Consumer startups on Carta raised just $800 million in Q1 2025, the lowest level since 2019, while Series A valuations jumped 36% to $45.3 million. Deal counts declined 32% quarter-over-quarter as investors grew more selective amid tariff uncertainty and extended funding timelines. The gap between seed and Series A has stretched to three years from 1.7 years in 2024, challenging founders to sustain momentum.
This guide offers founders a roadmap for understanding funding options, targeting the right investors, and preparing pitch materials that stand out. Investors and business professionals will find strategic market analyses and founder-readiness indicators to refine their consumer investment frameworks.
Let's get started!
What is Early-Stage Funding?
Early-stage funding spans angel, pre-seed, and seed rounds, each serving a distinct purpose. First institutional funding often ranges from $500,000 to $5 million for early-stage companies. This provides a baseline for founders preparing seed and pre-seed roadmaps. Understanding this range helps frame realistic expectations before targeting investors, ensuring preparation aligns with industry norms.
- Angel Investors: Individuals investing $25K–$250K to validate early product concepts.
- Pre-Seed Rounds: $1.4M median checks fuel prototype development and initial traction.
- Seed Rounds: $2M–$5M checks expand teams, refine product-market fit, and build early revenue streams.
Recent trends show a tighter funding climate. Seed-stage startups on Carta raised 12.5% less capital in 2024 compared to 2023. This shift underscores investor caution and signals the need for founders to refine their fundraising approach for current conditions.
Why Funding Early Matters for Consumer Startups
Consumer businesses face three unique realities:
- Network effects and virality. Early capital amplifies marketing flywheels before competitors saturate the channel.
- High burn for growth. Paid user acquisition, inventory, and supply-chain deposits often precede revenue.
- Winner-takes-most dynamics. The first brand to capture mindshare sets switching costs that lock in consumers.
For further perspective, median seed round in 2024 reached $3.5 million. This benchmark clarifies expectations for founders and helps quantify whether table estimates reflect current fundraising reality. Setting sights on this median value can guide more effective pitch and milestone planning.
While consumer startups tend to focus on brand-led growth, marketplace ventures must often prove liquidity and supply-demand balance early on. The funding guide for consumer & marketplace startups unpacks how to navigate these differences during early fundraising.
Mapping the Funding Journey
Identifying Suitable Investors For Consumer Startup Ventures
Not all investors fit every startup. Consumer founders should consider:
- Angel Networks: Ideal for early proof-of-concept and network introductions.
- Specialized VCs: Firms focusing on D2C, marketplace, or consumer tech that can offer category expertise.
- Corporate Venture Arms: Strategic investors seeking partnerships or distribution channels.
- Crowdfunding Platforms: Channels for both capital and customer validation.
Research investor portfolios and theses to identify those backing brands with similar business models or customer segments. For example, funds prioritizing sustainability may favor eco-friendly consumer goods, while AI-centric VCs look for startups embedding machine learning into personalization or logistics. Geographic considerations matter too: investors in coastal hubs often prefer digitally native brands, whereas Midwestern funds may focus on physical products with regional manufacturing ties.
Leveraging Strategic Networking for Investor Access
Building on targeted investor research, founders should prioritize strategic networking to secure warm introductions. Engaging with curated investor lists, industry events, and online platforms increases the likelihood of meaningful connections. Warm introductions from trusted contacts often lead to faster responses and higher investor engagement. These efforts help founders bypass cold outreach and improve fundraising efficiency.
Some angels bring more than capital, especially those who’ve seen the movie before. This list of angel investors focused on consumer tech reflects that.
Maximizing Investor Outreach Through Regional Events
These efforts extend to participating in regional startup events, which attract large investor audiences and facilitate pitch competitions. Founders gain exposure to potential partners and funding sources in concentrated settings. Events like Venture Atlanta offer opportunities to accelerate capital formation and build strategic relationships. Leveraging these venues strengthens a founder’s fundraising network and market presence.
Pre-Seed Capital: From Bootstrapping to Friends & Family
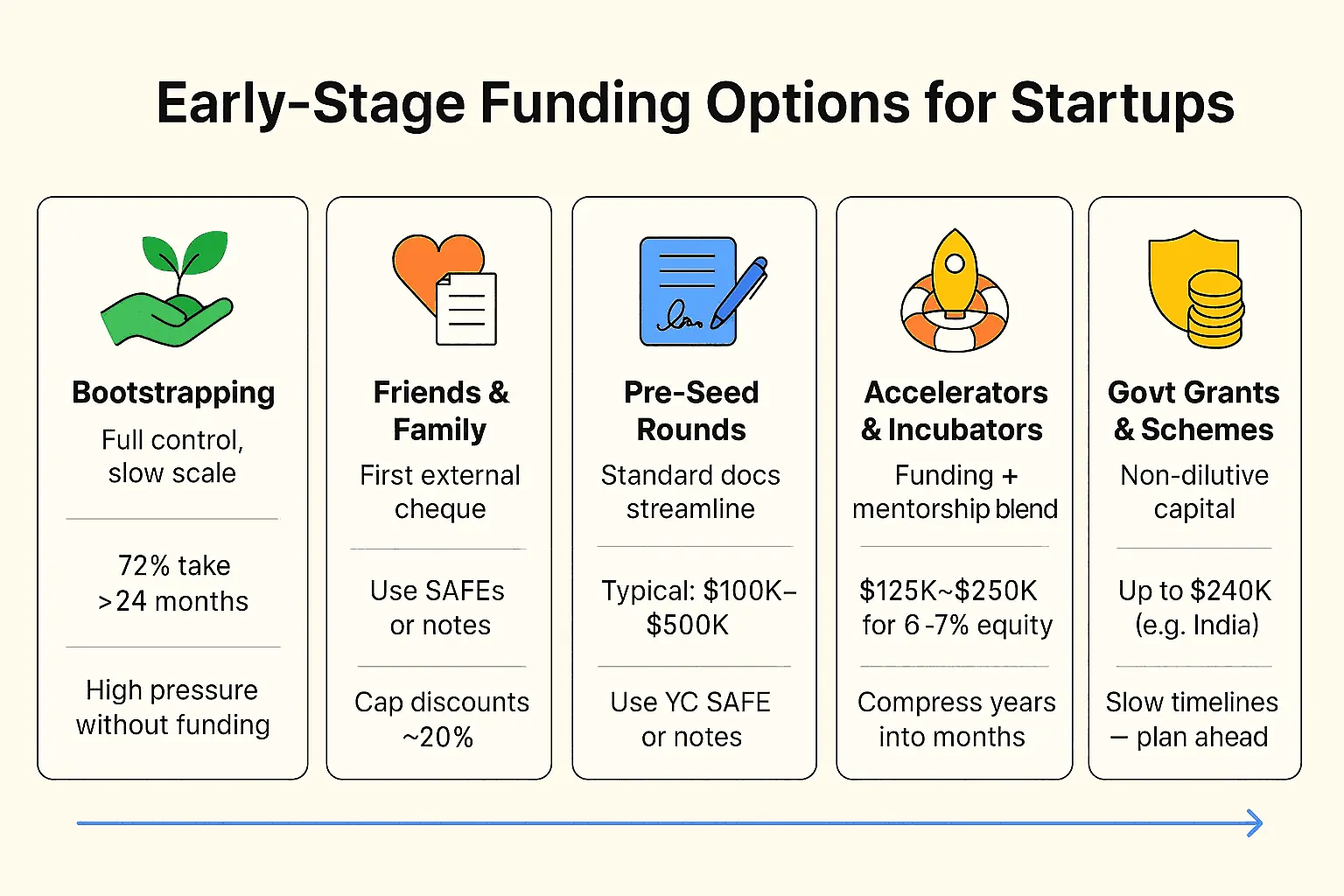
1. Bootstrapping
- Pro: You keep full control and show serious founder commitment.
- Con: It can slow you down. Around 72% of bootstrapped consumer apps take more than 24 months to hit 10,000 users.
Most consumer founders don’t realize how much pressure external capital adds to retention goals, something this piece on bootstrapping vs external funding for consumer apps doesn’t shy away from.
2. Friends & Family
Once you’ve pushed things as far as you can on your own, friends and family are often the first external cheque.
- Keep terms simple.
- Convertible notes or SAFEs (Simple Agreements for Future Equity) with around a 20% discount cap are common.
- Clearly document expectations, timelines, and risks to protect both the relationship and the business.
3. Streamlining Pre-Seed Rounds with Standardized Instruments
As founders move beyond bootstrapping, typical pre-seed rounds fall between $100,000 and $1 million, occasionally going up to $5 million. Many experts advise keeping early raises below $500,000 to preserve equity and stay aligned with realistic milestones.
This is where standardized financing documents help:
- Use YC’s SAFE or convertible notes for early-stage fundraising.
- These tools simplify negotiation, reduce legal costs, and make terms easy to understand.
- Consistent deal structures also build investor trust and speed up closing.
4. Accelerators & Incubators
Programs like Y Combinator, Antler, and Techstars typically provide:
- $125K–$250K in funding
- In exchange for about 6%–7% equity
- Plus mentorship, investor access, and structured programs that can compress years of learning into a few months.
5. Government Grants & Schemes
Non-dilutive capital can sit alongside pre-seed equity.
- In India, the Startup India Seed Fund Scheme offers up to ₹2 crore (around $240K) for prototype development and early-stage support.
- Grants are non-dilutive, but application and disbursement timelines can be slow—so plan them as part of a longer runway strategy, not an emergency lifeline.
Series A and Beyond: Scaling with Institutional Capital
Series A rounds are a critical inflection point for consumer startups. Median valuations reached $45.3 million in Q1 2025 (a 36% yearly increase). Now institutional investors expect strong evidence of product-market fit and scalable unit economics.
Institutional VC Requirements:
- Revenue Traction: >$1M ARR with 20%+ month-over-month growth
- Unit Economics: Customer acquisition cost (CAC)—the price spent to obtain a new customer—payback period <12 months.
- Market Size: Total addressable market (TAM) >$1 billion with clear expansion paths
- Team Completeness: C-level hires in place for marketing, operations, and finance
The extended timeline from seed to Series A, now averaging three years, means founders must demonstrate sustained execution over longer periods. This “prove-it” phase requires careful capital management and consistent milestone achievement.
If you’re at the “too early for Series A, too big for angels” stage, exploring all seed funding options for consumer startups becomes a survival strategy.
Series B+ Growth Capital:
Later rounds focus on market expansion, channel diversification, and operational scaling. Growth investors evaluate customer lifetime value (LTV), retention rates, and gross margins, and path to profitability within 18-24 months of the round.
Preparing Compelling Pitch Materials
Consumer startup pitch decks must balance emotional storytelling with rational investment criteria. The most successful presentations demonstrate both brand resonance and business fundamentals.
Essential Deck Components
Slide 1-3: Problem & Solution
- Lead with a relatable consumer pain point
- Quantify the friction cost of existing alternatives
- Position your solution as 10× better, not 10% better
Slide 4-6: Market Opportunity
- Bottom-up market sizing based on customer segments
- Competitive landscape with clear differentiation
- Go-to-market strategy with channel-specific CAC estimates
Slide 7-9: Business Model & Traction
- Revenue model clarity (subscription, transaction, advertising)
- Key metrics dashboard: MAU, retention, lifetime value (LTV), customer acquisition cost (CAC) ratio
- Customer testimonials and usage patterns
Slide 10-12: Team & Financials
- Founder-market fit demonstration
- 3-year financial projections with scenario planning
- Clear use of funds and milestone timeline
Consumer-Specific Considerations
- Brand Story Integration: Unlike B2B pitches, consumer decks should reflect brand personality and customer experience. Visual design matters, investors evaluate whether the presentation demonstrates the aesthetic sensibility needed to build a consumer brand.
- Unit Economics Deep Dive: Consumer investors scrutinize lifetime value (LTV)/customer acquisition cost (CAC) ratios more intensively. Include cohort analysis showing retention curves and customer value evolution over time. Address seasonality, marketing channel performance, and competitive acquisition pressures.
- Technology Differentiation: With AI dominating 50% of venture investment, consumer startups must articulate how they leverage technology for competitive advantage, whether through personalization algorithms, operational efficiency, or customer experience enhancement.
Current Market Challenges
The Q1 2025 funding environment presents unique obstacles that savvy founders can navigate with strategic preparation.
1. Tariff Uncertainty Impact
“Consumer startups, especially those with physical goods or cross-border supply chains, are acutely exposed to tariff-related uncertainty,” notes Rachel Springate, founding general partner at Muse Capital. Founders should proactively address supply chain risks by:
- Supplier Diversification: Map alternative sourcing options across multiple regions
- Pricing Elasticity Models: Build scenarios for 10%-30% cost increases
- Nearshoring Options: Evaluate North American manufacturing alternatives early
2. Extended Funding Timelines
With seed-to-Series A gaps stretching to three years, capital efficiency becomes paramount. Successful founders are:
- Mastering Storytelling: Regular investor updates maintain relationships during extended cycles
- Optimizing Burn Rates: Target 30+ months of runway at seed stage
- Building Revenue Early: Focus on customer-funded growth to extend runway
3. Investor Selectivity Trends
“Investors are being more selective and focusing on unit economics, not just brand,” observes Springate1. The new baseline requirements include:
- Earlier Traction Expectations: MVP quality standards have risen due to AI-enabled development tools
- Profitability Timelines: Investors now ask about profitability paths at pre-seed stage
- Lower Valuation Multiples: Revenue multiples have compressed from 10-12× to 7-7.5
Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
Funding Strategy Mistakes
- Raising Too Early: Without sufficient traction metrics, founders waste precious time and burn credibility with investors. Wait until you have compelling usage or revenue data.
- Misaligned Investor Targeting: Generic outreach to investors who don't back consumer plays wastes everyone's time. Research portfolio fits meticulously.
- Inadequate Runway Planning: Consumer startups require longer development cycles than SaaS. Plan for 24-30 months of runway, not 12-18 months.
Pitch Execution Errors
- Overemphasizing TAM: While market size matters, investors prioritize your specific path to capturing market share. Focus on bottom-up customer acquisition strategies.
- Ignoring Competitive Reality: Claiming “no competition” signals poor market research. Acknowledge competitive threats and articulate clear differentiation.
- Weak Unit Economics: Fuzzy CAC calculations or unrealistic LTV assumptions undermine credibility. Use conservative estimates with clear methodology.
Operational Blind Spots
- Neglecting Regulatory Considerations: Consumer products often face compliance requirements (FDA, FTC, data privacy) that affect timelines and costs.
- Underestimating Supply Chain Complexity: Physical goods require inventory management, quality control, and logistics capabilities that many software founders underestimate.
- Team Gaps: Consumer businesses need marketing, operations, and customer success expertise earlier than pure technology plays.
Emerging Trends Shaping Consumer Investment
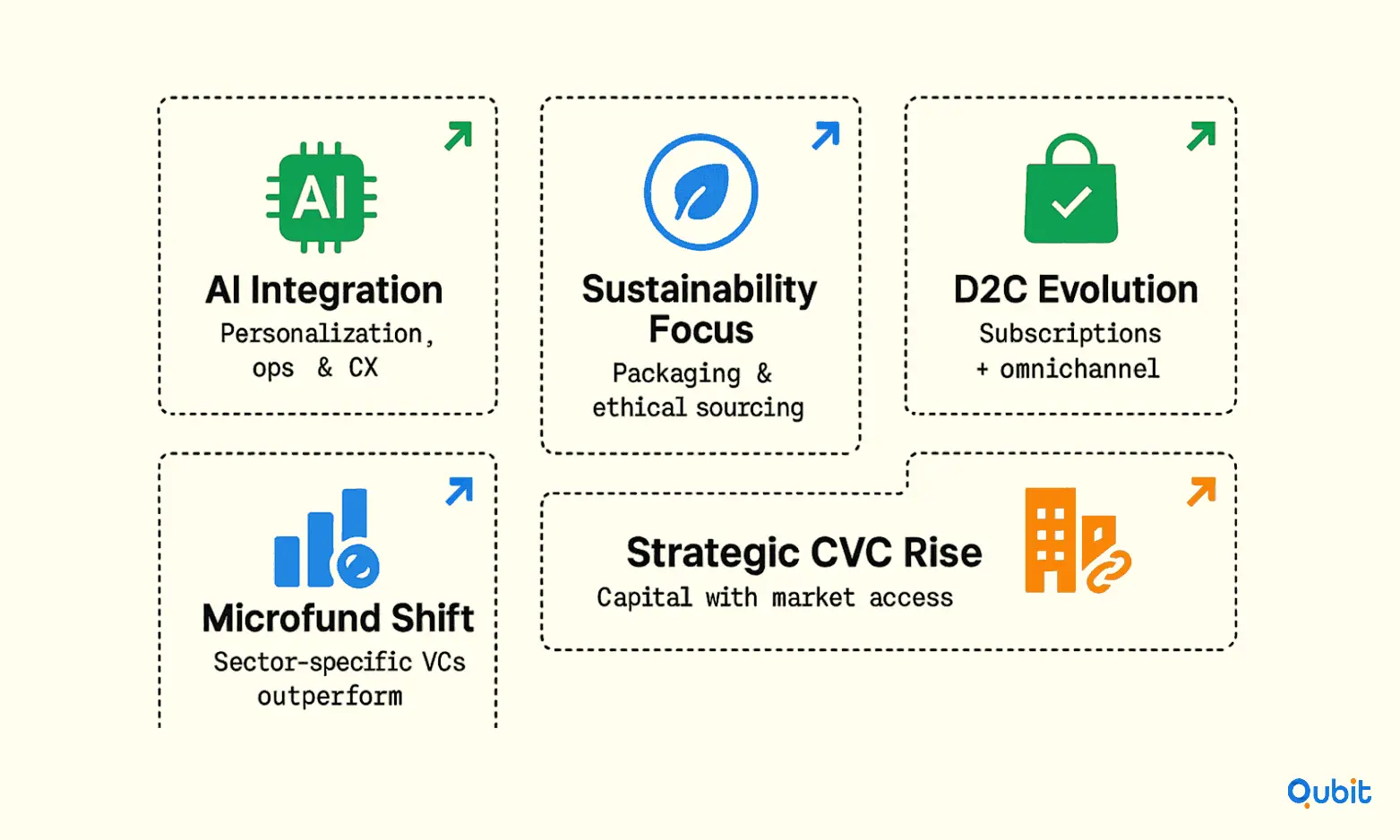
AI Integration Imperative
Consumer startups can no longer ignore artificial intelligence. Successful integration patterns include:
- Personalization Engines: Recommendation systems that improve customer experience and increase LTV
- Operational Automation: AI-powered inventory management, customer service, and marketing optimization
- Predictive Analytics: Forecasting demand, churn risk, and optimal pricing strategies
Sustainability as Competitive Advantage
ESG considerations increasingly influence consumer purchasing decisions and investor evaluation criteria. Startups demonstrating environmental consciousness through:
- Circular Economy Models: Subscription services that reduce waste
- Sustainable Manufacturing: Carbon-neutral production and ethical sourcing
- Social Impact Metrics: Measurable community benefits beyond profit
Direct-to-Consumer Evolution
The D2C model continues evolving beyond simple disintermediation:
- Subscription Transformation: Even traditionally transactional businesses explore recurring revenue models with loyalty programs offering exclusive access and premium experiences at a discount.
- Omnichannel Distribution: Successful brands integrate online and offline touchpoints, with 65% of leading D2C companies now operating physical showrooms or pop-up experiences to build deeper customer relationships.
- Community Building: Brands leverage social media and user-generated content for authentic marketing, with 54% of Gen Z consumers influenced by creator recommendations when making purchasing decisions.
Rise of Sector-Specific Investment
- Microfund Specialization: The venture landscape is shifting toward sector-specific microfunds with deep operational expertise rather than generalist approaches. These focused funds demonstrate superior performance in consumer categories like CPG, beauty, and wellness.
- Corporate Venture Capital Growth: Q1 2025 saw record corporate-backed funding rounds, with strategic investors seeking distribution partnerships and supply chain synergies. Consumer startups benefit from corporate venture arms offering market access alongside capital.
- Creator Economy Integration: Investors increasingly favor startups that demonstrate authentic creator partnerships and social commerce capabilities, recognizing that traditional advertising channels face declining effectiveness.
Supporting this sector focus, pre-seed has become the fastest growing round type, now responsible for over 20% of global venture rounds. This emphasizes both microfund and founder need to navigate early-stage specialization. Adapting to these trends can unlock more targeted investor engagement.
Technology-Driven Consumer Innovation
- AI-First Consumer Products: Beyond operational AI, successful consumer startups embed intelligence directly into product experience, from personalized nutrition apps to smart home ecosystems that learn user preferences.
- Quantum Computing Preparation: Forward-thinking consumer tech companies explore quantum computing applications for complex optimization problems in logistics, personalization, and supply chain management. While early-stage, quantum advantages in machine learning could revolutionize customer experience optimization.
- Sustainability Tech: Environmental consciousness drives innovation in packaging, manufacturing, and distribution. Startups demonstrating measurable environmental impact alongside strong unit economics attract premium valuations from ESG-focused funds.
Conclusion
Early-stage fundraising for consumer startups has entered its “no shortcuts” era. There’s less capital, higher Series A bars, and a much longer road between seed and A, so hope is not a strategy. Founders who win from here will treat capital as a tool, not a trophy: raising the right amount at the right time from the right investors.
That means building real traction, proving sharp unit economics, and showing exactly how every dollar compounds growth, not just buys ads. Layer in AI, sustainability, and community as deliberate moats, not buzzwords, and you move from “another consumer brand” to a fundable outlier. In this market, discipline, clarity, and execution are the new superpowers.
Our Investor Discovery and Mapping service helps you strategically identify mission-aligned VCs and impact funds, craft tailored engagement plans, and confidently secure the capital that truly supports your vision. Connect With us!
Key Takeaways
- Less capital, higher valuations, and longer seed-to-Series A gaps mean a tougher, more selective market.
- Early-stage funding now demands clear traction, realistic round sizes, and disciplined runway planning.
- Investor fit matters: target angels, microfunds, and VCs aligned with your category, model, and stage.
- Capital efficiency and strong unit economics beat “growth at any cost” narratives.
- AI, sustainability, and community are key differentiators—when tied to revenue and retention, not hype.
- Great decks balance emotional brand storytelling with hard metrics, cohorts, and a clear path to profitability.
- Strategic networking, regional events, and creator partnerships now sit at the core of effective fundraising.
Frequently asked Questions
What are the major trends influencing consumer startup funding?
AI integration, sustainability initiatives, and sector-specific investment microfunds are reshaping consumer startup funding. Founders should adapt to these trends to attract the right investors.






