Securing funding is often the most critical challenge for healthcare startups aiming to transform innovative ideas into impactful solutions. Among the many funding options available, NIH SBIR & STTR Grants stand out as a reliable and strategic choice for early-stage ventures. These grants, designed to support small businesses in research and development, offer not only financial assistance but also credibility and access to valuable resources.
For those new to the funding landscape, understanding the basics is essential. This comprehensive guide, outlined in how to secure funding for healthcare startups, offers a broad view of funding strategies that underpin the detailed discussions in this article. Whether you're exploring NIH SBIR & STTR Grants for the first time or seeking to refine your approach, this guide will help you navigate the process with clarity.
Overview of NIH SBIR/STTR Programs: Eligibility and Differences
The NIH SBIR & STTR Grants play a pivotal role in advancing public health innovation by funding small businesses that develop cutting-edge technologies and solutions. These programs are designed to bridge the gap between groundbreaking research and real-world application, ensuring that innovative ideas can make a tangible impact on healthcare.
Key Differences Between SBIR and STTR
While both programs aim to foster innovation, they differ in their approach to research partnerships. The SBIR program allows small businesses to conduct research independently or collaborate with other organizations. In contrast, the STTR program mandates a formal collaboration between the small business and a nonprofit research institution. Additionally, the Principal Investigator (PI) in the SBIR program must primarily work for the small business, whereas the STTR program offers more flexibility in this requirement. For further details, refer to the NIH Seed Fund funding information.
Eligibility Criteria
To qualify for these programs, businesses must meet specific criteria. They must be U.S.-based, for-profit entities with no more than 500 employees. Ownership must be primarily by U.S. citizens or permanent residents. Additional requirements may vary depending on the NIH institute or center providing the funding. A complete description of eligibility can be found in the Eligibility information for NIH Seed.
NIH Structure and Compliance
The NIH comprises 27 institutes and centers, each focusing on distinct areas of medical research. This structure allows for targeted funding opportunities tailored to specific health challenges. As federally funded grants, SBIR and STTR awards require rigorous compliance with accounting and reporting standards, ensuring transparency and accountability throughout the research process.
For small businesses aiming to contribute to public health advancements, these programs offer unparalleled opportunities to turn innovative ideas into impactful solutions.
Funding Opportunities & Application Process: A Step-by-Step Guide
The NIH Seed Fund offers an impressive $1.2 billion in non-dilutive funding, making it a vital resource for small businesses in the health and life sciences sectors. This funding is distributed across several phases, each designed to support businesses at different stages of innovation. Whether you're just starting out or scaling your solution, the NIH SBIR & STTR Grants provide a structured pathway to success.
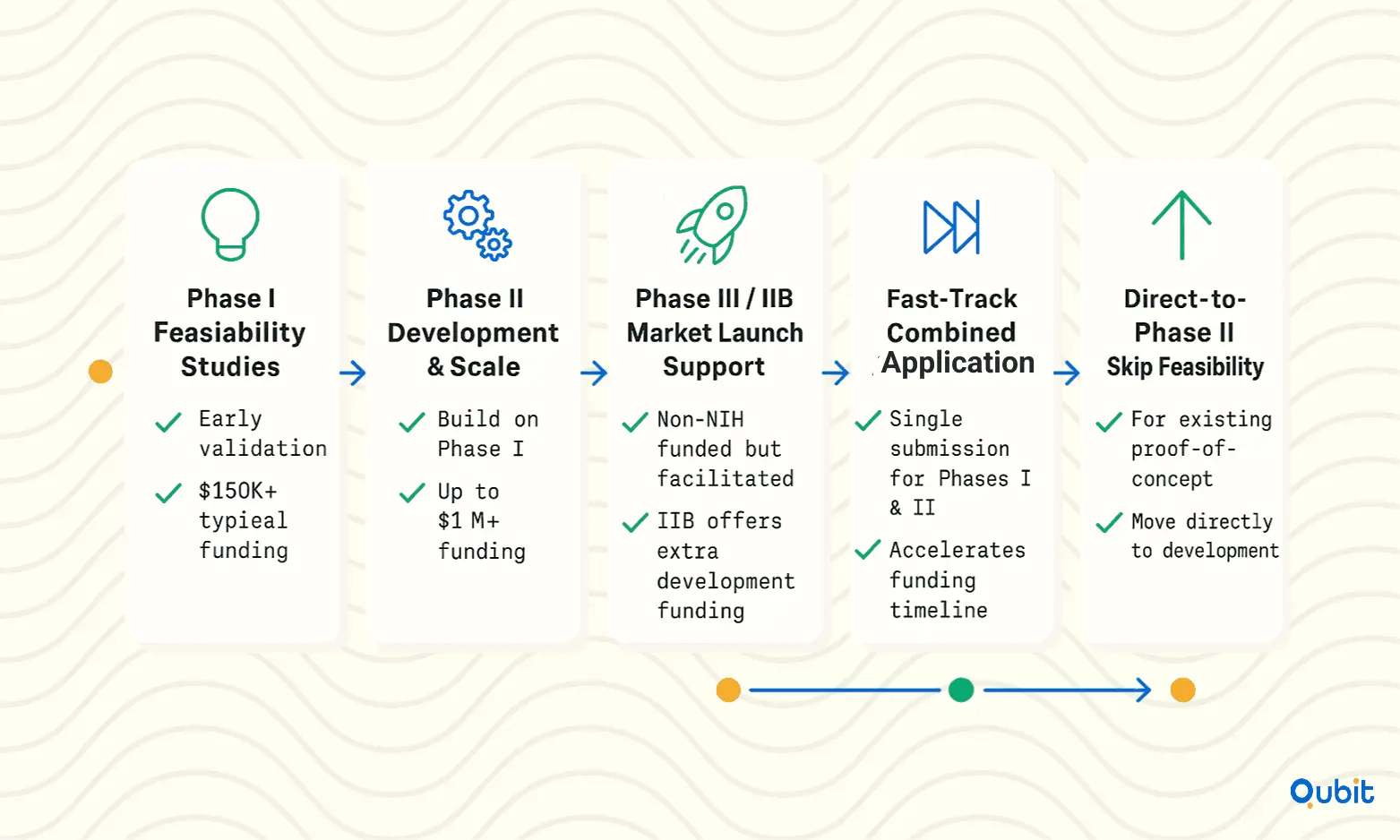
Understanding the NIH Funding Phases
The NIH Seed Fund operates through distinct funding phases, each tailored to meet the unique needs of applicants:
- Phase I: This initial phase focuses on feasibility and proof-of-concept studies. It’s ideal for businesses looking to validate their ideas before moving to full-scale development.
- Phase II: Building on Phase I, this phase supports the development and commercialization of your product or service.
- Phase III/Phase IIB: While NIH does not directly fund Phase III, it facilitates partnerships with external investors or agencies to help businesses bring their innovations to market. Phase IIB, however, provides additional funding for projects requiring further development.
- Fast-Track: This combined approach allows applicants to submit a single application for both Phase I and Phase II, expediting the funding process.
- Direct-to-Phase II: For businesses that have already completed feasibility studies, this option skips Phase I and directly supports development and commercialization efforts.
The Application Process Simplified
Applying for NIH SBIR & STTR Grants involves a clear, step-by-step process:
- Access the NIH Online Application System: Begin by utilizing the NIH online application preparation and submission system. This platform provides all the necessary forms and tools to prepare and submit your proposal.
- Monitor and Resolve Issues with the NIH Service Desk: Throughout the submission process, the NIH service desk is available to help you track your application status and address any technical challenges.
- Leverage the TABA Program for Guidance: The Technical and Business Assistance (TABA) program offers expert advice to help applicants refine their proposals and maximize their chances of success.
For businesses in the healthtech sector, exploring additional government grants healthtech can provide further insights into public funding opportunities.
The NIH Seed Fund’s structured phases and robust support system ensure that small businesses have the resources they need to innovate and thrive.
Discover Funded Topics: Exploring Funded Innovations
NIH SBIR & STTR Grants offer a wealth of opportunities for startups aiming to innovate in healthcare and life sciences. By examining the topics funded by the NIH, startups can uncover areas ripe for exploration and assess their potential eligibility for support. These grants not only reflect current market trends but also highlight shifts influenced by policy changes, such as the recent $4 billion reduction in NIH overhead funding. This adjustment has created cash flow challenges for grant-dependent startups, emphasizing the importance of staying informed about funding volatility.
Understanding these dynamics can help startups identify emerging opportunities and adapt to evolving funding trajectories. For instance, policy-driven funding volatility underscores the need for strategic planning to mitigate risks and capitalize on available resources.
To further explore funding options that maintain ownership while supporting growth, check out our article on non-dilutive funding healthcare startups. This resource complements the insights shared here by offering additional strategies for securing financial support without equity dilution.
By staying attuned to NIH-funded topics and the broader funding landscape, startups can position themselves to thrive in a competitive and ever-changing environment.
Startup Success Stories: Real-World Impact of NIH Grants
Securing funding can be a pivotal moment for startups, and NIH SBIR & STTR Grants have proven to be a game-changer for many. One standout example is Genzyme, a biotech company that started with a modest $62,000 SBIR grant from the Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). This initial funding supported their research into enzyme purification for biotherapeutics, laying the groundwork for their groundbreaking innovations. Over time, this small grant catalyzed Genzyme’s growth, culminating in its acquisition by Sanofi for an astounding $20.1 billion.
Genzyme’s journey underscores the transformative potential of NIH funding. For early-stage startups, these grants not only provide financial support but also validate their research and open doors to additional opportunities. Programs like SBIR and STTR are designed to empower startups to turn innovative ideas into impactful solutions, particularly in the healthtech sector.
For those exploring funding options, it’s worth noting that early-stage support programs like healthtech accelerator seed funding can complement NIH grants. These programs offer mentorship and resources to help startups refine their strategies and scale effectively.
Why These Grants Matter for Startups
- Scale and Impact: NIH’s SBIR/STTR programs collectively offer over $1.2 billion annually to small businesses, making them the largest source of early-stage biomedical R&D funding in the world
- De-risking Innovation: Provides crucial R&D funding before companies are ready for venture capital, especially for preclinical and discovery-stage projects.
- Commercialization Focus: NIH emphasizes not just research, but also the pathway to market—helping startups bridge the “valley of death” between invention and adoption.
How to Get Started
- Identify Fit: Review NIH’s participating Institutes and their priority areas.
- Prepare a Strong Proposal: Clearly articulate the innovation, technical approach, commercial pathway, and societal impact.
- Leverage Resources: Use NIH webinars, application guides, and topic lists to strengthen your submission.
- Apply on Time: Standard deadlines are January 5, April 5, and September 5 each year.
- Consider Partnerships: For STTR, collaborate with a nonprofit research institution.
Conclusion
Securing NIH funding requires a clear understanding of program distinctions, funding phases, and the application process. Throughout this guide, we’ve highlighted the importance of tailoring your pitch to align with NIH priorities and provided actionable strategies to help you stand out. A well-prepared pitch not only increases your chances of success but also demonstrates your commitment and readiness to potential funders.
If you’re looking to turn a sharp aims page into a fundable NIH package, at Qubit we understand FOAs, study sections, and SBIR/STTR phases. Move faster with healthtech fundraising assistance and book a quick strategy call.
Key Takeaways
- Clarifies the distinctions between NIH SBIR and STTR programs.
- Outlines key funding phases and the step-by-step application process.
- Highlights the impact of the $1.2 billion NIH Seed Fund.
- Showcases successful case studies like Genzyme’s transformative journey.
- Provides actionable insights for health startups seeking non-dilutive funding.
Frequently asked Questions
What are SBIR/STTR grants?
SBIR (Small Business Innovation Research) and STTR (Small Business Technology Transfer) grants are U.S. government–backed, non-dilutive funding programs that support early-stage R&D at small businesses. SBIR focuses on in-house research, while STTR requires collaboration with a nonprofit research institution.






