Pre-seed rounds usually range from $100,000 to $2 million, although some deals now exceed that as investors lean into early consumer potential. The stage is designed to turn an idea into a real product and early traction, not to scale a proven engine.
Investor behavior also shifted after recent shocks. During COVID-19, global economic output fell 3.1%, compared to a 1.7% decline in the 2008 crisis, pushing founders and investors to rethink risk and deal terms.
This guide breaks down practical pre-seed strategies, funding sources, and decisions that help consumer startups raise their first institutional capital.
Understanding Pre-Seed Funding for Consumer Startups
Pre-seed funding enables consumer startups to validate ideas and build prototypes. Recent data reveals substantial market changes. By 2023, pre-seed funding rounds made up 14% of all seed stage deals, a jump from just 5% in 2020. This shift demonstrates growing recognition of early-stage validation by investors, underscoring the rising importance of pre-seed strategy.
What Makes Pre-Seed Different
Pre-seed funding is the initial capital that helps take your business idea from concept to reality. It differs significantly from later investment rounds in several key ways:
- Stage Focus: Validates ideas and develops prototypes rather than scaling operations
- Investment Amounts: Smaller rounds focused on reaching specific milestones
- Investor Types: Angels, micro-VCs, and specialized pre-seed funds rather than growth investors
- Due Diligence: Less formal process with emphasis on founder potential and market opportunity
- Timeline: Often faster decision-making compared to institutional Series A rounds
In 2024, 35% of startups featured solo founders, more than double the share from 2015. This surge signals that investors increasingly back single-founder consumer ideas when pre-seed rounds set the stage.
Founder/Team Structure Differences often emerge between consumer startups and marketplace models, affecting capital needs and investor expectations.
Expanding into new geos means recalibrating everything from your go-to-market (GTM) strategy to funding expectations. That’s where raising capital for international expansion in consumer startups becomes a strategic roadmap.
Why Consumer Startups Need Pre-Seed Capital
Consumer startups face unique challenges that make pre-seed funding particularly valuable:
- Product Development Costs: Creating consumer-facing products often requires significant upfront investment in design, development, and user testing to achieve market-ready quality standards.
- Market Validation Expenses: Consumer products need extensive testing and feedback collection to ensure product-market fit, requiring resources for surveys, focus groups, and pilot programs.
- Brand Building Investment: Consumer startups must invest early in brand development, marketing materials, and customer acquisition strategies to establish market presence.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many consumer products require safety testing, certifications, and regulatory approvals that demand capital before revenue generation.
Pre-Seed Funding Sources for Consumer Startups
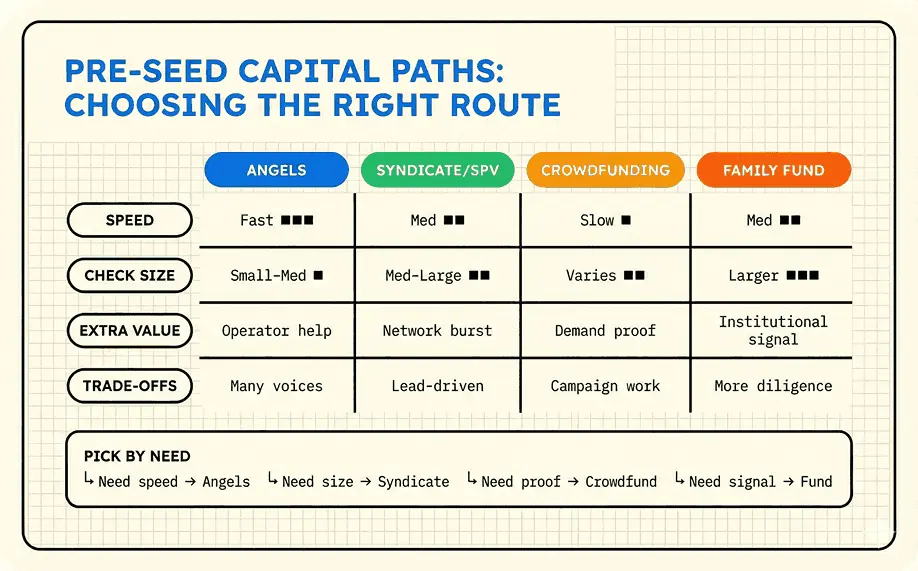
1. Family Fund
Friends and family rounds represent the most accessible initial funding source for many consumer entrepreneurs. These investors typically bet on their relationship with the founder rather than deep market analysis.
Advantages:
- Quick decision-making with minimal due diligence
- Flexible terms and structures
- Emotional investment in founder success
- No requirement for accredited investor status
Considerations:
- Not available to all entrepreneurs due to network limitations
- Potential relationship strain if business fails
- Limited check sizes may not meet capital needs
- Lack of professional investor guidance and networks
2. Angel Investors
Angel investors are high-net-worth individuals who invest their personal capital in early-stage startups, often bringing valuable industry experience and connections. For consumer startups, finding angels with relevant retail, e-commerce, or consumer product experience can provide strategic value beyond capital.
Key Characteristics:
- Must be accredited investors with $1 million net worth or $200,000 annual income
- Typical investment range: $25,000 to $100,000 per individual
- Often former entrepreneurs with operational expertise
- Can provide introductions to customers, partners, and future investors
Finding Angel Investors:
- Industry networking events and conferences
- Angel investor groups and syndicates
- Online platforms like AngelList
- Warm introductions through mutual connections
3. Angel Syndicates and SPVs
Angel syndicates pool resources from investors through special purpose vehicles (SPVs, which are legal entities created for investment purposes). This enables larger investment amounts, while still allowing individual participation.
Benefits for Consumer Startups:
- Access to larger funding rounds than individual angels can provide
- Diversified expertise from multiple experienced investors
- Streamlined fundraising process with single syndicate leader
- Broader network effects from multiple investor relationships
Knowing who’s actively writing checks in your vertical isn’t optional. This list of top investors backing consumer & marketplace startups helps cut through outdated intros.
Using SAFEs and Convertible Notes in Pre-Seed Rounds
Building on these funding sources, founders should understand the role of convertible instruments like SAFEs and convertible notes. These tools allow startups to raise capital quickly without setting a fixed valuation, deferring that negotiation to a later round.
The structure of pre-seed fundraising continues to modernize. In 2024, 92% of pre-seed rounds used SAFEs, up from just 54% in 2019. Convertible notes fell to 9%. Founders must understand instrument trends to ensure competitive deal structures.
This flexibility appeals to both founders and early investors by simplifying terms and speeding up the fundraising process. Choosing the right instrument can help maintain cap table clarity and reduce legal complexity.
SAFE vs. Convertible Note: Key Differences
| Characteristic | SAFE | Convertible Note |
|---|---|---|
| Valuation Timing | Deferred to next equity round | Deferred to next equity round |
| Interest Rate | No interest accrual | Accrues interest over time |
| Maturity Date | No maturity date | Has a fixed maturity date |
| Legal Complexity | Simpler, fewer terms | More terms, added complexity |
| Investor Appeal | Preferred for speed and simplicity | Preferred by some for added protections |
Why Pre-Seed Round Size Matters
This approach to deal structure works best when founders limit pre-seed round size, often to under $500,000. Smaller rounds help maintain a clean cap table, making the company more attractive to future investors. Overly large rounds can create dilution and complexity that hinder later fundraising. Careful sizing ensures flexibility and preserves founder ownership for subsequent growth stages.
The volume of capital at pre-seed is significant. In Q2 2025 alone, $815M was deployed in sub-$5M SAFE/Note rounds. This underscores the size and liquidity of today's instruments-driven market.
Crowdfunding Platforms
Crowdfunding has emerged as particularly effective for consumer-facing products or mission-driven startups. Platforms like Kickstarter, Indiegogo, and equity crowdfunding sites offer different models for raising pre-seed capital.
Types of Crowdfunding:
Crowdfunding Success Strategies:
- Set realistic funding goals and timelines
- Create compelling video and visual content
- Build email lists and social media following before launch
- Offer attractive rewards that incentivize contributions
- Maintain active engagement with backers throughout campaign
Accelerators and Incubators
Accelerator and incubator programs provide structured support beyond just funding, offering mentorship, network access, and intensive business development assistance.
Program Benefits:
- Capital investment (typically $125,000-$250,000)
- Structured curriculum and mentorship
- Peer network of fellow entrepreneurs
- Demo day exposure to investor audiences
- Ongoing alumni network support
Notable Consumer-Focused Programs:
- Y Combinator: $500,000 for 6% equity
- Techstars: $120,000 investment plus mentor network
- 500 Startups: Consumer product focus with global reach
- Target Accelerator: Retail-specific program
- Plug and Play: Consumer-focused verticals
Micro-VCs and Pre-Seed Funds
Specialized pre-seed venture capital funds focus specifically on earliest-stage investments, often providing more capital than individual angels while maintaining founder-friendly terms.
Leading Pre-Seed Funds:
- Pear VC: Consumer and enterprise focus
- Precursor Ventures: Pre-seed specialists
- First Round Capital: Dorm Room Fund
- Initialized Capital: Y Combinator alumni fund
- Founder Collective: Founder-led investment approach
From acquisition cost thresholds to retention curves, this investor’s guide to consumer & d2c startups breaks down what experienced investors actually look for.
Strategic Preparation for Pre-Seed Fundraising
To navigate pre-seed, founders should take early, structured steps that build a solid foundation and evidence of traction.
- Validate market demand
- Build a minimum viable product (MVP)
- Assemble your team and financials
- Prepare a compelling pitch deck
- Network with early-stage investors
The financial prep graphic shows categories such as cost breakdowns, milestone mapping, and funding schedules necessary for pre-seed plans.
Building Your Foundation
Successful pre-seed fundraising requires thorough preparation across multiple business dimensions before approaching potential investors.
Business Plan Development
Your business plan serves as the roadmap demonstrating vision, market understanding, and growth potential. Key elements include:
- Executive Summary: Concise overview of business concept and opportunity
- Market Analysis: Target customer research and competitive landscape
- Product Description: Clear explanation of value proposition and differentiation
- Business Model: Revenue strategy and monetization approach
- Financial Projections: Realistic forecasts showing path to profitability
- Team Overview: Founder backgrounds and key hire plans
Current benchmarks highlight the need for grounded expectations. In Q1 2024, median pre-seed startup valuations fell 10%, breaking a longstanding plateau near $5 million. Fidelity to present realities increases investor trust.
Prototype and MVP Creation
Having a tangible representation of your product significantly improves investor confidence. For consumer startups, this might include:
- Functional Prototype: Working version demonstrating core features
- Design Mockups: Visual representations of user interface and experience
- Product Videos: Demonstrations showing product functionality
- User Testing Results: Feedback from potential customers
- Manufacturing Samples: Physical products for tactile evaluation
Market Validation Strategies
Consumer startups must demonstrate genuine market demand before raising pre-seed funding. Effective validation approaches include:
Customer Discovery
- Conduct extensive interviews with target customers
- Survey potential users about pain points and willingness to pay
- Test pricing sensitivity and feature prioritization
- Validate distribution channels and customer acquisition strategies
Market Testing
- Launch minimal viable products (MVPs) for feedback collection
- Run “smoke test” marketing campaigns to gauge interest
- Create waitlists to demonstrate demand
- Pilot programs with early adopters
Competitive Analysis
- Map competitive landscape and identify differentiation opportunities
- Analyze competitor pricing, features, and market positioning
- Identify market gaps and underserved customer segments
- Assess barriers to entry and competitive advantages
Financial Planning and Modeling
Realistic financial planning demonstrates fiscal responsibility to potential investors. Key components include:
Funding Requirements
- Detailed breakdown of capital needs by category
- Milestone-based funding deployment schedule
- Contingency planning for various scenarios
- Clear explanation of how funds will drive growth
Revenue Projections
- Bottom-up revenue modeling based on customer acquisition
- Multiple scenario planning (conservative, base, optimistic)
- Unit economics and customer lifetime value analysis
- Path to profitability timeline and assumptions
Pitch Development and Investor Engagement
Crafting Your Compelling Story
Your pitch deck serves as your calling card with potential investors. For consumer startups, effective pitch decks typically include:
Essential Slide Elements:
- Problem: Clear articulation of consumer pain point
- Solution: Your product and its unique value proposition
- Market: Size, growth, and target customer analysis
- Product: Demonstration or detailed explanation
- Traction: Early customers, sales, or user engagement
- Business Model: Revenue strategy and unit economics
- Competition: Landscape analysis and differentiation
- Team: Founder backgrounds and key personnel
- Financials: Projections and funding requirements
- Ask: Specific investment amount and use of funds
Consumer Startup Specific Considerations:
- Visual product demonstrations or prototypes
- Customer testimonials and feedback
- Brand development and marketing strategies
- Distribution channel partnerships
- Seasonal or cyclical business patterns
Building Investor Relationships
Relationship building should begin long before formal fundraising. Successful strategies include:
Network Development
- Attend industry events and startup meetups
- Join entrepreneur organizations and accelerator programs
- Engage on social media platforms like LinkedIn and Twitter
- Seek introductions through mutual connections
Early Investor Engagement
- Schedule informal coffee meetings for advice and feedback
- Share regular updates on product development and traction
- Invite potential investors to product demonstrations or events
- Request introductions to other relevant investors or advisors
Advisory Board Creation
- Recruit experienced advisors with consumer market expertise
- Leverage advisor networks for investor introductions
- Demonstrate external validation through quality advisory relationships
- Use advisor expertise to strengthen business strategy and execution
Consumer Startup Specific Strategies
Product Demonstration
Consumer products benefit significantly from tangible demonstrations that allow investors to experience the product directly.
Demonstration Strategies:
- Bring physical prototypes to investor meetings
- Create interactive product demos or applications
- Use video demonstrations for software-based consumer products
- Provide samples or trial access for testing
- Set up booth demonstrations at investor events
Customer Validation and Social Proof
Consumer startups can demonstrate market validation through various forms of social proof and customer engagement.
Validation Methods:
- Pre-orders and crowdfunding campaign success
- Social media engagement and follower growth
- Customer testimonials and case studies
- Media coverage and industry recognition
- Partnership agreements with retailers or distributors
Seasonal and Timing Considerations
Consumer products often have seasonal sales patterns that affect fundraising timing and strategy.
Timing Strategies:
- Align fundraising with peak sales seasons for your product category
- Consider holiday shopping seasons for retail-focused products
- Account for manufacturing and inventory lead times
- Plan funding runway to cover seasonal cash flow variations
- Demonstrate understanding of cyclical business patterns to investors
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Over-Optimistic Projections
Unrealistic financial projections undermine credibility with experienced investors who have seen numerous pitches.
Best Practices:
- Base projections on comparable company data and market research
- Present multiple scenarios with clear assumptions
- Focus on achievable milestones rather than hockey stick growth
- Demonstrate understanding of customer acquisition costs and challenges
Inadequate Market Research
Insufficient market validation signals lack of customer-centric thinking that concerns consumer-focused investors.
Avoidance Strategies:
- Conduct extensive primary research with target customers
- Validate assumptions through testing and feedback collection
- Understand competitive landscape and differentiation opportunities
- Demonstrate clear path to customer acquisition and retention
Poor Team Composition
Consumer startups require diverse skill sets that investors expect to see represented in the founding team or early hires.
Team Building Considerations:
- Include technical, marketing, and business development expertise
- Recruit advisors with consumer market experience
- Demonstrate ability to attract and retain talent
- Show complementary skills rather than overlapping capabilities
Premature Fundraising
Raising money too early without sufficient validation can result in unfavorable terms or fundraising failure.
Readiness Indicators:
- Clear product-market fit signals
- Initial customer traction or revenue
- Completed prototype or MVP
- Defined customer acquisition strategy
- Realistic funding requirements and deployment plan
Implementation Timeline and Action Steps
6 Months Before Fundraising
Foundation Building Phase:
- Complete market research and customer discovery
- Develop prototype or MVP with user testing
- Build founding team and advisory board
- Create initial business plan and financial projections
- Begin networking with potential investors
3 Months Before Fundraising
Preparation Phase:
- Finalize pitch deck with compelling storytelling
- Gather customer testimonials and validation data
- Prepare legal documents and corporate structure
- Create investor target list with warm introduction paths
- Develop fundraising timeline and milestone tracking
Active Fundraising Period
Execution Phase:
- Launch investor outreach through warm introductions
- Conduct investor meetings with consistent messaging
- Manage due diligence requests and follow-up
- Negotiate term sheets and select optimal investors
- Close funding round and communicate with stakeholders
Many first-time founders struggle to understand how investor expectations shift between consumer apps and marketplace platforms. This funding guide for consumer & marketplace startups outlines the structural differences in how these businesses should approach capital strategy.
Conclusion
Pre-seed funding is a pivotal phase for consumer startups, laying the foundation for validating ideas, developing prototypes, and establishing early market traction. Successfully navigating this stage requires a strategic approach that blends diversified funding sources, rigorous market validation, and strong investor relationship building.
Get your financials right the first time, explore our Financial Model Creation services and let us help you build models that support your vision.
Key Takeaways
- Pre-seed funding ranges from $100K-$2M and focuses on idea validation and prototype development rather than scaling operations.
- Diversify funding sources across friends/family, angels, crowdfunding, and accelerators to optimize terms and reduce dependency risks.
- Consumer startups must demonstrate product-market fit through customer validation, prototypes, and early traction before fundraising.
- Build investor relationships 6+ months before formal fundraising through networking, regular updates, and advisory board connections.
- Realistic financial projections with multiple scenarios demonstrate fiscal responsibility and improve credibility with experienced investors.
Frequently asked Questions
What are the best sources of pre-seed funding for consumer startups?
The best sources include angels, crowdfunding platforms, micro-VCs, and family and friends. Each source offers different advantages and strategies for consumer startups.






