that were previously inaccessible. For instance, ai financial modeling tools automate repetitive tasks, enhancing accuracy and saving valuable time. These advancements allow businesses to refine their KPIs continuously, ensuring alignment with both strategic goals and regulatory requirements.
Compliance Insights: A Global Perspective
Regulatory compliance is no longer a static checklist—it’s a dynamic process influenced by global trends. There is a need for businesses to integrate compliance metrics into their KPI frameworks. By doing so, organizations can proactively address regulatory shifts while maintaining operational agility. Continuous refinement of KPIs ensures businesses are not only compliant but also prepared to adapt to emerging challenges.
Strategic Agility Through Emerging Trends
The integration of AI-powered tools and compliance insights enables businesses to achieve strategic agility. This agility is crucial for navigating unpredictable market conditions and capitalizing on opportunities.
The Path Forward
Future-proofing KPI integration requires a proactive approach. Businesses must embrace emerging technologies and stay informed about global compliance trends to ensure their metrics remain relevant and actionable. By combining AI-driven analytics with compliance insights, organizations can build robust KPI frameworks that support both financial growth and regulatory adherence.
Conclusion
Integrating KPIs into financial models requires a thoughtful and structured approach. By focusing on the strategies outlined, such as aligning KPIs with business objectives and utilizing advanced tools, businesses can unlock valuable insights for strategic growth. These practices not only enhance decision-making but also ensure that financial models remain dynamic and responsive to evolving market conditions.
At Qubit Capital, we get that raising funds is a big deal. Our Fundraising Assistance service is here to help you secure the capital you need—let's turn your vision into reality.
Key Takeaways
- Integrating KPIs aligns financial models with strategic objectives.
- A structured, step-by-step approach is essential for effective KPI tracking.
- Real-life case studies demonstrate the tangible impact of KPI integration.
- Emerging technologies and automation are transforming traditional KPI measurement.
- Utilizing advanced tools boosts forecasting accuracy and operational efficiency.
Frequently asked Questions
What is KPI in financial analysis?
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) in financial analysis are measurable metrics used to evaluate the financial health and performance of a business. They provide insights into areas such as profitability, liquidity, and operational efficiency, helping stakeholders make informed decisions. Common examples include net profit margin, return on investment (ROI), and current ratio.


 Back
Back



