The consumer technology sector has seen explosive growth, with startups raising billions in venture capital to fuel innovation and market expansion. But the traditional, equity-heavy approach to funding is increasingly being complemented by venture debt, giving consumer tech companies a way to access growth capital without giving up additional ownership.
In India alone, venture debt reached a record $1.2 billion in 2023, a 50% surge from the previous year. Globally, 2024 marked a major inflection point as venture debt investment climbed to $53.3 billion in the U.S. alone, clear evidence of rising confidence in debt-driven growth strategies and a broader evolution in how startups are financed.
For consumer tech startups operating in intensely competitive markets, where timing, speed, and scale often decide the winners, venture debt can provide the financial flexibility to seize growth opportunities without the lengthy fundraising cycles and dilution that come with additional equity rounds. However, startups typically need to demonstrate strong revenue traction and existing investor backing to qualify.
This comprehensive guide explores how consumer tech entrepreneurs can leverage venture debt solutions to accelerate growth while maintaining strategic control.
Understanding Venture Debt in the Consumer Tech Context
Venture debt is a loan product specifically designed for fast-growing, investor-backed startups that provides access to non-equity capital with minimal dilution. Unlike traditional lending that focuses on historical cash flows and tangible assets, venture debt underwriting considers the startup's ability to raise additional venture capital and the quality of existing investor backing.
Core Characteristics:
- Loan Amounts: Typically 20-40% of the most recent equity round
- Interest Rates: 10-18% annually in the Indian market, varying by risk profile
- Terms: 2-4 year repayment periods with interest-only phases
- Collateral: Secured by company assets and intellectual property
- Equity Component: Warrants for 1–5% equity (warrants are rights to purchase shares at a future date and price)
It’s easy to overlook how differently marketplace and consumer business models perform under funding pressure, the funding guide for consumer & marketplace startups helps clarify the trade-offs.
Why Consumer Tech Startups Choose Venture Debt:
- Rapid Market Entry: Consumer tech markets often reward first movers, making speed of execution critical for success. Venture debt enables faster scaling without the 3-6 month timeline typical of equity fundraising.
- Seasonal Capital Needs: Many consumer tech companies experience seasonal revenue fluctuations or require working capital for inventory, marketing campaigns, or product launches that don't justify full equity rounds.
- Runway Extension: Venture debt can provide 6-18 months of additional runway, allowing startups to achieve key milestones that improve valuation for subsequent equity rounds.
Advantages of Venture Debt for Consumer Tech Growth
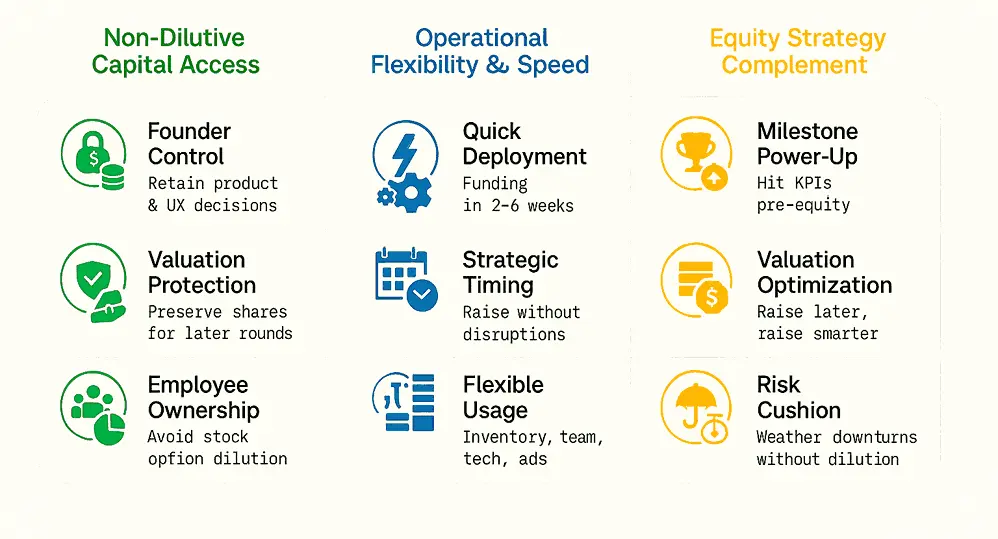
1. Non-Dilutive Capital Access
Venture debt provides substantial growth capital. It does not require founders to surrender equity ownership.
As venture debt matures, its integration with equity strategies has become widespread. According to recent research, venture debt now appears in over a third of startups during financing lifecycles and accounts for 15% of total startup financing. This demonstrates the growing role of debt capital as a strategic complement to equity.
- Founder Control: Maintaining decision-making authority over product development, user experience, and brand positioning
- Future Valuation Protection: Preserving equity for later rounds when company valuations may be significantly higher
- Employee Ownership: Protecting employee stock option pools from dilution during growth phases
2. Operational Flexibility and Speed
Consumer tech markets demand rapid response to user needs and competitive dynamics. Venture debt offers distinct advantages:
- Quick Deployment: Approval and funding processes typically take 2-6 weeks compared to 3-6 months for equity rounds
- Strategic Timing: Access capital when market opportunities arise without disrupting ongoing operations for fundraising activities
- Flexible Usage: Deploy capital for inventory, marketing, team expansion, or technology infrastructure based on immediate business needs
3. Complementary to Equity Strategy
- Milestone Achievement: Use debt capital to reach key performance indicators that improve positioning for larger equity rounds
- Valuation Optimization: Delay equity fundraising until achieving metrics that command premium valuations in the market
- Risk Mitigation: Maintain financial cushion against unexpected challenges or market volatility without emergency equity dilution
Not every D2C or marketplace startup should chase scale the same way, and this breakdown of scaling capital for marketplaces & d2c brands helps define why.
Key Venture Debt Providers for Consumer Tech Startups
Leading Consumer Tech Portfolio Examples
Consumer Sector Success Stories: Venture debt has powered growth for prominent consumer tech companies including Zepto (quick commerce), Chaayos (food & beverage), Rebel Foods (cloud kitchens), and Bliss Club (fitness). These companies leveraged debt capital for:
To illustrate typical deal structuring, a company raising $10 million in equity would be eligible for $2–$3.5 million in venture debt. This enables funding for expansion and major operational initiatives without immediate equity dilution.
- Inventory scaling during growth phases
- Geographic expansion into new markets
- Technology infrastructure development
- Marketing campaign financing for user acquisition
Eligibility Requirements and Assessment Criteria
Primary Qualification Framework
Venture Capital Backing: Startups must have raised at least one institutional venture capital round to qualify for venture debt financing. This requirement ensures:
- Professional investor validation of business model
- Governance standards and financial reporting systems
- Access to additional capital sources for debt repayment
- Strategic guidance from experienced venture capital partners
Revenue and Traction Metrics: While specific requirements vary by lender, consumer tech startups typically need:
- Monthly Revenue: $50K-500K+ recurring revenue depending on business model
- Growth Rate: Demonstrated 15-30% month-over-month growth over 6+ months
- Customer Metrics: Strong retention rates and expanding user base
- Unit Economics: Clear path to profitability with improving contribution margins
Recent market analysis indicates nearly 40% of startup founders now focus on debt financing at the pre-IPO level. This trend underscores how eligibility criteria directly shape access to critical growth capital.
Business Model Considerations
- Scalable Technology Platform: Lenders evaluate the startup's technology infrastructure and its ability to support rapid user growth without proportional cost increases
- Market Opportunity: Total addressable market size and the startup's positioning within competitive landscape influence debt capacity and terms
- Team Experience: Management team's track record in scaling consumer technology businesses and operational execution capabilities
Strategic Implementation Process
Phase 1: Readiness Assessment (3-6 Months)
Financial Infrastructure Development
- Implement professional accounting systems and monthly financial reporting
- Establish cash flow forecasting with scenario planning capabilities
- Develop key performance indicator tracking for consumer metrics
- Complete legal entity structure optimization for debt requirements
Business Case Documentation
- Create comprehensive business plan with growth projections
- Compile competitive analysis and market positioning strategy
- Document technology architecture and scalability roadmap
- Prepare customer case studies and retention analysis
Phase 2: Lender Engagement (1-3 Months)
Provider Research and Selection
- Identify venture debt firms with consumer tech expertise and portfolio alignment
- Evaluate term structures, interest rates, and covenant requirements across options
- Assess lender value-add services beyond capital provision
- Secure warm introductions through venture capital investors or portfolio companies
Due Diligence Preparation
- Organize financial statements, cap table, and legal documents in structured data room
- Prepare management presentations highlighting growth metrics and capital deployment plans
- Coordinate customer and investor reference calls to validate business performance
- Engage legal counsel experienced in venture debt documentation and negotiation
Phase 3: Structuring and Closing (4-8 Weeks)
Term Negotiation Strategy
- Balance interest rates against covenant flexibility and prepayment options
- Structure warrant coverage to align with long-term equity strategy
- Negotiate financial reporting requirements and milestone tracking systems
- Establish clear guidelines for additional capital deployment and growth investments
Negotiating Favorable Venture Debt Terms
Building on the structuring phase, founders should prioritize negotiating interest-only periods and flexible covenant terms to reduce early repayment pressure. Reasonable warrant coverage can help balance funding costs with long-term ownership retention. These strategies ensure that debt obligations do not constrain growth initiatives or operational flexibility. Proactive negotiation of these terms strengthens the startup’s financial position and supports sustainable scaling.
Integration and Deployment
- Implement debt service management and compliance monitoring systems
- Deploy capital according to strategic priorities and milestone achievement timelines
- Establish regular communication protocols with lenders for performance updates
- Monitor financial metrics and covenant compliance to maintain optimal lender relationships
Prepare comprehensive legal documentation for lender review and approval.
Aligning Venture Debt Strategy with Equity Stakeholders
This approach requires founders to coordinate venture debt plans with existing equity investors and board members to maintain transparency and secure their endorsement. Such alignment optimizes the capital structure and builds investor confidence in the company’s financial strategy. Engaging stakeholders early can also facilitate smoother negotiations and more favorable loan terms. This collaborative process supports long-term growth and risk management.
For marketplace founders, showing network depth matters as much as revenue, something this insight into preparing for series a funding in marketplace startups explains well.
Risk Management and Mitigation Strategies
Financial Risk Considerations
Repayment Obligations: Unlike equity financing, venture debt creates mandatory payment obligations that can strain cash flow during challenging periods. Consumer tech startups should:
- Cash Flow Planning: Maintain 6-12 months of debt service coverage in cash reserves
- Scenario Modeling: Develop financial projections under various growth and market scenarios
- Covenant Management: Monitor financial metrics closely to avoid technical defaults
- Refinancing Strategy: Plan for debt refinancing or equity raises before maturity dates
Operational Risk Management
Debt obligations can create pressure for short-term revenue generation that conflicts with long-term strategic positioning. Mitigation approaches include:
- Milestone-Based Deployment: Structure debt drawdowns tied to specific growth achievements rather than immediate full deployment
- Strategic Reserve Maintenance: Preserve portion of debt capacity for unexpected opportunities or market challenges
- Investor Communication: Maintain transparent dialogue with both debt and equity investors about strategic priorities and resource allocation
Transparent Reporting for Lender Relationship Management
Building on financial risk planning, founders should implement transparent financial reporting and regular communication with lenders to maintain trust and covenant compliance. Timely updates on performance and challenges enable lenders to respond flexibly to temporary setbacks. This practice reduces the risk of misunderstandings and supports access to future capital. Strong reporting habits also reinforce the startup’s credibility in the venture debt ecosystem.
Market Risk Adaptation
Consumer tech markets can experience rapid shifts in user preferences, competitive dynamics, or technology adoption patterns. Protective measures include:
- Diversified Revenue Streams: Develop multiple monetization channels to reduce dependence on single revenue sources
- Flexible Cost Structure: Maintain variable cost components that can adjust with revenue fluctuations
- Technology Investment: Allocate debt capital toward technology infrastructure that supports multiple product lines or market expansions
Some startups with erratic revenue or weak investor backing may not qualify or benefit from debt.
When brand velocity outpaces your burn rate, aligning with the right growth-equity options for d2c brand expansion becomes more about timing than dilution.
Consumer Tech Success Case Studies
E-Commerce and Marketplace Platforms
Consumer tech companies in e-commerce have successfully leveraged venture debt for inventory financing, geographic expansion, and technology infrastructure development. Quick commerce platforms like Zepto utilized venture debt to scale inventory management systems and expand delivery networks across multiple cities without diluting equity during rapid growth phases.
Key Success Factors:
- Predictable revenue streams from transaction fees and commissions
- Asset-light business models with strong cash conversion cycles
- Clear metrics for measuring market penetration and user engagement
- Ability to deploy capital incrementally based on market response
Consumer Financial Services
Fintech startups focusing on consumer financial products have emerged as significant venture debt recipients, with companies like Slice and Jupiter using debt capital to fund loan portfolios, regulatory compliance, and user acquisition campaigns.
Strategic Advantages:
- Revenue-generating assets that serve as natural collateral for debt financing
- Regulatory capital requirements that benefit from non-dilutive funding sources
- Recurring revenue models that support predictable debt service capabilities
- Scalable technology platforms that improve unit economics with growth
Food and Lifestyle Brands
Consumer brands in food service and lifestyle categories have leveraged venture debt for supply chain optimization, geographic expansion, and brand building initiatives. Companies like Rebel Foods used debt financing to expand their cloud kitchen network and develop new food brands without equity dilution.
Implementation Strategies:
- Working capital financing for inventory and supply chain management
- Marketing campaign funding for brand awareness and customer acquisition
- Geographic expansion capital for new market entry and local operations
- Technology infrastructure investment for omnichannel customer experiences
Common Challenges and Strategic Solutions
1. Balancing Debt Service with Growth Investments
Consumer tech startups often face the challenge of balancing debt service obligations with growth investments. Successful navigation of this balance requires disciplined financial planning and dedicated cash flow management that segregates funds for debt repayment from those allocated for growth initiatives.
Establishing rolling 18-month cash flow forecasts that model various growth scenarios helps maintain a financial cushion of 6-12 months' worth of debt service coverage. Additionally, structuring debt facilities with flexible drawdown options that align capital deployment with milestone achievement, rather than demanding immediate full utilization, provides startups with essential operational flexibility.
2. Managing Financial Covenant Compliance
Failing to meet financial covenants represents another significant risk associated with venture debt. Violations of these covenants can trigger default provisions, potentially accelerating loan repayment or prompting immediate negotiations with lenders.
Proactive covenant management involves monthly monitoring, early communication with lenders about any financial concerns, and maintaining strong relationships with equity investors capable of providing bridge capital if necessary. Many venture debt agreements offer grace periods and cure options to accommodate temporary covenant breaches, aiding in effective risk mitigation.
3. Evaluating Venture Debt Providers
The venture debt industry now offers substantial opportunities for consumer tech startups. In 2024, the worldwide venture debt market expanded 46%, reaching an aggregate deal value of $83.4 billion. These figures highlight the importance of carefully evaluating lender relationships in an increasingly competitive landscape.
Consumer tech founders must thoroughly evaluate venture debt providers based on sector expertise, portfolio references, covenant flexibility, and the ability to offer value beyond capital.
Prioritizing lenders who understand consumer tech business models and can support companies during market volatility is crucial. Moreover, assessing the provider's track record with startups at similar stages often outweighs considerations of slight differences in interest rates, as the strength of the lender relationship is paramount for sustainable success.
Conclusion
Venture debt lets consumer tech startups access growth capital without giving up equity. It is ideal for post-seed companies with strong revenue.
Venture debt solutions present consumer tech startups with a powerful financing tool that balances the need for growth capital with preservation of ownership and strategic control. While venture debt offers distinct advantages such as non-dilutive capital, faster deployment, and flexibility in repayment structures, startups must carefully prepare to leverage this option successfully.
For founders committed to balancing growth aspirations with operational control, venture debt presents a compelling and effective growth capital strategy. Explore our Investor Discovery and Mapping service shows to connect with the investors who actually “get” you.
Key Takeaways
- Venture debt gives growth capital with far less dilution than a full equity round.
- It works best for post-seed startups with real revenue, not idea-stage experiments.
- Typical facilities equal 20–40% of the last equity round, with 2–4 year terms.
- Lenders underwrite investor quality, unit economics, and scalability, not just collateral.
- Use it for inventory, marketing, and runway extension, not to subsidize weak fundamentals.
- Covenants and repayments require tight cash-flow planning and transparent reporting.
- Chosen well, venture debt strengthens, not stresses, your relationship with existing equity investors.
Frequently asked Questions
What are the key eligibility criteria for consumer tech venture debt?
Consumer tech startups need at least one VC funding round and strong monthly revenue, usually above $50K, to qualify for venture debt.






