Biotech companies are transforming how they approach public market strategies for life sciences, with IPOs and SPAC deals becoming pivotal pathways. As of July 22nd, 82 firms went public via IPO, while 47 opted for SPACs, according to Endpoints report. Together, these methods raised a staggering $25.86 billion, highlighting their significance in the industry.
The innovation driving biotech IPO readiness is explored in-depth on the BDO Life Sciences page, showcasing how companies prepare for the complexities of going public. Additionally, a comprehensive review in "biotech series A valuation benchmarks 2025" offers defined metrics that support your assessment of valuation trends during key funding rounds.
This guide will delve into the essentials of IPO and SPAC readiness, offering actionable insights to help biotech firms thrive in public markets.
Strategic IPO Transformation for Biotech Firms
An IPO represents a defining milestone for biotech companies, often marking the transition from innovation-focused startups to publicly traded entities. This transformation requires careful planning and strategic decision-making to ensure long-term success.
Biotech firms can pursue various paths to IPO transformation, each tailored to their unique operational and market circumstances. Some may opt for a traditional IPO route, focusing on building investor confidence through robust financial disclosures and a compelling growth narrative. Others might explore alternative strategies, such as reverse mergers or SPACs, which can expedite the process but demand equally rigorous preparation.
Evaluating operational readiness is critical before selecting a transformation strategy. Companies must assess their financial systems, compliance frameworks, and scalability to meet the demands of public markets. This includes ensuring transparent reporting mechanisms, robust governance structures, and the ability to sustain growth post-IPO.
Choosing the right strategy hinges on aligning the company’s strengths with market opportunities. A biotech firm with groundbreaking research may prioritize showcasing its innovation pipeline, while one with established revenue streams might focus on financial stability.
Strengthening Financial Reporting for IPO Readiness
Preparing for an IPO demands a meticulous approach to financial reporting, especially for biotech companies aiming to meet stringent compliance standards. Robust systems are essential to ensure accuracy, transparency, and alignment with regulations such as ASC 606 (Revenue Recognition) and ASC 842 (Lease Accounting).

Conducting an Internal Assessment
A thorough internal assessment is the cornerstone of IPO readiness. This process identifies gaps in current reporting practices and simulates the operational demands of a public entity. Key areas to evaluate include:
- Revenue Recognition Compliance: Ensure adherence to ASC 606 by reviewing contracts, revenue streams, and performance obligations.
- Lease Accounting Standards: Validate compliance with ASC 842 by assessing lease agreements and their financial impact.
- Data Integrity: Confirm the accuracy and completeness of financial data across all systems.
- Audit Preparedness: Evaluate the readiness of financial statements for external audits, ensuring they meet public company standards.
- System Scalability: Assess whether existing systems can handle the increased complexity and volume of reporting required for a public entity.
Aligning Talent and Governance for IPO Success
Preparing for an IPO demands more than financial readiness; it requires aligning talent and governance structures to meet the rigorous expectations of public company operations. A strong foundation in leadership and compliance ensures that your biotech company can thrive under public scrutiny.
Building Leadership for IPO Readiness
Experienced leadership is the cornerstone of a successful IPO. Evaluating your executive team’s ability to navigate the complexities of public markets is essential. This includes assessing their track record in strategic decision-making, financial management, and stakeholder communication. Companies should prioritize leaders who can adapt to the demands of increased transparency and accountability.
Strengthening Governance Structures
Robust governance frameworks are non-negotiable for public companies. Implementing systems that adhere to Sarbanes-Oxley (SOX) compliance is critical for maintaining investor confidence. SOX compliance ensures accurate financial reporting and mitigates risks associated with corporate misconduct. Establishing an independent board with diverse expertise further enhances governance, providing oversight and strategic guidance during the IPO process.
Actionable Steps for IPO Success
- Conduct Leadership Evaluations: Regularly assess the capabilities of your executive team to ensure alignment with public company expectations.
- Implement SOX Compliance: Develop internal controls and audit processes to meet SOX requirements.
- Form an Independent Board: Assemble a board with varied expertise to strengthen governance and decision-making.
For companies exploring alternative financing strategies during their IPO journey, a focused discussion on biotech venture debt royalty financing reveals complementary options to traditional capital approaches.
Long-Term Strategic Planning for Sustainable Growth Post-IPO
Achieving sustainable growth after an IPO requires a deliberate focus on scaling operations, safeguarding intellectual property, and navigating complex tax landscapes. Companies must prioritize operational scaling by assessing infrastructure, workforce capabilities, and funding channels to ensure they can meet increased market demands. This process often involves identifying inefficiencies and implementing scalable systems that support long-term biotech planning.
Protecting intellectual property (IP) is equally critical. As public companies attract heightened scrutiny, securing patents, trademarks, and proprietary technologies becomes a cornerstone of maintaining competitive advantage. Comprehensive assessments of IP security should be conducted regularly to mitigate risks and ensure compliance with evolving regulations.
Tax strategies also play a pivotal role in post-IPO growth. Understanding domestic and international tax implications in biotech IPOs is essential for optimizing financial outcomes. Companies expanding globally must account for varying tax codes, transfer pricing regulations, and potential tax treaties to avoid costly penalties.
Digital Transformation Readiness for Biotech Firms
Preparing for an IPO demands more than financial readiness—it requires a robust digital foundation. For biotech firms, integrating modern digital tools and cybersecurity systems is essential to meet the expectations of both investors and regulators. Upgrading IT infrastructure ensures seamless operations, while compliance with frameworks like GDPR and HIPAA safeguards sensitive data and builds trust.
Digital transformation in biotech is not just about adopting new technologies; it’s about creating a secure and scalable environment that supports innovation. For example, implementing advanced cybersecurity measures can protect proprietary research and intellectual property from cyber threats.
Moreover, aligning IT systems with regulatory requirements ensures that firms can handle audits and maintain transparency, which are critical for IPO readiness. Investors are increasingly scrutinizing the technological capabilities of biotech companies, making digital transformation a key factor in securing funding and achieving operational excellence.
Understanding SPACs in the Biotech Sector
Special Purpose Acquisition Companies (SPACs), often referred to as "blank check companies," have emerged as a transformative tool for biotech firms seeking rapid entry into public markets. These entities raise capital through an initial public offering (IPO) with the sole purpose of acquiring or merging with another company, streamlining the path to public trading.
For biotech firms, SPACs offer distinct advantages over traditional IPOs. One key benefit is speed: while conventional IPOs can take 12–18 months to complete, SPAC mergers typically finalize within 3–6 months, according to data from SPAC & Biotech Opportunities. This accelerated timeline allows biotech companies to capitalize on market opportunities and secure funding faster. Additionally, SPACs can reduce the costs associated with lengthy IPO processes, making them an attractive option for firms with limited resources.
However, success in SPAC deals for biotech depends on preparation. Companies that are well-positioned with robust pipelines, clear regulatory strategies, and compelling market narratives can gain a competitive edge. The strict timeline for SPACs—usually two years or less to identify and acquire a target—means that biotech firms must act decisively to align with SPAC sponsors and investors.
Comparing SPACs, Reverse Mergers, and Traditional IPOs
Choosing the right pathway to go public is a critical decision for biotech firms. SPAC deals for biotech companies have gained traction due to their streamlined process and reduced costs compared to traditional IPOs. However, understanding the nuances between SPACs, reverse mergers, and IPOs is essential to make an informed choice.
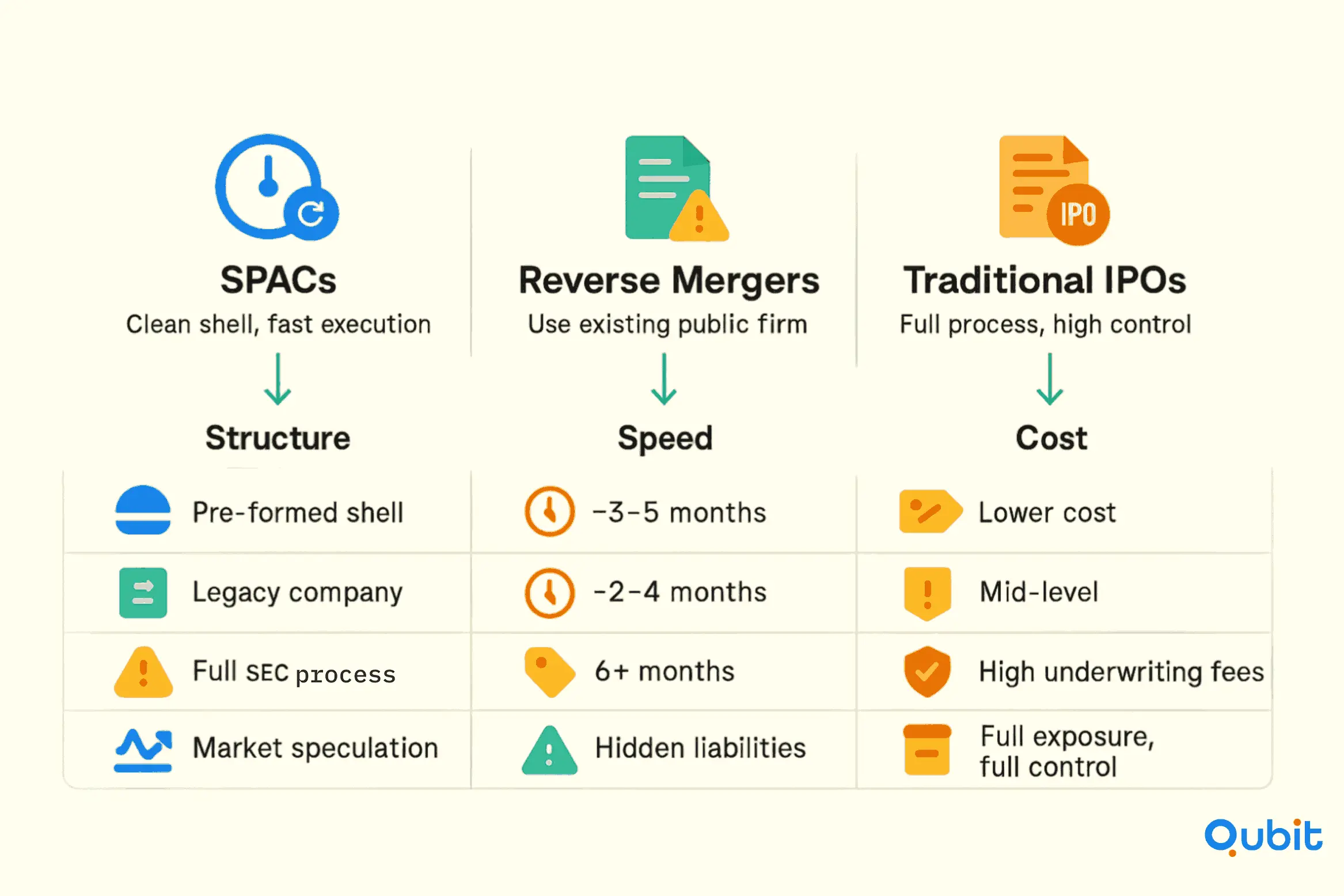
Structural Differences
SPACs (Special Purpose Acquisition Companies) are pre-existing entities created solely to merge with a target company, offering a clean shell with minimal legacy liabilities. In contrast, reverse mergers involve merging with an existing public company, which may carry historical liabilities or operational baggage. Traditional IPOs, on the other hand, require a company to go public independently, often involving extensive regulatory filings and underwriting processes.
Timelines and Costs
SPAC transactions typically outpace traditional IPOs in terms of speed, often completing within a few months. This expedited timeline appeals to biotech firms aiming for rapid market entry. Reverse mergers also offer a faster route but may involve additional due diligence to address legacy issues. Traditional IPOs, while offering greater control over valuation, demand a longer timeline—often exceeding six months—and higher costs due to underwriting fees and compliance requirements.
Key Considerations
For biotech firms assessing IPO readiness, SPACs provide a cost-effective and efficient alternative with fewer encumbrances. Reverse mergers may suit companies willing to navigate legacy challenges for quicker access to public markets. Traditional IPOs remain the gold standard for firms seeking maximum transparency and valuation control, albeit at a higher expense.
Exploring the Advantages of SPACs for Biotech Companies
Special Purpose Acquisition Companies (SPACs) have emerged as a transformative option for biotech firms seeking to go public. Unlike traditional IPOs, SPAC deals for biotech companies offer unique benefits that align with the fast-paced nature of the industry.
Accelerated Time-to-Market
Biotech companies often face time-sensitive challenges, especially when advancing groundbreaking therapies or technologies. SPAC transactions enable firms to go public within months, significantly reducing the time-to-market compared to traditional IPO processes. This expedited timeline allows biotech innovators to focus on their core mission, developing life-saving solutions, without prolonged delays.
Efficient Upfront Capital
SPAC deals provide finite, upfront capital, eliminating the need for multiple funding rounds. This streamlined approach ensures companies have the resources they need to scale operations, conduct clinical trials, and accelerate product development—all without the uncertainty of piecemeal financing.
Market Stability Through Price-Lock Mechanisms
Volatility in public markets can be particularly challenging for biotech firms, whose valuations often hinge on clinical milestones. SPAC transactions incorporate price-lock mechanisms, offering market stability and reducing exposure to unpredictable fluctuations. This stability fosters investor confidence and creates a more predictable environment for growth.
SPACs are reshaping how biotech companies approach public offerings, offering speed, financial efficiency, and stability. For firms aiming to capitalize on these advantages, understanding the nuances of SPAC transactions is essential.
Strategies to Attract a SPAC Partner
Securing a SPAC partner demands a strategic approach that combines operational excellence with a compelling market narrative. Biotech firms aiming for SPAC deals must demonstrate IPO readiness by showcasing robust internal controls, adherence to SEC regulations, and a clear pathway to public market success.
1. Strengthen Internal Controls and Compliance
A biotech company’s ability to meet stringent SEC requirements is a critical factor in attracting SPAC sponsors. This includes maintaining accurate financial reporting, implementing cybersecurity measures, and ensuring compliance with accounting standards. For example, Semnur Pharmaceuticals successfully prepared for a $2.5 billion SPAC merger by emphasizing regulatory readiness and securing $40 million in capital for its non-opioid pain therapy development.
2. Highlight Public Market Potential
SPAC sponsors prioritize companies with scalable growth opportunities and a clear value proposition for public investors. Medera Gene Therapy, for instance, secured a $623 million SPAC merger to fund its cardiovascular gene therapy programs, enabling critical phase 2b trials and a Nasdaq listing. This example underscores the importance of presenting a strong case for immediate capital infusion and long-term market viability.
3. Communicate Effectively with Investors
Transparent communication about market potential and operational readiness builds sponsor confidence. Biotech firms can benefit from foundational insights in biotech startup fundraising strategies, which provide a comprehensive overview of early-stage capital acquisition and public market preparation.
Conclusion
Preparing for an IPO or SPAC requires a strategic alignment of financial, governance, and digital transformation efforts. By implementing actionable checklists and tailoring strategies to the unique needs of biotech ventures, businesses can position themselves for success in public markets. For those exploring funding rounds prior to a public offering, a nuanced explanation in biotech follow-on round dilution management provides approaches to maintain equity balance during successive funding rounds while you explore public offering options.
At Qubit we understand audit & governance, and follow-on dilution math. Make the public-markets leap with our biotech fundraising assistance and book a readiness review.
Key Takeaways
- Biotech IPO readiness requires a detailed evaluation of financial, governance, and digital systems.
- Different IPO transformation paths exist, each necessitating tailored operational strategies.
- SPACs provide a faster, cost-effective route to public markets, especially for biotech firms.
- Long-term planning must address tax implications and sustainable growth post-IPO.
- Integrating digital transformation and modern governance is critical for success.
Frequently asked Questions
What is the process for a biotech company to go public?
A biotech company typically assesses its financial reporting, governance structures, digital readiness, and market positioning through detailed checklists and expert consultations before opting for an IPO or SPAC route.






