Financial modeling is more than just crunching numbers; it’s about crafting a blueprint for informed decision-making. Whether you're refining projections or exploring new methodologies, understanding advanced financial modeling techniques can transform your approach. Building robust financial projections is the cornerstone of financial modeling, as outlined in our guide on how to create a financial model for investors.
This blog dives into cutting-edge strategies and tools designed to elevate your financial models, bridging technical expertise with actionable insights. From exploring innovative approaches to integrating practical examples, we’ll equip you with the knowledge to create models that not only stand out but also drive results. Ready to unlock the full potential of your financial models? Let’s jump right in.
Foundations of Financial Modeling
Financial modeling serves as a powerful tool for forecasting and strategic decision-making, enabling businesses to predict financial outcomes and assess potential risks. At its core, a financial model combines quantitative data and assumptions to simulate future scenarios, offering insights that guide critical decisions.
The foundation of financial modeling lies in three essential components: the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow analysis. These financial statements provide the structure for understanding a company’s profitability, financial position, and liquidity, respectively. By integrating these elements, a financial model can offer a comprehensive view of a business’s financial health.
Key techniques such as simulation and scenario planning further enhance the utility of financial models. Simulation involves creating multiple iterations of a model to account for uncertainties, while scenario planning allows users to explore various "what-if" situations. For instance, incorporating discounted cash flow (DCF) analysis into your model can help determine present values under varying risk scenarios.
15 Advanced Financial Modeling Techniques
Financial modeling techniques are the backbone of strategic decision-making in finance. From evaluating investment opportunities to forecasting financial outcomes, advanced methods provide the precision and depth required for complex analyses. This section explores 15 sophisticated techniques, including discounted cash flow (DCF), leveraged buyouts (LBO), and Monte Carlo simulations, detailing their practical applications and unique purposes.
1. Discounted Cash Flow (DCF)
DCF is a cornerstone of valuation, used to estimate the present value of future cash flows. By discounting these cash flows using an appropriate rate, this technique helps assess whether an investment is worth pursuing. Its practical application lies in evaluating projects, acquisitions, and company valuations.
2. Leveraged Buyouts (LBO)
LBO modeling is essential for analyzing acquisitions financed primarily through debt. This technique focuses on projecting cash flows to determine the feasibility of debt repayment while achieving targeted returns. It’s widely used by private equity firms to assess potential buyout opportunities.
3. Monte Carlo Simulations
Monte Carlo simulations introduce probabilistic analysis into financial modeling. By simulating thousands of possible outcomes based on variable inputs, this technique is ideal for risk assessment and scenario planning, particularly in volatile markets.
4. Three-Statement Model
The three-statement model integrates the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement into a cohesive framework. It’s fundamental for understanding the interdependencies between a company’s financial statements and forecasting future performance.
5. Option Pricing Models
These models, including Black-Scholes and binomial methods, are used to value financial derivatives. Their application is critical in assessing the fair value of options and other complex financial instruments.
6. Sensitivity Analysis
Sensitivity analysis evaluates how changes in key assumptions impact financial outcomes. It’s a powerful tool for identifying risks and understanding the robustness of a financial model under varying conditions.
7. Scenario Analysis
Unlike sensitivity analysis, scenario analysis examines multiple predefined scenarios to assess potential outcomes. This technique is particularly useful for strategic planning and stress testing.
8. Comparable Company Analysis (CCA)
CCA involves benchmarking a company’s valuation metrics against similar firms in the industry. It’s a quick and effective method for estimating a company’s value based on market trends.
9. Merger and Acquisition (M&A) Models
M&A models are tailored for analyzing the financial impact of mergers or acquisitions. They focus on synergies, purchase price allocation, and post-transaction financial projections.
10. Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM)
CAPM calculates the expected return on an investment based on its risk relative to the market. It’s widely used in portfolio management and cost of equity calculations.
11. Dividend Discount Model (DDM)
DDM values a company based on its future dividend payments. This technique is particularly relevant for investors focused on income-generating stocks.
12. Budgeting Models
Budgeting models help organizations plan and allocate resources effectively. They are essential for setting financial targets and monitoring performance.
13. Financial Ratio Analysis
This technique involves analyzing key ratios, such as liquidity, profitability, and efficiency, to assess a company’s financial health. It’s a foundational tool for both internal and external stakeholders.
14. Debt Schedule Modeling
Debt schedule modeling tracks repayment schedules and interest expenses over time. It’s crucial for managing debt obligations and ensuring financial stability.
15. Project Finance Models
These models focus on evaluating the feasibility and profitability of large-scale projects, such as infrastructure or energy developments. They incorporate detailed cash flow projections and risk assessments.
By mastering these advanced financial modeling techniques, professionals can refine their assumptions, improve decision-making, and gain deeper insights into complex financial scenarios.
Critical Role of Financial Modeling in Strategic Decision-Making
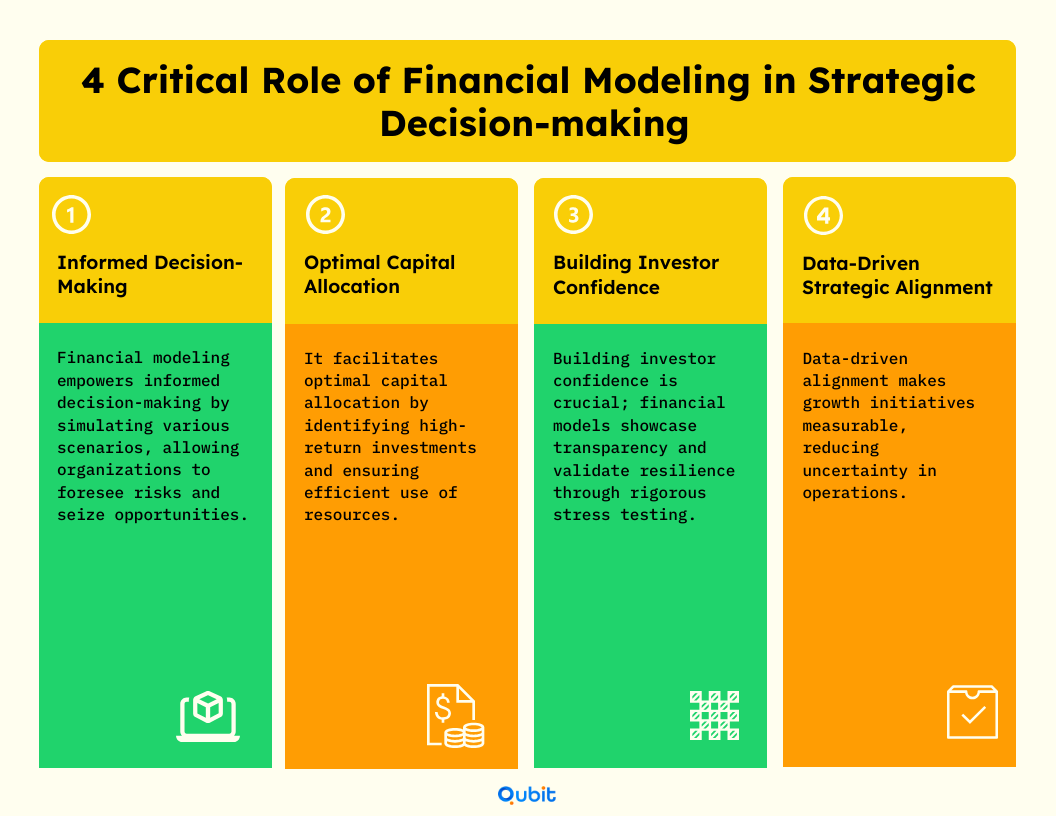
Informed Decision-Making
Financial modeling provides a framework for analyzing outcomes, assessing risks, and allocating resources efficiently. By simulating various scenarios, companies can anticipate challenges and seize opportunities that align with long-term objectives.
Optimal Capital Allocation
- Investment Prioritization: Detailed models help identify where investments yield the highest returns.
- Resource Efficiency: Optimized financial projections ensure every dollar is directed toward initiatives that enhance profitability and sustainability.
Building Investor Confidence
- Transparency & Preparedness: A well-constructed model demonstrates a company’s ability to adapt to market changes, instilling trust among investors.
- Stress Testing Financial Models: Rigorous Financial Stress testing validates resilience under dynamic market conditions, reinforcing strategic confidence.
Data-Driven Strategic Alignment
Financial models act as a compass, guiding decisions on expanding operations, entering new markets, or optimizing processes. Integrating detailed projections and scenario analyses reduces uncertainty and aligns strategies with measurable outcomes, fostering trust among all stakeholders.
Essential Tools and Software for Creating Dynamic Financial Models
Building effective financial models requires the right combination of tools and software tailored to your specific needs. From traditional spreadsheet solutions to advanced modeling platforms, selecting the appropriate tool is crucial for creating adaptable and accurate models.
MS Excel: A Timeless Standard
MS Excel remains a cornerstone for financial modeling due to its flexibility and customization capabilities. Its robust features, such as custom formulas and pivot tables, allow users to dynamically forecast cash flows and model various scenarios. Whether you’re crafting a corporate modeling framework or exploring a financial modeling example, Excel’s versatility makes it indispensable. MS Excel continues to be a go-to tool for professionals seeking detailed control over their models.
Specialized Financial Modeling Software
For more complex or industry-specific needs, specialized software offers advanced functionalities that go beyond traditional spreadsheets. These platforms often include pre-built templates, automated calculations, and integration with external data sources, streamlining the modeling process. Choosing the best financial forecasting software for startups can streamline projections and enhance model accuracy.
Choosing the Right Tool
The complexity of your financial model should guide your choice of software. For straightforward models, Excel may suffice. However, for intricate forecasting or scenario analysis, specialized tools can save time and reduce errors. Evaluate your requirements, including scalability, ease of use, and compatibility with existing systems, before committing to a solution.
Key Professionals Behind Robust Financial Models
Financial models are the backbone of strategic decision-making in businesses, crafted by experts who bring specialized skills and analytical precision to the table. Professionals such as investment bankers, equity researchers, and corporate developers play pivotal roles in creating and refining these models, each contributing unique methodologies to ensure accuracy and relevance.
Investment Bankers: Structuring Complex Models
Investment bankers excel in building intricate financial models tailored to mergers, acquisitions, and capital raising. Their expertise lies in forecasting cash flows, valuing companies, and analyzing potential returns. Using tools like discounted cash flow (DCF) analysis, they evaluate the financial viability of transactions, ensuring that every variable aligns with market realities. Their models often serve as the foundation for high-stakes negotiations, providing clarity on risks and rewards.
Equity Researchers: Insights for Market Dynamics
Equity researchers focus on assessing the performance of publicly traded companies. They utilize business financial models to analyze revenue streams, cost structures, and market trends, offering actionable insights for investors. By incorporating private equity financial modelling techniques, they can predict stock movements and identify undervalued assets. Their work supports investment decisions, ensuring alignment with broader financial goals.
Corporate Developers: Driving Strategic Growth
Corporate developers specialize in creating financial models that guide internal business strategies. Whether evaluating new ventures or optimizing existing operations, they rely on scenario analysis and sensitivity testing to anticipate outcomes. Their models are instrumental in shaping long-term growth plans, balancing risk with opportunity.
Each of these professionals employs distinct analytical approaches, yet their collective efforts converge to create robust financial models that drive informed decision-making. Whether it's structuring deals, analyzing market trends, or planning corporate strategies, their expertise ensures that businesses can navigate complex financial landscapes with confidence.
Industry-Specific Financial Modeling
Financial modeling is a cornerstone of strategic planning for businesses, but its effectiveness depends on how well it aligns with the unique dynamics of each industry. A business financial model for real estate, for instance, must account for property valuation, rental income projections, and market cycles. On the other hand, e-commerce models prioritize inventory turnover, digital marketing ROI, and customer acquisition costs.
Startups and established companies alike are increasingly adopting financial models for purposes like runway management, capital raising, and long-term planning. As more businesses integrate advanced modeling techniques, they gain a competitive edge in securing investments and optimizing operations. To illustrate, integrating advanced financial modeling techniques into your processes can help businesses adapt to evolving market demands.
Tailoring financial models to specific industries ensures that they address sector-specific challenges and opportunities. In real estate, factors such as location, zoning regulations, and interest rates play a pivotal role in shaping forecasts. Meanwhile, e-commerce models must adapt to trends like seasonal demand and platform-specific fees. This customization not only enhances accuracy but also empowers businesses to make informed decisions.
The widespread use of financial models underscores their importance across industries. Whether you're in real estate, e-commerce, or another sector, the ability to adapt your modeling approach to your market's nuances can be a game-changer.
Financial Model Variations: Examples and Key Highlights
Understanding the nuances of financial modeling is essential for businesses aiming to make informed decisions. This section delves into ten widely-used financial models, offering practical examples, pre-built templates, and actionable insights to enhance your modeling expertise.
1. Three-Statement Model
The Three-Statement Model integrates the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement into a single framework. This dynamic approach ensures that changes in assumptions ripple across all financial forecasts, providing a comprehensive analysis. A clear trend in finance modeling is the adoption of integrated analysis, where these three statements are linked dynamically.
2. Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) Model
The DCF Model is a cornerstone of valuation techniques, focusing on calculating the Net Present Value (NPV) of projected cash flows. Using tools like the XNPV function in Excel, this model discounts irregular cash flows based on Weighted Average Cost of Capital (WACC).
3. Mergers and Acquisitions (M&A) Model
M&A models evaluate the financial impact of mergers or acquisitions, incorporating pro forma analysis, synergy integration, and sensitivity testing. To refine your skills, consider the M&A Course for advanced insights into building these models.
4. Leveraged Buyout (LBO) Model
The LBO Model is designed to assess the feasibility of acquiring a company using significant debt. It integrates complex debt schedules, circular references, and cash flow waterfalls. A detailed example can be found in the LBO Model Example, which demonstrates techniques to accurately reflect capital structures.
5. Pre-Built Templates
Pre-built templates are increasingly popular for accelerating model development and ensuring accuracy. These downloadable resources serve as a reliable starting point for advanced financial modeling projects.
6. Integrated Financial Models
Integrated models dynamically link financial statements, enabling seamless propagation of changes across forecasts. This approach is particularly effective for businesses seeking clarity in their financial projections.
For businesses looking to optimize their projections, AI financial modeling tools are revolutionizing efficiency by automating complex calculations and streamlining workflows.
Conclusion
Advanced financial modeling techniques serve as a powerful tool for startups aiming to make informed strategic decisions. Throughout this blog, we’ve explored key strategies that enhance financial planning, streamline investor communication, and ultimately drive business growth. By implementing these insights, startups can build a strong foundation for success and confidently approach their next steps.
We at Qubit Capital believe that the right financial model can make all the difference when connecting with investors. Explore our Financial Model Creation service to build a robust, detailed narrative that attracts the best-fit investors. Let’s begin your journey today.
Key Takeaways
- Advanced financial modeling uniquely blends theory with actionable strategies.
- Fifteen distinct techniques offer a robust framework for forecasting and analysis.
- Selecting the right tools, such as MS Excel and specialized software, is critical for model precision.
- A step-by-step approach ensures the integration of historical data, market conditions, and valuation methods.
- Industry-specific customization is essential for addressing unique market dynamics.
Frequently asked Questions
What is advanced financial modeling?
Advanced financial modeling integrates techniques such as scenario planning, sensitivity analysis, and simulation to forecast outcomes with precision.


 Back
Back