The rapid adoption of Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) and Zero-Trust frameworks has reshaped how organizations approach cybersecurity. For investors, these platforms represent not just technological innovation but also a significant opportunity for returns. However, understanding what metrics matter most to investors is crucial for startups aiming to secure funding in this competitive space.
Your analysis of investor metrics gains additional context when you explore the cybersecurity startup fundraising guide, which presents a comprehensive overview of modern fundraising approaches in cybersecurity. This blog delves into the key performance indicators (KPIs) that investors prioritize, such as ROI models, budget efficiency, and risk mitigation strategies. Let’s jump right in to uncover the metrics that drive investment decisions in SASE and Zero-Trust platforms.
Fundraising Benchmarks and Trends in Cybersecurity 2025
The fundraising landscape in cybersecurity remains robust, even as broader tech investment shows signs of selectivity. In Q2 2025 alone, the sector raised an impressive $4.2 billion across 100 funding rounds, a 25% year-over-year increase, with the average deal size rising sharply. Notably, more than half of this quarter's capital went into just eight rounds exceeding $100 million each, indicating that while early-stage interest remains strong, there’s a pronounced appetite for scale and category leadership.
Knowing what to expect at each stage removes guesswork, startup fundraising rounds in 2025 lays out investor expectations from seed through cloud security network rounds.
What is Zero Trust?
Zero Trust is a modern cybersecurity framework built on the principle of "never trust, always verify." Unlike traditional security models that assume trust within a network perimeter, Zero Trust requires strict identity verification for every user, device, and application attempting access, whether inside or outside the network. This approach ensures that no entity is automatically trusted, minimizing vulnerabilities from both external and internal threats.
At its core, Zero Trust emphasizes rigorous access controls and micro-segmentation. By dividing networks into smaller, isolated segments, organizations can limit the scope of potential breaches and ensure that access is granted only to authenticated and authorized users. This granular control reduces the risk of lateral movement by attackers, offering a more robust defense against advanced cyber threats.
The rise of hybrid work environments and increasingly sophisticated attacks has highlighted the inadequacy of traditional security tools like VPNs and firewalls. While these tools provide a basic layer of protection, they lack the dynamic, continuous verification required to address modern threat landscapes.
Identity and Access Management (IAM) plays a pivotal role in Zero Trust, ensuring that only verified identities gain access to sensitive systems. IAM solutions continuously authenticate users across the environment, reinforcing the "always verify" principle. As organizations adapt to evolving security demands, Zero Trust is becoming an essential strategy for safeguarding critical assets and maintaining operational resilience.
What is SASE?
Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) represents a transformative approach to networking and security, combining these critical functions into a unified, cloud-native framework. Designed to address the challenges of modern IT environments, SASE simplifies the management of distributed workforces and cloud-first strategies by integrating advanced technologies like Firewall-as-a-Service (FWaaS), Secure Web Gateway (SWG), SD-WAN, Cloud Access Security Broker (CASB), and Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA).
This framework eliminates the need for siloed solutions, offering organizations a scalable and agile way to secure their networks while optimizing performance. For example, FWaaS provides centralized control over inbound and outbound traffic, reducing reliance on costly on-premises hardware while enhancing scalability. Similarly, SD-WAN ensures seamless connectivity across geographically dispersed locations, enabling businesses to adapt quickly to changing demands.
The rapid adoption of SASE underscores its growing importance. According to Gartner, 60% of enterprises are expected to implement SASE by 2025, a significant increase from just 10% in 2020. This shift highlights the urgency for organizations to embrace solutions that align with the evolving digital landscape.
By consolidating networking and security into a single framework, SASE empowers businesses to maintain robust protection without compromising efficiency. Its cloud-native architecture ensures that security policies are consistently enforced across all endpoints, whether employees are working remotely or accessing resources from multiple devices. As companies continue to prioritize flexibility and scalability, SASE emerges as a vital tool for navigating the complexities of modern IT infrastructure.
Difference and Comparison between Zero Trust and SASE
Zero Trust and Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) represent two distinct yet interconnected approaches to modern cybersecurity. While both frameworks aim to enhance security in increasingly complex IT environments, their methodologies and focus areas differ significantly.
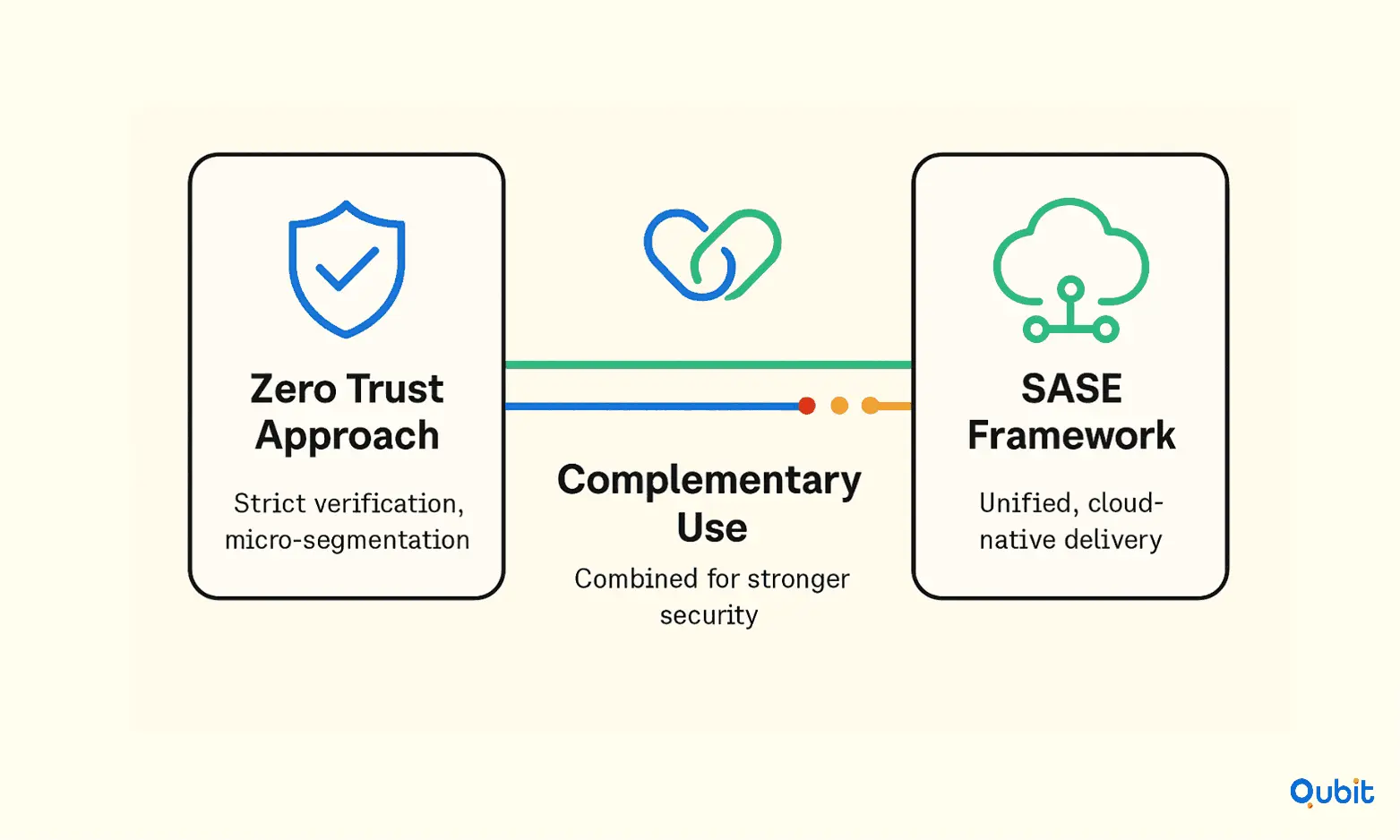
Zero Trust operates on the principle of "never trust, always verify." It emphasizes strict access controls and continuous identity verification, ensuring that no user or device is granted access without meeting predefined security criteria. This model is highly adaptable, making it suitable for various infrastructures, including on-premises, hybrid, and cloud environments.
On the other hand, SASE combines networking and security functions into a unified, cloud-delivered model. Designed primarily for cloud-native and distributed environments, SASE integrates capabilities such as secure web gateways, cloud access security brokers (CASBs), and software-defined wide-area networking (SD-WAN). This holistic approach simplifies management and enhances performance by delivering security and connectivity through a single platform.
Despite their differences, Zero Trust and SASE can complement each other effectively. Zero Trust ensures granular access control and continuous monitoring, while SASE provides the scalability and integration needed for modern, distributed networks. Organizations can benefit from combining these frameworks to create a robust, end-to-end security strategy.
Ultimately, the choice between Zero Trust and SASE—or the decision to integrate both—depends on an organization’s specific needs, infrastructure, and security goals. By understanding their unique strengths, businesses can build a security framework that is both comprehensive and future-ready.
What Investors Value Most Today
Performance metrics such as Annual Recurring Revenue (ARR), revenue growth, and retention rates remain foundational in assessing early- and mid-stage cybersecurity companies. For SASE and Zero Trust startups, investors are evaluating:
- Efficiency Ratios: Capital efficiency, i.e., how much revenue is generated per dollar of investment raised, is under greater scrutiny as markets mature.
- Revenue Multiples by Niche: In 2025, verticals like Cloud Security, Identity and Access Management (IAM), and Data Security command the highest valuation multiples, given their centrality to enterprise risk mitigation strategies. Revenue multiples vary widely but are highest in segments directly enabling regulatory compliance and digital trust.
- ARR and Funding Milestones: Attractive benchmarks for fast-growing startups often include $5–$10M ARR at Series B and $20M+ at Series C, though earlier rounds are seeing premium valuations for clear product-market fit and proven scalability.
Partnering with hyperscalers can fast-track growth. The co-selling with hyperscalers to attract cloud-security investment guide explains how to craft joint solutions and pitch them for maximum impact.
SASE ROI and Investment Analysis
While the metrics for evaluating ROI remain consistent across implementations, the actual outcomes hinge on specific use cases and architecture requirements. This section explores the critical components of SASE investment analysis, including cost reduction, efficiency improvements, Capex/Opex considerations, and detailed ROI modeling.
Breaking Down SASE ROI Metrics
SASE ROI is shaped by three primary factors: capital expenditures (Capex), operational expenditures (Opex), and risk mitigation. These metrics provide a framework for assessing the financial and operational benefits of adopting a SASE platform.
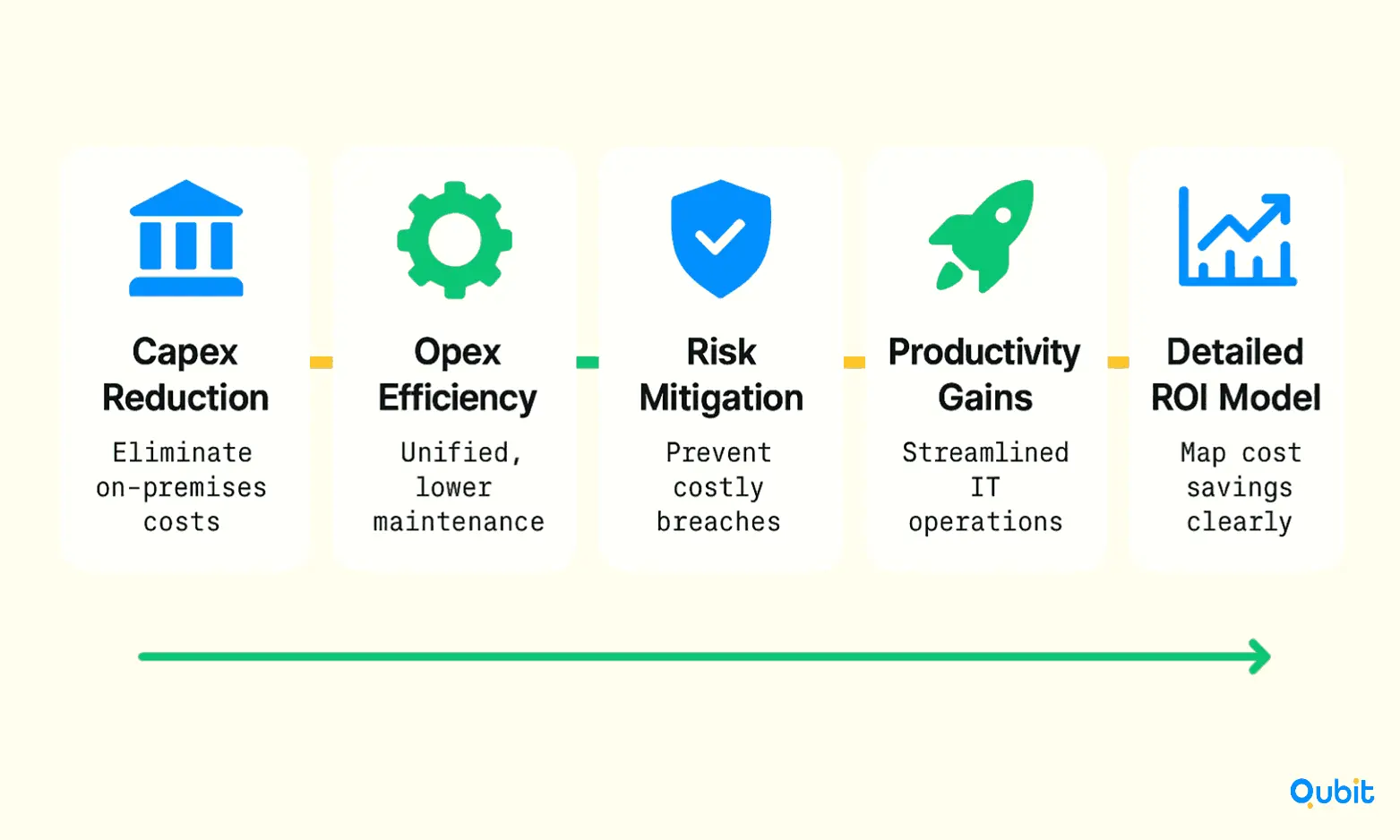
1. Capital Expenditures (Capex)
Investing in SASE often involves upfront costs for hardware, software, and deployment. However, organizations transitioning to cloud-native solutions can significantly reduce Capex by eliminating the need for on-premises infrastructure. For example, North American Oil and Gas Corporation successfully deployed a cloud-native SASE platform integrating SD-WAN, a global private backbone, and a full security stack within 30 days. This rapid deployment not only minimized initial costs but also demonstrated tangible efficiency gains.
2. Operational Expenditures (Opex)
Opex savings are a cornerstone of SASE ROI. By consolidating networking and security functions into a unified platform, organizations can reduce ongoing maintenance costs and streamline operations. SASE platforms also enable automation, which cuts down on manual processes and frees up IT resources for strategic initiatives.
3. Risk Reduction and Efficiency Gains
Risk mitigation is another critical ROI driver. SASE platforms enhance security by integrating features like Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) and advanced threat detection. These capabilities reduce the likelihood of costly data breaches and downtime. Additionally, efficiency gains from centralized management and improved connectivity contribute to long-term savings.
Detailed ROI Modeling
To quantify the benefits of SASE, organizations must develop a detailed ROI model that accounts for both tangible and intangible factors. Key steps include:
- Identifying Use Cases: Determine specific scenarios where SASE can deliver value, such as remote workforce enablement or secure cloud access.
- Calculating Cost Reductions: Assess savings in hardware, software, and operational expenses.
- Measuring Productivity Gains: Evaluate improvements in employee efficiency and IT resource allocation.
- Estimating Risk Mitigation: Factor in reduced exposure to cyber threats and compliance penalties.
Optimizing IT Budgets with SASE
SASE platforms offer a pathway to optimize IT budgets by consolidating multiple tools into a single solution. This reduces redundancy and simplifies vendor management, freeing up funds for innovation. Organizations can also scale their SASE deployments based on evolving needs, ensuring cost-effectiveness over time.
Investment Hotspots and Emerging Opportunities
- Consolidation and M&A: Investors are also eyeing strategic exits, with M&A activity outpacing direct investments in parts of Europe and North America. Startups that build for interoperability and easy integration into established security stacks increase their attractiveness for acquisition.
- AI-Driven Capabilities: Over 53% of new cybersecurity startups have woven AI into their core offerings, and funding flows favor those that offer practical, real-time threat detection or incident automation.
- International Expansion: Firms demonstrating scalability beyond their home market—especially those with products relevant to global regulatory frameworks or adaptable to multi-cloud environments—consistently attract larger rounds and premium valuations.
How to Stand Out: Must-Have Fundraising Attributes for 2025
| Attribute | Why It Matters for Investors | Example Proof Points |
|---|---|---|
| Product Stickiness | Low churn and high expansion rates translate to predictable growth | Cohort retention metrics, customer NRR >120% |
| Ecosystem Fit | SASE/Zero Trust solutions that integrate broadly are easier to scale or bundle in partnerships | Technical integrations, channel partnerships |
| Regulatory Relevance | Investors prize solutions that address new compliance mandates or industry-specific data risks | Case studies in healthcare, financial or government verticals |
| Repeatable Sales Motion | Demonstrates product is not consulting-heavy or custom-only | Growth in standardized deployments, minimal professional services required |
Actionable Fundraising Tips for SASE & Zero Trust Startups
- Benchmark Your Metrics: Gather accurate, current data about valuations and funding sizes in your specific niche, see how your ARR, customer count, and pipeline compare to what recent deals have commanded.
- Emphasize Ecosystem Positioning: Articulate how your solution fits into the broader security stack, and reference any partnerships, major integrations, or certifications you’ve achieved.
- Highlight Global Appeal: Investors reward platforms that can adapt to diverse regulatory and business climates; highlight wins or pilots in multiple regions or verticals.
- Prepare for Rigorous Diligence: With larger checks come greater scrutiny; ensure your security claims, customer references, and product ROI are fully documented and easily defensible.
By weaving in these current market insights, benchmarks, and tactical recommendations, your fundraising section will be more actionable, investor-savvy, and directly relevant for leaders seeking capital in today’s SASE and Zero Trust era.
Conclusion
Aligning cybersecurity metrics with investor expectations is not just a technical necessity; it’s a strategic imperative. Throughout this article, we’ve explored actionable strategies for integrating SASE and Zero Trust frameworks into measurable ROI models. These insights are designed to help organizations not only enhance their security posture but also communicate value in terms that resonate with stakeholders.
By focusing on metrics that bridge technical performance with financial outcomes, businesses can foster investor confidence and secure long-term partnerships. The tools and strategies discussed here provide a roadmap for aligning cybersecurity investments with broader business goals.
If you're looking to better understand investor metrics and connect with the right partners, we at Qubit Capital can help. Explore our Investor Discovery and Mapping service to gain strategic insights. Let’s work together to position your business for success.
Key Takeaways
- SASE and Zero Trust platforms significantly enhance cybersecurity and operational efficiency.
- Investors prioritize clear ROI metrics, cost optimization, and risk reduction.
- Understanding the interplay between Capex and Opex is crucial for evaluating SASE investments.
- Strict identity verification and micro-segmentation underpin effective Zero Trust strategies.
- Real-world case studies reinforce the value of integrated security frameworks.
Frequently asked Questions
What is SASE in cybersecurity?
SASE in cybersecurity is a converged, cloud-delivered framework that integrates networking and security services, ensuring secure, scalable access for distributed workforces.