Securing capital for a startup often feels like solving a complex puzzle. While traditional venture capital remains a popular choice, emerging funding alternatives like micro VCs and super angels are reshaping the landscape. These early-stage investors offer tailored support, smaller funding rounds, and a more personal approach to nurturing startups. For founders exploring these options, platforms like Quora question and answer site provide valuable insights into common challenges and strategies for success.
As we delve deeper into this topic, you'll discover how micro VCs and super angels are redefining startup funding, their unique advantages, and actionable strategies to secure early-stage investment.
How Super Angels and Micro VCs Offer Agile Funding for Early Stages
The dynamic world of early-stage funding is witnessing a fascinating evolution. Super angels, known for investing their personal capital, are increasingly transitioning into structured roles as micro venture capitalists (VCs). This shift not only enhances their ability to support innovative startups but also preserves the agility that makes them invaluable to founders navigating the early stages of growth.
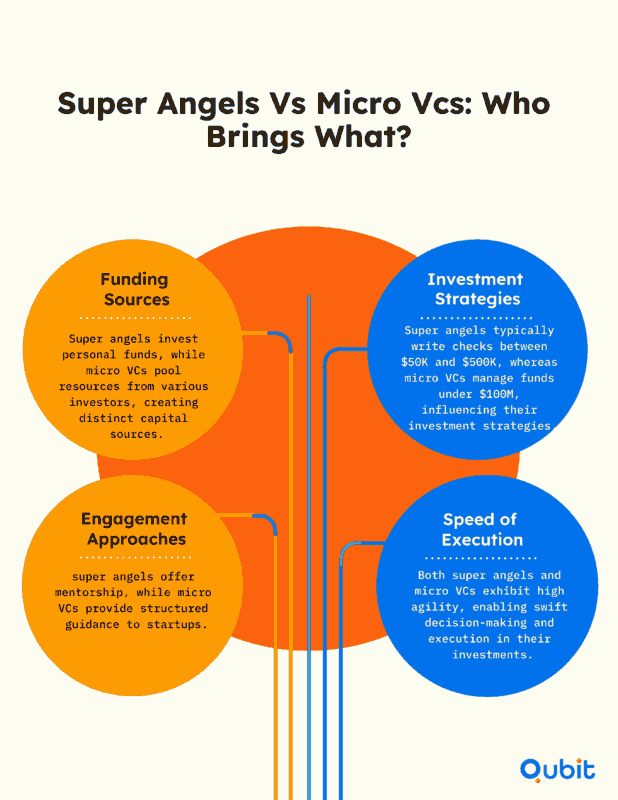
Super Angels: Flexible Investors with a Personal Touch
Super angels are individual investors who bring more than just capital to the table. By investing their own money, they offer unmatched flexibility in decision-making, often bypassing the bureaucratic hurdles associated with larger institutional investors. Their involvement typically extends beyond financial support, as they frequently act as mentors, sharing their expertise and networks to help startups thrive.
This hands-on approach is particularly beneficial for founders seeking guidance in areas like scaling operations, refining product-market fit, or securing additional funding. Super angels are often celebrated for their ability to act quickly, making them ideal partners for startups that require immediate financial backing and strategic advice.
The Rise of Micro VCs
A structural shift is underway as super angels evolve into micro VCs, creating funds that typically fall under $100 million. This transition allows them to pool resources, diversify their portfolios, and formalize their investment strategies while maintaining the agility that defines their earlier roles.
Micro VCs focus on early-stage investments, targeting startups with high growth potential. Their smaller fund size enables them to operate with precision, concentrating on niche markets or specific industries. This targeted approach is particularly appealing to founders who value personalized attention and tailored strategies over the generalized support offered by larger VC firms.
Learn how super angels transition into micro VCs under $100M from this detailed trend analysis here.
Agility Meets Structure
The evolution from super angel to micro VC reflects a balance between flexibility and structure. While micro VCs operate with a more formalized framework, they retain the ability to act swiftly—an essential trait for early-stage funding. This agility is crucial for startups that need to seize opportunities or address challenges in real time.
Moreover, micro VCs often maintain close relationships with founders, ensuring that their investments align with the startup’s vision and goals. This collaborative approach fosters trust and enables startups to grow in a supportive environment.
Exploring Alternative Funding Options
For startups seeking alternatives to private investment sources, government-backed investment programs can provide valuable support. A detailed look at government-backed investment programs startups helps you see how public initiatives can support innovative ventures.
By understanding the roles of super angels and micro VCs, founders can better navigate the complexities of early-stage funding, choosing partners who align with their needs and aspirations.
How Angel Investors Overcome Challenges and Find Opportunities
Angel investors play a pivotal role in the startup ecosystem, offering not just financial backing but also mentorship to early-stage companies. These wealthy individuals often invest their personal funds, typically in pre-seed or seed rounds, helping startups bridge the gap between ideation and scalability. However, their journey is not without challenges, from accreditation controversies to ensuring effective investment strategies.
Understanding Angel Investors
Angel investors are defined by their willingness to take calculated risks on unproven ventures. Unlike institutional investors, they use their own capital, which allows for greater flexibility but also demands rigorous verification processes. Accreditation remains a critical factor, as it ensures that investors meet financial thresholds and understand the risks involved. Controversies surrounding accreditation highlight the importance of stringent checks to protect both investors and startups.
For example, Naval Ravikant, a renowned super angel, has reportedly made over 130 investments with an average check size of $50,000. His portfolio demonstrates the impact of active participation in diverse markets, showcasing how strategic investments can yield significant returns. Similarly, SuperAngel.Fund’s portfolio strategy, which includes 198 investments with a median check size of $50,000, reflects a balanced approach to risk management, achieving an unrealized IRR of 15.56%.
Typical Investment Sizes and Market Trends
Angel investors often operate within specific financial ranges. Data from AngelList reveals that check sizes typically hover around $50,000, with some high-frequency investors making 20 or more investments, totaling $1 million or more. Out of over 12,000 angel investors, only 35 have made 50+ investments, while 116 have made 20+ investments, underscoring the elite group shaping the pre-seed market.
Historical data, such as the 2018 AngelList statistics, provides insights into investment frequency and trends. By analyzing these patterns, startups can identify potential angel investors who align with their industry focus. Referencing resources like AngelList can be invaluable for startups seeking to connect with investors who share their vision.
Case Studies: Rigorous Verification and Effective Strategies
Case studies offer a deeper understanding of how angel investors overcome challenges. Naval Ravikant’s portfolio exemplifies proactive participation, with investments spanning various industries and stages. His approach highlights the importance of diversification and mentorship in driving startup success.
Another notable example is SuperAngel.Fund, which balances risk across multiple startups to achieve consistent returns. Their strategy demonstrates how a well-managed portfolio can mitigate the inherent risks of early-stage investments.
For startups aiming to attract angel investors, understanding the types of investors in startups is crucial. This resource outlines distinct investor profiles, helping founders tailor their approach to secure funding effectively.
Accreditation and Verification Challenges
Accreditation controversies often stem from differing interpretations of financial thresholds and investor qualifications. These challenges emphasize the need for rigorous verification processes to ensure that angel investors are adequately prepared for the risks associated with early-stage funding.
Legal and regulatory considerations also play a role, particularly when comparing angel investments to sovereign capital. Exploring legal issues with sovereign investments provides valuable insights into compliance requirements, helping investors navigate complex regulatory landscapes.
Angel investors are indispensable to the startup ecosystem, but their success hinges on strategic decision-making and thorough verification processes. By analyzing case studies and leveraging resources like AngelList, both investors and startups can unlock opportunities while mitigating risks.
How Micro VC Firms Are Evolving and Shaping Global Markets
Micro VC firms are redefining early-stage investing by focusing on smaller funds and targeted strategies. These firms typically manage funds under $100 million, enabling them to prioritize agility and niche opportunities. As super angels transition into micro VC roles, they bring a wealth of experience, reshaping global market dynamics and creating new pathways for startups.
The Rise of Micro VC Firms Globally
The global footprint of micro VC firms is expanding rapidly, with 58% of them based in the United States. While the US remains the central hub, emerging markets like India are gaining traction, boasting 228 micro VC firms as of 2024. This growth highlights the increasing opportunities for founders worldwide, particularly in regions where traditional venture capital has been less accessible.
Micro VCs are also embracing innovative structures, such as syndicate-led special purpose vehicles (SPVs), to diversify their portfolios and democratize access to early-stage deals. These SPVs allow a broader base of limited partners to participate, fostering inclusivity in the investment ecosystem.
Performance Advantages of Micro VCs
Research underscores the competitive edge of micro VC firms, revealing that they achieve 7.5% higher returns compared to the top quartile of traditional venture capital funds. This performance advantage stems from their ability to focus on early-stage startups with high growth potential, often overlooked by larger funds.
Case studies further illustrate the impact of micro VC strategies. For instance, Honeywell Aerospace adopted agile hardware development processes, reducing product development cycle time by 30%. While this example pertains to internal R&D, it mirrors the nimble approach micro VCs use to structure their investments and operations.
Emerging Trends in Micro VC Investments
Micro VC firms are increasingly allocating funds to startups with measurable social and environmental impact. This trend aligns with the growing emphasis on ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) metrics, appealing to a broader investor base. By incorporating these metrics, micro VCs not only drive financial returns but also contribute to meaningful change.
Micro VC firms are proving that smaller funds can deliver outsized results, both financially and socially. Their evolution is shaping global markets, creating opportunities for startups and investors to thrive in an increasingly interconnected world.
Using Accelerators and Incubators Wisely for Strategic Growth
Accelerators and incubators are more than just funding platforms; they serve as vital ecosystems for mentorship, networking, and structured growth. These programs often provide founders with access to industry experts, potential investors, and tailored resources designed to fast-track business development. However, while their benefits are undeniable, founders must weigh the equity trade-offs and long-term implications carefully before committing.
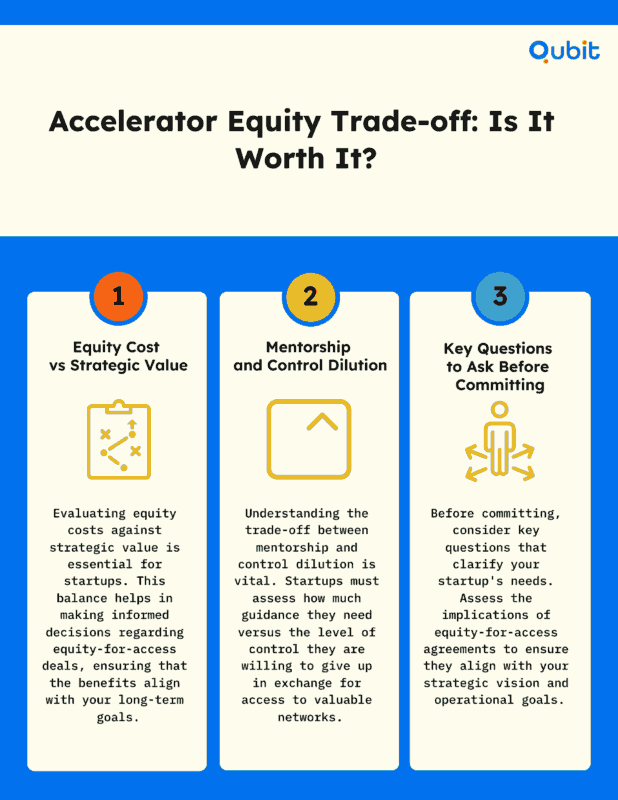
The structured support offered by accelerators and incubators can catalyze rapid scaling, but it often comes with significant control trade-offs. For instance, many programs require startups to exchange equity for access to their resources, which could dilute ownership and influence over time. Founders should critically assess whether the short-term benefits align with their long-term strategic goals.
Additionally, mentorship and networking opportunities provided by these programs can be transformative, but they are not one-size-fits-all. The right accelerator or incubator should align with the startup’s industry, growth stage, and vision. Without this alignment, the resources offered may not deliver the intended impact, leaving founders with less control and fewer benefits than anticipated.
Ultimately, accelerators and incubators can be powerful tools for strategic growth when approached wisely. Founders should conduct thorough research, evaluate equity implications, and ensure the program aligns with their business trajectory.
Conclusion
Securing early-stage funding requires a strategic approach and a clear understanding of the options available. From super angels and angel investors to micro VCs and accelerators, each funding avenue offers unique benefits and challenges. Rigorous investor verification is crucial to ensure alignment with your startup’s vision and goals. Strategic funding choices, backed by real-world examples and data-driven insights, can significantly enhance your chances of success.
At Qubit Capital, we specialize in helping startups like yours navigate the complexities of fundraising. If you're ready to explore tailored funding strategies and secure the capital you need, our Fundraising Assistance service offers expert support every step of the way. Let us help you turn your vision into reality.
Key Takeaways
Super angels offer nimble, early-stage capital and quick decision-making but are increasingly evolving into micro VC structures, blending individual agility with institutional strategies.
Angel investors play a dual role by providing both funding and hands-on mentorship; however, working with them requires careful accreditation, due diligence, and investor verification processes.
Micro VC firms are gaining traction globally by deploying smaller, sector-specific funds with high-conviction, high-return strategies, particularly in underserved or emerging markets.
Accelerators and incubators offer structured growth support, including mentorship, networks, and resources, though they often involve equity dilution that startups must weigh carefully.
Leveraging data-backed insights and studying real-world case studies helps founders navigate this complex landscape and choose the most aligned funding pathway based on stage, strategy, and long-term goals.
Frequently asked Questions
What is the difference between angels and VCs?
Angel investors invest their own capital and provide flexible, hands-on support at early stages, while VCs manage funds from limited partners with more structured investment processes, larger check sizes, and increased oversight.


 Back
Back



