Scaling a startup successfully requires more than just ambition; it demands a clear understanding of the factors that drive sustainable growth. Investors and founders alike often grapple with identifying whether a business model can expand efficiently without compromising quality or profitability. This blog introduces a practical framework for evaluating startup scalability, offering actionable insights to help you assess growth potential early on.
The discussion of startup scouting strategies lays the groundwork for your exploration of how early-stage evaluations influence scalability potential. By examining key scalability metrics and aligning them with business goals, you can uncover hidden opportunities and mitigate risks.
Let’s dive into the essentials of assessing scalability and setting startups on the path to long-term success.
Assessing Startup Scalability
Startup scalability is critical for long-term success. Building a scalable foundation helps startups thrive and avoid common pitfalls. Many founders underestimate the risk presented after initial traction. 78% of startups fail during the scale-up stage, even after achieving product-market fit. This underscores the need for robust planning beyond early wins.
Understanding startup scalability is critical for long-term success. With 90% of startups failing,10% within the first year and 70% between years two and five, it’s evident that a scalable foundation can make the difference between thriving and folding.
1. Evaluating Business Model Scalability
A scalable business model is the cornerstone of sustainable growth. Startups must assess whether their revenue can grow exponentially without proportional increases in costs. For instance, subscription-based models often scale more efficiently than service-heavy models, as they require less incremental effort to onboard new customers.
For example, a social media platform can onboard millions of users quickly, leveraging network effects for organic growth with limited resource strain.
Key questions to consider include:
– Can the product or service be replicated without significant cost increases?
– Does the pricing structure support profitability at scale?
– Are there opportunities for automation to reduce operational overhead?
2. Analyzing Market Dynamics
Market dynamics play a pivotal role in scalability. Startups should evaluate the size of their target market, growth potential, and competitive landscape. A large, expanding market offers more room for growth, while a saturated or shrinking market may limit opportunities.
Additionally, understanding customer acquisition costs (CAC—the expense to acquire each customer) and lifetime value (LTV—the total revenue from a customer) ratios is essential.
3. Assessing Team Composition
A startup’s team is another critical factor in scalability. Founders must ensure they have the right mix of skills and expertise to support growth. This includes not only technical and operational capabilities but also leadership qualities that inspire and guide the team through scaling challenges.
Building a scalable team often involves:
– Hiring individuals who can adapt to changing roles as the company grows.
– Establishing clear communication channels to maintain alignment.
– Creating a culture that prioritizes innovation and efficiency.
4. Strengthening Operational Infrastructure
Operational infrastructure must be robust enough to handle increased demand without breaking down. This includes technology systems, supply chains, and customer support processes. Startups should invest in scalable solutions early to avoid costly retrofits later.
For example, cloud-based platforms can provide the flexibility to scale IT resources as needed, while automated customer support tools can handle higher volumes without requiring additional staff.
5. Align Short-Term Milestones with Long-Term Vision
Sustainable scalability requires more than just operational readiness; it demands that founders balance immediate milestones with a clear long-term vision. Startups often face pressure to deliver quick wins, but focusing solely on short-term results can undermine strategic growth. By aligning tactical objectives with the company's broader mission, founders ensure that every step forward contributes to lasting value and market relevance.
This alignment involves setting measurable short-term goals that serve as building blocks for long-term aspirations. For example, achieving a specific revenue target or launching a new product feature should directly support the startup’s overall growth strategy. Regularly revisiting and adjusting these milestones keeps the team focused and responsive to market changes while preventing mission drift.
- Review quarterly objectives to confirm they support the startup’s long-term vision and market positioning.
- Communicate the connection between daily tasks and strategic goals to keep teams motivated and aligned.
- Adapt milestones as market conditions evolve, ensuring flexibility without losing sight of the ultimate mission.
For instance, subscription-based models often scale more efficiently than service-heavy models, as they require less incremental effort to onboard new customers.
Key Indicators of Scalability
Startup scalability is often determined by a combination of financial, operational, and customer-centric indicators that reveal whether a business can grow efficiently without compromising quality or profitability.
Startups should evaluate the size of their target market and its growth potential. Assess the competitive landscape as well. Key indicators help investors and founders assess startup scalability early in the growth journey.
According to average projected revenue growth rates, startups expect 178% growth in Year 1, 100% in Year 2, and 71% in Year 3. These figures set a benchmark for evaluating performance.
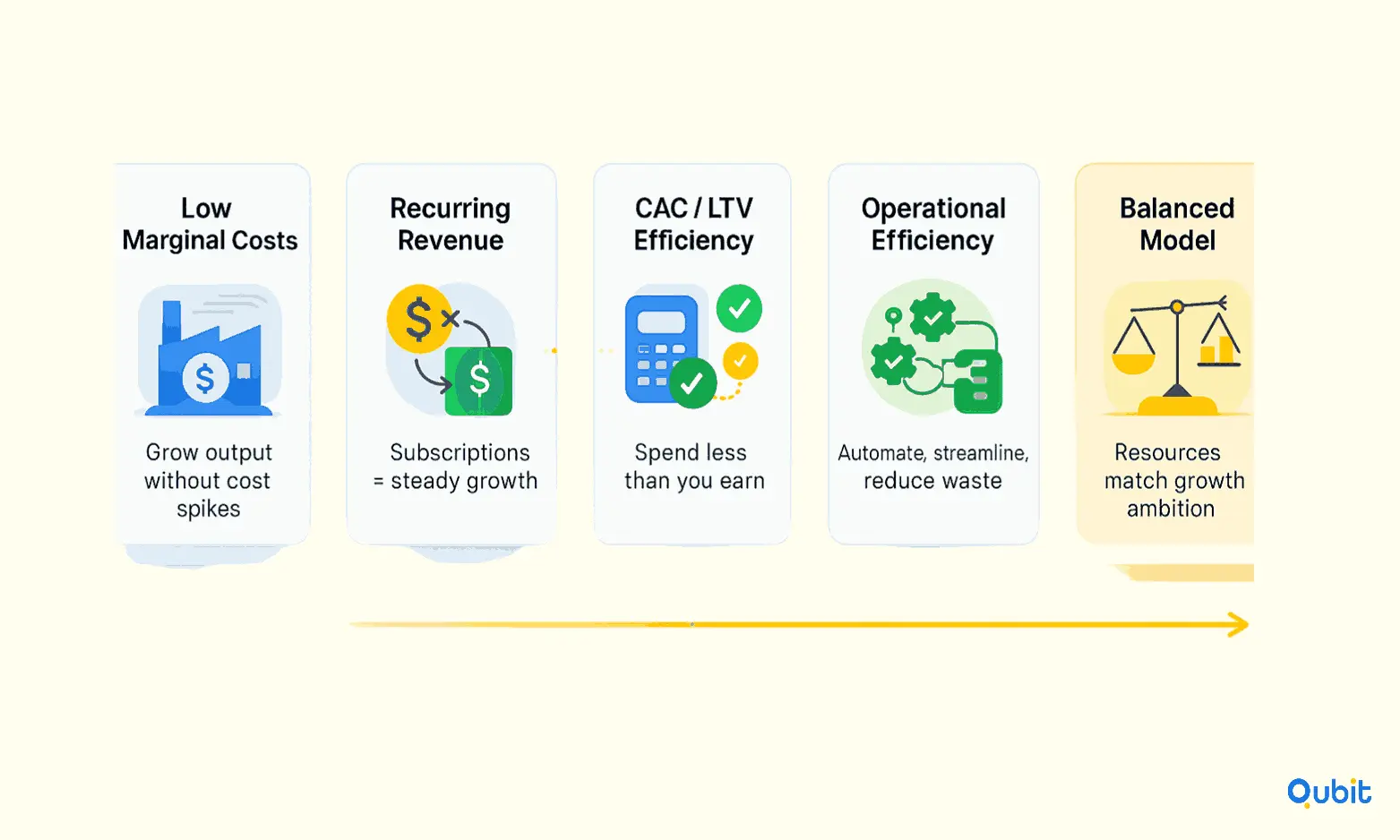
1. Low Marginal Costs
One of the most telling signs of scalability is the ability to increase production or service delivery without a proportional rise in costs. Startups that can maintain low marginal costs as they grow are better positioned to scale effectively. For instance, software-as-a-service (SaaS) companies often exhibit this trait, as their cost of serving additional users is minimal once the platform is developed.
2. Recurring Revenue Streams
A predictable and recurring revenue model is another critical scalability indicator. Subscription-based businesses, for example, benefit from consistent cash flow, which simplifies financial planning and supports sustainable growth. This model also reduces the dependency on constant customer acquisition, allowing startups to focus on retention and expansion.
3. Customer Acquisition Efficiency
Efficient customer acquisition is a hallmark of scalable startups. Businesses that achieve a low customer acquisition cost (CAC) relative to the lifetime value (LTV) of their customers demonstrate strong growth potential. Investors often evaluate this ratio to gauge scalability.
4. Network Effects
Startups that benefit from network effects—where the value of a product or service increases as more people use it—are inherently scalable. Social media platforms and marketplaces are prime examples, as their growth fuels further adoption, creating a self-reinforcing cycle.
5. Operational Efficiencies
Streamlined operations and effective cost management are vital for scalability. Startups that invest in automation, optimize workflows, and minimize waste can scale more seamlessly. To assess scalability comprehensively, it’s also important to consider the investor questions before match, which provide a framework for evaluating operational readiness.
6. Balanced Business Model
A scalable startup maintains a balanced business model that aligns growth ambitions with resource availability. This includes having the right team, technology, and infrastructure to support expansion without overextending.
By focusing on these indicators, startups can position themselves for sustainable growth while meeting the expectations of stakeholders and investors.
Market Size and Scalability
Understanding the dimensions of market size is essential for evaluating startup scalability. By analyzing Total Addressable Market (TAM), Serviceable Available Market (SAM), and Serviceable Obtainable Market (SOM), businesses can identify growth ceilings and assess customer acquisition potential. These metrics not only quantify opportunities but also provide a roadmap for scaling operations effectively.
Breaking Down TAM, SAM, and SOM
Total Addressable Market (TAM):
TAM represents the entire market demand for a product or service. It’s the broadest measure of opportunity, encompassing all potential customers without constraints like geography or competition. For startups, TAM serves as a visionary benchmark, highlighting the ultimate growth potential.Serviceable Available Market (SAM):
SAM narrows the focus to the portion of TAM that a business can realistically target based on its current offerings and operational scope. This metric is particularly useful for aligning resources with achievable goals.Serviceable Obtainable Market (SOM):
SOM further refines the market size to the segment a company can capture in the short term, considering factors like competition, pricing, and customer acquisition strategies. It’s a critical measure for early-stage startups to validate their immediate growth potential.
Why Market Size Matters for Scalability
A startup’s ability to scale hinges on the size and accessibility of its target market. Larger markets justify scaling efforts by offering increased customer acquisition opportunities and room for geographic expansion.
For instance, the 18.4% increase in venture funding in 2024, which totaled $89 billion, underscores the importance of capturing sizable markets early. This funding trend highlights how investors prioritize startups with validated market opportunities and clear scalability pathways.
Strategic partnerships expand scaling capacity. In 2023, corporate funding reached 12% of US startup investment, reflecting a shift toward collaborative growth. Startups can leverage alliances to access wider markets.
The Role of Risk Profiles in Scalability
Assessing risk profiles is another critical component of scalability evaluation. A nuanced review of assessing startup risk profiles demonstrates how understanding potential risks complements the broader framework for scalability assessment. By identifying and mitigating risks early, startups can position themselves for sustainable growth within their defined markets.
Unit Economics and Scalability
Understanding startup scalability begins with a deep dive into unit economics, the financial metrics that reveal how much value a business generates per customer. Metrics like Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC), Lifetime Value (LTV), payback period, and contribution margin play a pivotal role in scalability evaluation. These indicators reveal whether the business can sustain profitability as it grows.
Why CAC and LTV Matter
Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) measures the expense of acquiring a single customer, while Lifetime Value (LTV) estimates the total revenue a customer will generate over their relationship with the business. A healthy balance between these two metrics is critical. For instance, if the LTV significantly outweighs the CAC, it signals that the business is generating substantial returns on its customer investments. Conversely, a high CAC relative to LTV could indicate inefficiencies in marketing or product-market fit.
Many businesses fail to achieve sustainable unit economics. 21.5% of startups fail in their first year due to financial and business model weaknesses. This highlights why LTV and CAC matter so much.
Monitoring Burn Rate and Cash Runway
Building on robust unit economics, founders must closely monitor burn rate and cash runway during periods of rapid scaling. Burn rate reflects how quickly a startup spends its available capital, while cash runway indicates how long the business can operate before needing additional funding. Proactive financial oversight helps prevent unexpected cash shortages, enabling timely adjustments to spending and growth strategies.
Indicators of Scalability
Startups with short payback periods, where the revenue from a customer quickly offsets the acquisition cost—are better positioned for scalable growth. Similarly, high contribution margins, which measure the profitability of individual units after variable costs, suggest that the business can sustain growth without excessive financial strain. These metrics collectively highlight whether a startup is ready to expand or needs to refine its operations.
The Role of Robust Unit Economics
Strong unit economics serve as a compass for startups, pointing toward sustainable growth. They ensure that scaling doesn’t come at the expense of profitability, allowing businesses to grow without relying on unsustainable cost increases. For investors and founders alike, these metrics act as early indicators of long-term viability, reducing the risks associated with rapid expansion.
Timing: Scalability vs Product-Market Fit
Scaling a startup is an exciting milestone, but rushing into growth without securing product-market fit can lead to costly mistakes. Startup scalability depends on achieving product-market fit before pursuing rapid growth, making it essential to prioritize product-market fit before scaling efforts begin.
Premature scaling is a primary failure driver. 90% of startups ultimately fail, with scale missteps amplifying the risks even after initial traction. This shows how timing decisions can decide long-term survival.
Why Product-Market Fit Comes First
Achieving product-market fit means your product fulfills a genuine need for a specific audience, and customers are willing to pay for it. Without this validation, scaling can amplify inefficiencies, drain resources, and expose weaknesses in your business model. For instance, scaling prematurely might result in high customer acquisition costs or poor retention rates, which can jeopardize long-term sustainability.
Risks of Premature Scaling
Expanding operations before confirming product-market fit often leads to operational bottlenecks and financial strain. Startups may face challenges such as:
- Cash flow issues: Increased spending on marketing and infrastructure without sufficient revenue generation.
- Operational inefficiencies: Overwhelmed systems and processes that cannot handle the demands of rapid growth.
- Customer dissatisfaction: A product that fails to meet expectations, leading to negative reviews and reduced loyalty.
The Role of Repeatable Sales Processes
A repeatable sales process is another critical prerequisite for scaling. Once product-market fit is established, startups must ensure they can consistently acquire and retain customers. This involves refining marketing strategies, optimizing sales funnels, and delivering exceptional customer experiences.
Sustainable Growth Strategies
To scale successfully, startups should focus on building a stable foundation. This includes:
- Validating customer demand: Conducting market research and gathering feedback to confirm your product solves a real problem.
- Optimizing operations: Streamlining processes to ensure efficiency and scalability.
- Monitoring key metrics: Tracking performance indicators like customer acquisition cost (CAC) and lifetime value (LTV) to guide growth decisions.
Scaling is not just about expanding; it’s about growing sustainably. By prioritizing product-market fit, startups can avoid common pitfalls and set the stage for long-term success.
Founding Team and Scalability
The ability of a startup to scale effectively often hinges on the expertise and cohesion of its founding team. A well-rounded team with complementary skill sets can address challenges head-on, ensuring the business adapts seamlessly to rapid growth.
1. The Role of Experience in Startup Scalability
Founders with proven experience in scaling businesses bring invaluable insights to the table. They understand the complexities of expanding operations, managing resources, and maintaining product quality during periods of accelerated growth. This expertise minimizes risks and ensures the startup remains agile in competitive markets.
2. Complementary Skill Sets: A Key to Balanced Leadership
A founding team that combines technical expertise, strategic vision, and operational efficiency creates a balanced leadership structure. For example, while one founder might excel in product innovation, another might specialize in building scalable systems or fostering investor relationships. This synergy reduces internal bottlenecks and ensures every aspect of the business is prepared for growth.
3. Building a Scalable Organizational Culture
Effective leadership goes beyond operational strategies, it also involves cultivating a robust organizational culture. Founders who prioritize transparent communication, adaptability, and employee empowerment lay the groundwork for scalable operations. A strong culture not only attracts top talent but also ensures teams remain aligned with the company’s vision during expansion.
4. Using Equity Incentives for Team Alignment
Extending from a strong organizational culture, offering broad equity incentives can significantly enhance team motivation and retention. Equity aligns individual interests with the startup’s long-term success, encouraging commitment through periods of uncertainty and rapid change. This approach helps attract top talent and fosters a sense of shared ownership across the company.
Technological Factors in Scalability
Scalability in startups often hinges on the right technological foundation. Startup scalability thrives when infrastructure is adaptable, automation is prioritized, and technical debt is addressed early. These elements ensure businesses can expand rapidly without overwhelming their systems or budgets.
1. Infrastructure Flexibility: Building for Growth
A flexible infrastructure is the backbone of scalable operations. Startups that invest in cloud-native solutions gain the ability to scale resources up or down based on demand. This adaptability minimizes costs during low-traffic periods while ensuring performance during peak loads. Modular architecture further enhances this flexibility, allowing businesses to add or modify components without disrupting the entire system.
2. Automation: Streamlining Operations
Automation is a game-changer for startups aiming to scale efficiently. By automating repetitive and complex tasks, businesses can reduce manual errors, save time, and allocate resources to strategic initiatives. For instance, AI-driven approaches like predictive analytics, chatbot customer service, and automated data pipelines exemplify how technology can accelerate scalability. These tools not only enhance decision-making but also improve customer experiences, creating a solid foundation for growth.
3. Managing Technical Debt Early
Unchecked technical debt can cripple scalability. Startups that delay addressing outdated code, inefficient systems, or poorly integrated tools often face significant roadblocks as they grow. Proactively managing technical debt ensures that systems remain agile and capable of supporting expansion. Early investments in scalable technologies prevent costly overhauls later, enabling smoother transitions as the business evolves.
Startup tech projects often exceed budgets. 52.7% of software projects cost 189%+ of their initial estimates, mainly due to underestimating requirements. Anticipating technical debt is critical for sustainable scaling.
The Role of AI in Scalability
AI is no longer just a product feature; it has become an operational powerhouse. By automating complex processes and delivering data-driven insights, AI empowers startups to scale smarter and faster. Whether through predictive analytics or automated workflows, AI integration transforms scalability from a challenge into an opportunity.
Operational Readiness for Scaling
Scaling a startup requires more than just ambition; it demands a robust operational framework to support growth. Operational efficiency ensures that as demand surges, quality and customer satisfaction remain uncompromised.
Operational breakdowns are widespread. 70% of businesses struggle to scale effectively from startup to enterprise level. Preparing operations early addresses most common roadblocks.
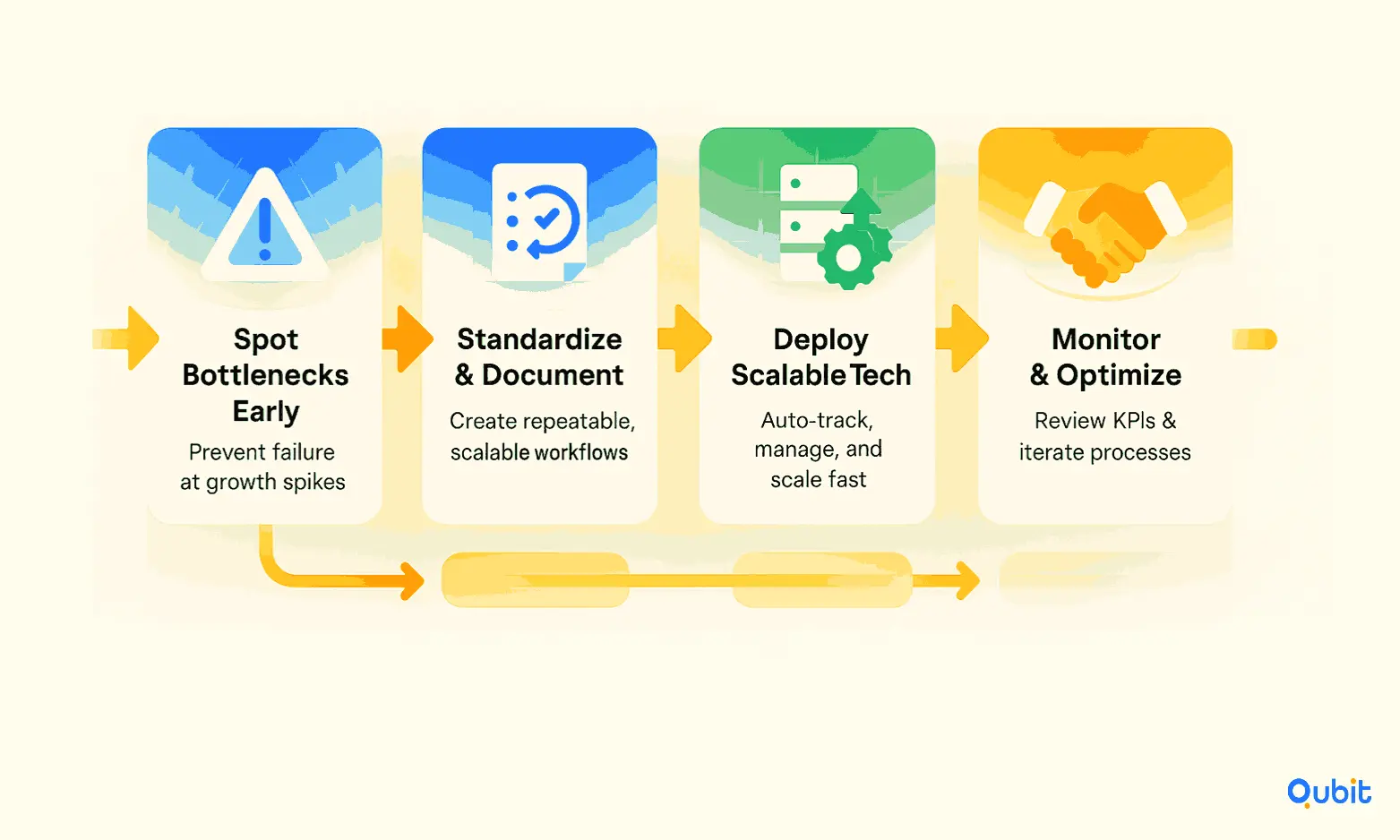
1. Identify and Address Bottlenecks Early
Operational readiness begins with a clear understanding of your current processes. Startups must identify potential bottlenecks in areas like production, fulfillment, and customer support. For instance, Alabaster Co. experienced a 135% spike in orders after a TikTok video went viral. This unexpected surge could have overwhelmed their logistics, but their proactive partnership with Shipfusion for scalable third-party logistics ensured they met two-day shipping requirements. This case highlights the importance of anticipating growth and preparing systems to handle it effectively.
2. Standardize and Document Processes
Standardization is key to maintaining consistency during rapid expansion. Documenting workflows, from inventory management to customer service protocols, creates a blueprint that can be scaled. This not only reduces errors but also simplifies onboarding new team members as the business grows.
3. Invest in Scalable Technology
Technology plays a pivotal role in operational scalability. Implementing tools for automation, inventory tracking, and customer relationship management (CRM) can streamline operations and reduce manual workload. Scalable solutions ensure that your systems can handle increased demand without requiring constant upgrades.
4. Build Strategic Partnerships
Collaborating with reliable partners can significantly enhance operational readiness. Whether it’s outsourcing logistics, like Alabaster Co., or partnering with suppliers who can scale production, these relationships provide the flexibility needed to adapt to fluctuating demand.
5. Monitor and Optimize Continuously
Scaling is not a one-time event; it’s an ongoing process. Regularly review performance metrics to identify inefficiencies and areas for improvement. Continuous optimization ensures that operations remain aligned with growth objectives.
Operational readiness is the backbone of startup scalability. By addressing bottlenecks, standardizing processes, and leveraging scalable solutions, startups can confidently meet the challenges of growth while maintaining quality and customer satisfaction.
Practical Frameworks for Evaluating Scalability
Evaluating startup scalability works best when you use a structured framework across multiple dimensions, such as market size, unit economics, operations, and execution capacity. A clear framework helps founders and investors judge growth potential objectively and spot the real bottlenecks early.
Clear frameworks reduce wasted effort. 46% of US startup founders spend 30% or more of their week fundraising, and 1 in 4 devote over half their time. Effective evaluation strategies free up resources for growth.
Key Components of Scalability Evaluation
Business Model Design
A scalable business model is the foundation for sustainable growth. It should demonstrate adaptability to increasing demand without proportionate cost increases. Evaluating the model involves analyzing its ability to expand across markets, diversify revenue streams, and maintain operational efficiency.Market Analysis
Understanding market size and dynamics is critical. Scalability depends on whether the target market can accommodate growth. Factors such as customer demand, competitive landscape, and industry trends should be assessed to determine the feasibility of scaling operations.Unit Economics
Metrics like Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC), Lifetime Value (LTV), payback period, and contribution margin play a pivotal role in scalability evaluation. These indicators reveal whether the business can sustain profitability as it grows.Team Capabilities
A strong, adaptable team is essential for scaling. Assessing leadership, operational expertise, and the ability to manage growth challenges ensures the business can handle increased complexity.
Conclusion
Startup scalability requires a structured, data-driven approach to minimize risks and ensure sustainable growth. By systematically analyzing market size, unit economics, team capabilities, and operational readiness, businesses can identify and address potential bottlenecks before they hinder growth. This proactive mindset not only minimizes risks but also sets the foundation for sustainable success.
The earlier startups embrace such frameworks, the better equipped they are to overcome scalability challenges. Whether it's refining processes or aligning resources, these strategies empower teams to focus on long-term goals rather than short-term fixes.
If you're ready to take the next step in scaling your startup, contact us at Qubit Capital to explore our Investor Outreach service. Together, we can help you secure the resources and partnerships needed to achieve your growth ambitions.
Key Takeaways
- Early scalability planning prevents costly retrofits.
- Robust unit economics and a large market size are strong indicators of growth potential.
- A balanced and experienced founding team is critical for successful scaling.
- Technological readiness and operational efficiency underpin sustainable expansion.
- Structured frameworks, like the Golden Egg Check Assessment Process, guide strategic scaling decisions.
Frequently asked Questions
What does scalability mean for a startup?
Scalability means a startup can grow revenue without increasing costs at the same rate. This ensures sustainable, efficient expansion. It reduces risks as the business grows. Investors often seek startups with strong scalability. Efficient scaling leads to long-term success.






