Understanding the nuances of Regulation S and Rule 144 is essential for businesses and investors seeking clarity in securities transactions. These regulations, while interconnected, serve distinct purposes in the realm of securities offerings.
Regulation S primarily governs offshore transactions, ensuring compliance with U.S. securities laws outside domestic borders. On the other hand, Rule 144 facilitates the resale of restricted securities within the U.S., offering a pathway for liquidity under specific conditions.
This article will explore their differences, applications, and implications for global and domestic markets. Let’s dive in!
Explore EMEA Debt Capital Market Issuance Models
Regulation S applies to non-U.S. offerings while Rule 144/144A targets U.S. domestic resales and institutional placements. Their boundaries define the types of investors and compliance paths.
The EMEA debt capital markets offer two prominent issuance models tailored to distinct investor bases and regulatory frameworks. These models, the US High Yield Model and the Eurobond Model, serve as essential mechanisms for raising capital across diverse geographies.
The US High Yield Model
Designed under New York law, the US High Yield Model primarily targets qualified institutional buyers (QIBs), which are entities meeting minimum asset thresholds under SEC rules, are the primary targets. This framework is governed by Rule 144A, enabling issuers to access a robust pool of sophisticated investors within the United States. Its streamlined regulatory structure facilitates efficient transactions, making it a preferred choice for issuers seeking high-yield opportunities.
According to the SEC OASB Report 2023, nearly $1.3 trillion was raised through Regulation S and Rule 144A offerings during 2022–2023, underscoring the model's significance in global capital markets. This underscores the model’s significance in global capital markets.
The Eurobond Model
In contrast, the Eurobond Model operates under English law and is tailored for offshore transactions. This model often excludes US investors, focusing instead on international markets. Regulation S governs these offerings, ensuring compliance with non-US jurisdictions while providing issuers access to a diverse investor base. The Eurobond Model is particularly advantageous for issuers seeking to avoid the complexities of US securities regulations.
Comparing the Models
While both models cater to distinct investor groups, their regulatory environments shape the scope of participation. The US High Yield Model thrives on its ability to attract QIBs, whereas the Eurobond Model excels in facilitating cross-border transactions outside the US.
Additionally, examining various funding models, you might find that private equity for startups offers a structured approach tailored to emerging companies.
Regulation S vs Rule 144/144A: Key Exemption Differences
Understanding Regulation S vs Rule 144/144A is essential for navigating SEC registration exemptions and selecting the right framework for your capital formation needs.
Exemptions from SEC registration play a pivotal role in facilitating capital formation, particularly for entities seeking alternative pathways to raise funds. Regulation S and Rule 144/144A are two distinct frameworks that cater to specific investor profiles and transaction types, each offering unique advantages.
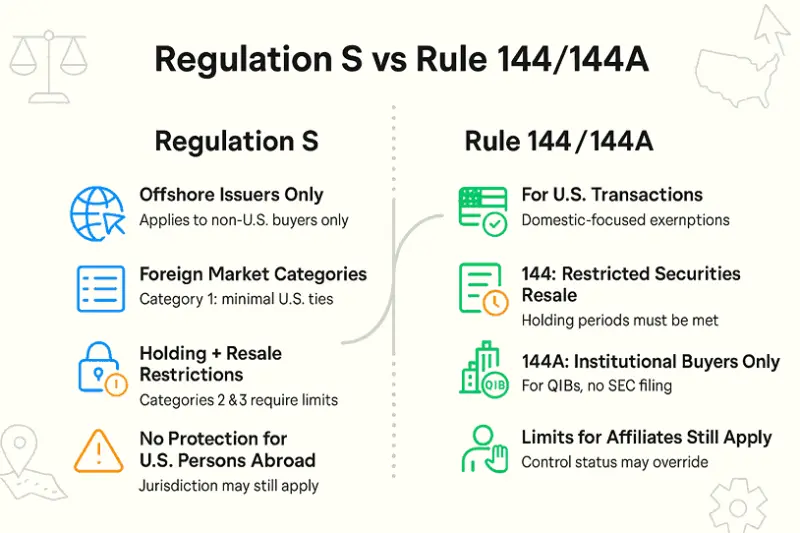
Regulation S: Offshore Transactions Simplified
Regulation S is designed to enable companies to conduct securities offerings outside the United States without adhering to SEC registration requirements. This exemption is particularly beneficial for issuers targeting non-U.S. investors, as it eliminates the complexities tied to domestic compliance.
Under Regulation S, securities must be sold exclusively to offshore buyers, and the transactions must occur outside U.S. borders. This framework is governed by two primary conditions:
- Category 1: Securities are offered in foreign markets with minimal U.S. involvement.
- Category 2 and 3: These categories impose stricter restrictions, including holding periods and limitations on resale to U.S. persons.
By focusing on international markets, Regulation S provides issuers with access to a broader investor base while bypassing the rigorous disclosure requirements mandated by the SEC.
Rule 144 and Rule 144A: Catering to Institutional Buyers
- Regulation S does not protect U.S. persons acting abroad; such activity may still trigger U.S. jurisdiction.
- Rule 144 may not apply to affiliates under certain holding or control situations, even if thresholds are otherwise met.
Rule 144 and Rule 144A, on the other hand, are tailored for transactions within the United States, specifically targeting qualified institutional buyers (QIBs).
Rule 144: This exemption facilitates the resale of restricted securities, allowing investors to trade them after meeting specific holding periods and conditions. It primarily benefits individual investors and smaller entities seeking liquidity for privately held securities.
Rule 144A: Designed for institutional investors, this exemption enables the sale of securities to QIBs without requiring SEC registration. By focusing on QIBs, Rule 144A ensures that transactions occur between sophisticated parties, reducing regulatory burdens while maintaining market integrity.
A detailed comparison of venture capital vs private equity sheds light on the distinct mechanisms behind each funding option, providing context for how Regulation S and Rule 144 fit into broader financial strategies.
Strategic Importance and Statistical Insights
Both Regulation S and Rule 144/144A have proven instrumental in capital formation. For instance, Rule 506(b) private placements raised nearly $2.7 trillion. Recent SEC updates clarify resale requirements for restricted securities. Under the new rule, Rule 144 holding periods mandate at least six months for SEC-reporting companies and one year for non-SEC reporting companies.
These holding periods define when investors can resell restricted securities, ensuring procedural compliance for capital formation.
Issuer Compliance Checklist for Dual Tranche Offerings
- Verify eligibility for Regulation S and Rule 144A exemptions based on transaction location and investor type.
- Prepare separate offering memoranda detailing terms, risks, and disclosure standards for each tranche.
- Assign distinct ISIN and CUSIP codes to Reg S and 144A notes for proper identification and settlement.
- Engage legal counsel to review marketing practices and ensure compliance with distribution restrictions and anti-fraud provisions.
- Coordinate with Clearstream, Euroclear, and DTC for custody, settlement, and ongoing reporting obligations.
- Document investor certifications and maintain records to support exemption status and regulatory filings.
At the fundraising stage, large issuers often combine Rule 144A and Regulation S to sell hundreds of millions or even billions in notes to institutions in the U.S. and offshore investors at the same time, deals like MicroStrategy’s $3 billion convertible notes or AECOM’s $1 billion bond issue are recent examples. Later, when insiders want liquidity, Rule 144 becomes the workhorse exemption, governing how restricted shares can slowly drip into the public market after a six-to-twelve-month holding period.
While Regulation S opens doors to international markets, Rule 144A strengthens domestic capital flows by targeting institutional buyers. Together, these frameworks offer issuers the flexibility to tailor their fundraising strategies based on geographic and investor-specific considerations.
Clearing and Settlement Infrastructure Comparison
Understanding the nuances of Regulation S and Rule 144/144A is essential for issuers aiming to optimize their capital-raising efforts. By leveraging these exemptions, companies can strategically navigate the complexities of global and domestic markets.
For readers interested in exploring the broader landscape of private equity and investment, insights into the top private equity firms 2024 provide valuable perspectives on market players that influence funding strategies.
How Antifraud Provisions and Due Diligence Help Mitigate Liability in US Securities Law
Rule 144A offerings, a cornerstone of private securities transactions in the United States, demand rigorous compliance to mitigate legal risks. Central to this compliance are antifraud provisions, particularly Rule 10b-5, and the implementation of thorough due diligence processes. These measures not only protect issuers and underwriters but also ensure transparency and trust in the marketplace.
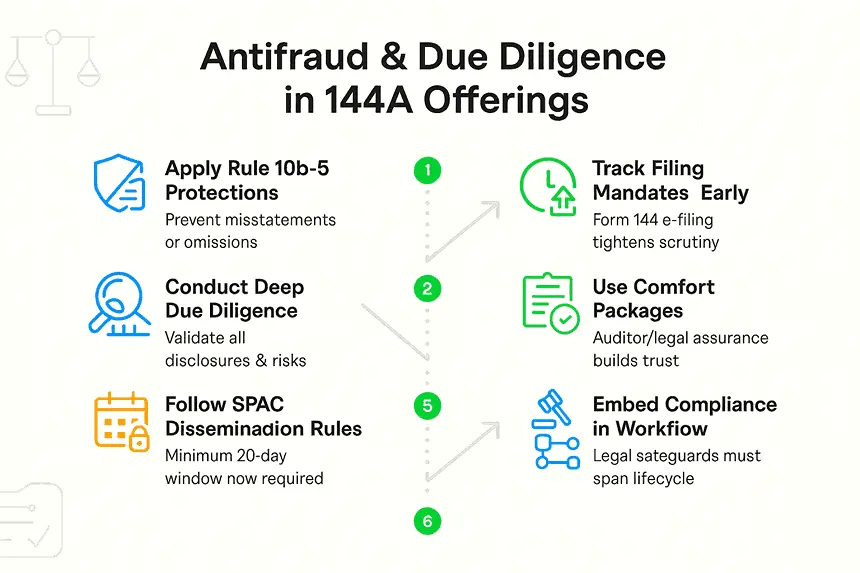
1. The Role of Antifraud Provisions in Rule 144A Offerings
Antifraud provisions, such as Rule 10b-5 under the Securities Exchange Act of 1934, are designed to prevent deceptive practices in securities transactions. Rule 144A offerings are no exception, as they are subject to these stringent measures. Any material misrepresentation or omission can expose issuers and underwriters to significant liability. This underscores the importance of ensuring that all disclosures are accurate, complete, and compliant with regulatory standards.
Emerging trends, such as the SEC's Accelerated Form 144 electronic filing mandates, further amplify the need for meticulous compliance. These mandates, set to take effect in 2024, require real-time disclosure of affiliate sales, increasing transparency pressures on Rule 144 transactions. As regulatory scrutiny intensifies, issuers must prioritize antifraud compliance to safeguard against potential legal repercussions.
2. Due Diligence: A Critical Shield Against Liability
Conducting comprehensive due diligence is a fundamental step in mitigating liability risks in Rule 144A offerings. This process involves verifying the accuracy of financial statements, assessing the issuer's operational integrity, and identifying potential legal or regulatory concerns. Robust due diligence not only minimizes the risk of antifraud violations but also strengthens the credibility of the offering.
Comfort packages are formal documents issued by auditors and lawyers, providing assurance to investors. Without such measures, issuers may face heightened exposure to legal challenges. This is especially true in cases of alleged fraud or misrepresentation.
3. Adapting to Regulatory Trends
The regulatory landscape is shifting quickly, and issuers and underwriters need to stay ahead of the curve rather than react after the fact. With the SEC tightening and accelerating filing requirements, real-time compliance is no longer a “nice to have” , it requires robust systems, clear workflows, and accurate, timely disclosures at every stage of a transaction.
Transparency rules are also becoming more explicit. For de-SPAC transactions, the SEC now mandates a 20-calendar-day minimum dissemination period for prospectuses and proxy materials. This built-in review window gives stakeholders more time to analyze disclosures, which in turn strengthens due diligence and reduces legal risk through better process discipline.
In parallel, Rule 144A offerings face higher expectations around antifraud protections and documentation quality. By embedding antifraud provisions and thorough due diligence into every phase of a 144A deal—from structuring to marketing to closing, issuers can both mitigate liability risk and reinforce investor confidence.
These developments aren’t just informal “best practices”; they flow directly from formal Commission action. The SEC’s new SPAC and de-SPAC rules, adopted by a 3-2 commission vote, show how market standards are being actively reset through regulation. The message is clear: firms that adapt their processes now will be better positioned as regulatory scrutiny continues to intensify.
How Market Trends Are Raising Disclosure Standards and Comfort Package Expectations
Market trends are pushing securities offerings toward higher transparency and tighter risk controls. Investors and underwriters are increasingly expecting Rule 144A–level disclosure standards even for offshore deals under Regulation S. The Disclosure Trend reflects this shift, showing a global push for robust, 144A-style disclosures in international high-yield offerings.
Key disclosure shifts to note:
- 144A-level disclosure is now often expected even for Regulation S transactions
- The line between Reg S and Rule 144A is blurring, as issuers aim to meet similar high standards across both frameworks
- The goal: consistent, comprehensive information for investors, regardless of where the securities are offered
A key data point from Fi Desk Analysis 2023:
- 48% of emerging market Reg S bonds do not have matching 144A tranches. Despite being Reg S-only, many of these offerings are still being pushed toward more detailed, 144A-style disclosure, as investors and underwriters prioritize information quality over formal labels. This trend is effectively bridging the gap between offshore and domestic standards.
Comfort packages: rising expectations, rising importance
As disclosure standards rise, comfort packages have become even more central to risk management:
- Underwriters rely on auditor assurances and financial statement reviews to validate key figures
- Comfort packages help confirm that disclosure is not just detailed, but accurate and supportable
- In a market demanding deeper transparency, these packages are now critical tools for building trust and reducing uncertainties
This all points to a broader shift: offshore offerings are being pulled toward the same rigorous expectations traditionally linked to Rule 144A deals. Issuers that adopt higher standards early are better positioned to satisfy investor demands and enhance the perceived quality of their offerings.
Structuring cross-border offerings under higher expectations
When structuring cross-border transactions, issuers and underwriters now need to think strategically:
- Adopting Rule 144A-level disclosures can
- Improve marketability
- Strengthen investor confidence
- Support issuers who may later transition to an IPO
- Regulation S-only offerings, by contrast, often struggle if their disclosures don’t meet the stringent expectations of global investors, which can limit demand and pricing power
Emerging technology is also reshaping how compliance is handled. AI-driven compliance monitoring, for example, machine learning systems that track offshore transaction patterns, is helping issuers reduce regulatory risk in cross-border offerings. The rise of AI-driven compliance monitoring for Reg S shows how tools can be used to stay ahead of regulatory scrutiny instead of just reacting to it.
For teams who find institutional or cross-border structures too complex, there are simpler paths. Exploring the pros and cons of friends and family funding offers a more relationship-driven alternative, with its own mix of relational and financial trade-offs that still need careful handling.
By combining robust disclosure practices, strong comfort packages, and innovative tools like AI-based monitoring, issuers can better navigate the rising standards in global markets, while positioning their cross-border offerings for credibility, investor confidence, and long-term success.
Conclusion
Understanding Regulation S vs Rule 144 and Rule 144A is no longer a nice-to-have; it’s core to modern capital markets strategy. Regulation S powers offshore offerings and Eurobond-style issuance, while Rule 144A and Rule 144 structure U.S. resales, liquidity, and high-yield deals for QIBs and insiders.
Together, these exemptions let issuers tailor dual-tranche offerings across EMEA and U.S. markets, using Clearstream, Euroclear, and DTC to anchor settlement infrastructure. But the bar is rising: 144A-level disclosure, antifraud controls, comfort packages, and AI-driven compliance are quickly becoming baseline expectations, even for Reg S-only bonds.
Issuers that treat disclosure and due diligence as strategic assets, not paperwork, will price better, access deeper demand, and stay ahead of tightening SEC and global standards.
If you’re ready to secure funding while navigating regulatory challenges, we at Qubit Capital offer Fundraising Assistance to help you achieve your capital goals.
Key Takeaways
- Regulation S vs Rule 144/144A defines the split between offshore offerings and U.S. restricted securities resales.
- Rule 144A offerings and the US High Yield Model focus on QIBs and institutional liquidity in domestic markets.
- The Eurobond Model and Regulation S enable cross-border issuance while minimizing direct U.S. securities law friction.
- New Rule 144 holding periods and electronic Form 144 filings tighten timelines and disclosure expectations.
- Market trends are pushing Reg S bonds toward 144A-level disclosure, comfort packages, and deeper investor diligence.
- Clearstream, Euroclear, and DTC form the core infrastructure for Reg S and Rule 144A clearing and settlement.
- AI-driven compliance and robust antifraud processes now differentiate credible cross-border offerings from regulatory headaches.
Frequently asked Questions
How do Regulation S and Rule 144A impact debt capital market issuance models?
Regulation S and Rule 144A create pathways for issuers to access international and U.S. institutional investors. Each model offers unique compliance and liquidity advantages for debt capital markets.






