High-growth startups do not win by moving faster. They win by solving a real problem that customers cannot solve well today.
That is harder than it sounds. Nearly one-third of startups will not make it past their third year. This is exactly why guessing is expensive, and why market research matters.
Competitive-gap analysis gives you a repeatable way to find what the market is missing. It helps you spot underserved customers, weak alternatives, and hidden friction that competitors ignore.
Ahead, you will learn how to run a competitive-gap analysis step by step, then turn those insights into sharper positioning and stronger product bets.
Understanding and Identifying Unmet Needs
An unmet need is a customer problem that existing products do not solve well enough. Sometimes it is obvious, like direct complaints or visible churn. Other times it is hidden. Customers may accept the pain as “normal” until someone proves a better way exists.
A useful way to think about it is this: the current solution might meet the basic need, but it fails on the outcomes customers actually care about, like speed, ease, trust, cost, or convenience.
Example
Before ride-sharing apps, the need was not just transportation. It was convenient, reliable, cashless rides that you could access through a smartphone. Traditional taxis handled the core job, but broke down on convenience, payment, and reliability.
Why Identifying Unmet Needs Is Crucial For Startups
Unmet needs are where startups get leverage. When you solve a problem better than the status quo, growth becomes easier because the product sells itself through clear value.
This is also the foundation of product-market fit. If you are not solving a real, urgent gap, everything else becomes harder: acquisition costs rise, retention drops, and differentiation turns into marketing copy.
When you identify a true unmet need, you can:
- Avoid crowded markets where customers have too many similar options
- Build clear differentiation, which reduces price-based competition
- Increase loyalty by delivering value customers cannot easily replace
- Open new segments or even create a new category
If you want to connect this to broader evaluation, startup scouting strategies can help link market research signals with investment-grade analysis.
Examples of Unmet Needs in Various Industries
- Healthcare: Digital health platforms, such as telemedicine, address barriers of access and convenience unmet by traditional clinics.
- Education: Online learning platforms serve students needing flexible, self-paced education inaccessible through brick-and-mortar institutions.
- Financial Services: Robo-advisors meet the demand for affordable, automated investment advice once restricted to high-net-worth clients.
- Retail: Subscription models and curated shopping services fulfill consumers’ desire for personalized and time-saving experiences.
Competitive-Gap Analysis Explained
Competitive-gap analysis is a structured way to compare your startup against existing options in the market. The goal is not to prove you are “better” in general. The goal is to find specific gaps where customers are underserved, then build a product and position that closes those gaps.
Direct vs. Indirect Competitors in Gap Analysis
This approach requires founders to examine both direct and indirect competitors. Direct competitors offer similar products or services, while indirect competitors address the same customer needs through different solutions. Including both types in your analysis prevents blind spots and reveals alternative threats or opportunities. Overlooking indirect competitors can result in missed innovation trends or disruptive market shifts.
What To Compare In A Competitive-Gap Review
Look beyond surface-level features. A useful analysis checks multiple dimensions, such as:
- Product features and usability
- Pricing and value proposition
- Customer service and onboarding
- Branding and market reach
- Operational efficiency and innovation
This keeps you from falling into the trap of “feature checklist wars” while missing the real reasons customers choose one solution over another.
How Gap Analysis Uncovers Market And Product Opportunities
When you map competitor weaknesses, you usually uncover patterns in customer frustration. Those pain points are where startups can win through:
- Better user experience
- Faster time to value
- Simpler workflows
- Lower total cost or higher perceived value
Example
If competitors have a steep learning curve, a startup can differentiate by being easier to adopt, faster to set up, and clearer to use.
For a deeper dive into how AI solutions enhance deal sourcing, explore our insights on data platforms for startup scouting.
Difference Between Market Gap and Competitive Gap
- Market Gap: Refers to an entire customer need or segment that the current market is ignoring or not addressing at all. This may represent large, untapped pools of customers.
- Competitive Gap: Involves shortcomings in existing offerings within a known market. Competitors may serve the market but imperfectly, leaving room for startups to outperform in specific aspects.
Understanding both types is crucial. Startups that address market gaps pioneer new categories, while those focusing on competitive gaps aim to outcompete incumbents by fixing their weaknesses.
Step-by-Step Guide to Conducting Competitive-Gap Analysis
Here is a practical process to spot what competitors miss, validate real customer pain, and turn the highest-value gaps into an execution plan.
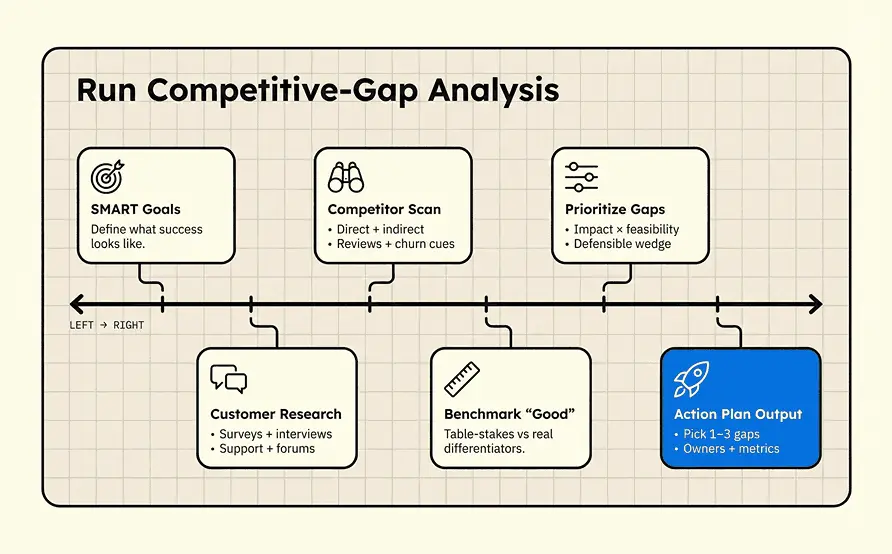
Step 1: Setting SMART Goals
Start your competitive-gap analysis by setting SMART goals that guide the entire process.
- Set SMART Goals
- Conduct Market & Customer Research
- Analyze Competitors
- Benchmark Against Industry
- Prioritize & Create Action Plan
Step 1a: Setting Competitive Criteria
Define objectives that are Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound (SMART).
For example:
- Identify three major feature gaps in top competitors’ software. Complete this within 90 days.
- Discover at least two new customer segments underserved by the current market by year-end.
Setting targets provides focus and helps measure success.
Step 2: Market and Customer Research
Now collect data on what customers want, where they struggle, and how they choose alternatives. Use multiple sources to avoid bias.
- Surveys: Quantitative data on satisfaction, preferences, and pain points.
- Interviews: Qualitative insights from direct conversations, uncovering attitudes and unmet desires.
- Focus Groups: Group dynamics can reveal consensus or divergent opinions on unmet needs.
- Analysis of Customer Support Data: Patterns in complaints often highlight shortcomings.
- Social Media & Forums: Unfiltered customer discussions where frustrations and wishes are voiced.
Recent trends demonstrate widespread adoption of advanced research practices. A survey reported 88% of investors increased their use of ESG information in the past year. Prioritizing robust data collection enables startups to align with stakeholder expectations.
A multifaceted approach minimizes blind spots and ensures robust understanding.
Step 3: Competitor Analysis
Review both direct and indirect competitors to avoid missing substitutes or new approaches that solve the same underlying need.
- Catalogue features and benefits offered.
- Analyze pricing models, promotional activities, and sales channels.
- Study customer reviews, testimonials, and churn reasons.
- Evaluate brand perception and customer loyalty.
Indirect competitors might include substitutes or emerging innovations that fulfill the same fundamental needs differently.
Step 4: Benchmark Against Industry Standards
Use third-party reports, standards, and case studies to understand what “good” looks like in your category. Benchmarking helps you:
- Avoid overbuilding for minor gains
- Set realistic targets
- Identify table-stakes features versus true differentiators
Step 5: Prioritize and Create an Action Plan
Not every gap is worth solving. Prioritize based on business impact and execution reality.
A practical prioritization checklist:
- Size of the affected market segment
- Revenue or strategic impact if solved
- Time and cost to build
- Risk and feasibility
- Ability to differentiate, not just catch up
Then turn priorities into a roadmap:
- A plan to test demand before full build where possible
- 1 to 3 high-impact gaps to address first
- Clear owners, timelines, and success metrics
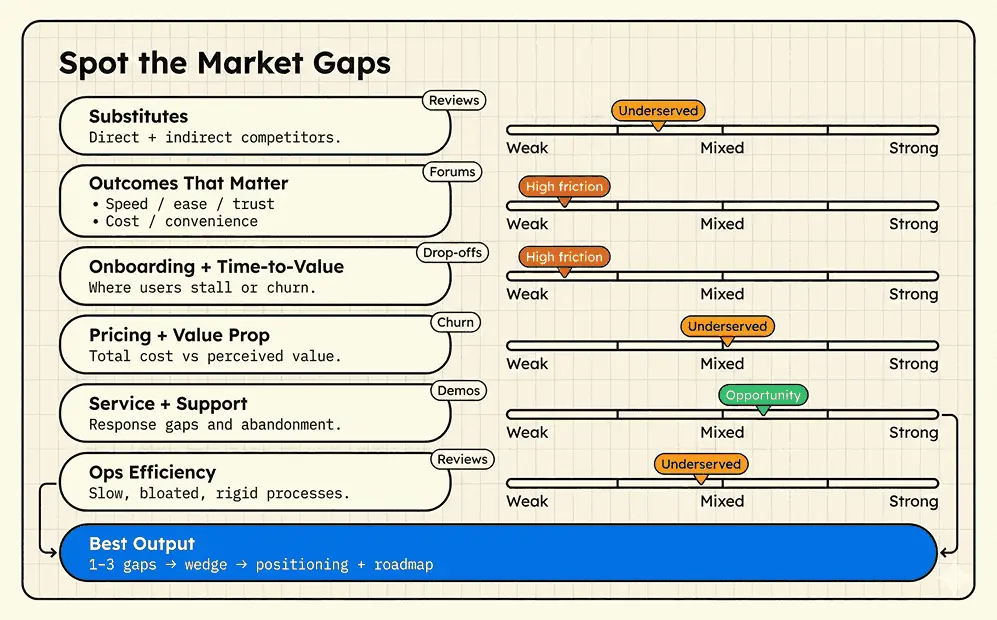
Tools and Techniques for Competitive-Gap Analysis
Use these methods to uncover where competitors fall short, validate what customers actually need, and pinpoint the best angles for differentiation.
1. SWOT Analysis
Use SWOT to map strengths and weaknesses inside your startup, and opportunities and threats in the market. It helps you see whether a gap is worth pursuing, or if it will be blocked by a major constraint like distribution, regulation, or switching costs. The output should be a short list of the top 3 plays to lean into and the top 3 risks to manage.
2. Customer Journey Mapping
Map the end-to-end customer experience from discovery to onboarding to daily use and renewal. This makes it easier to spot friction points where customers hesitate, get confused, or drop off, which often signals the real gap. The output should be 3 to 5 moments of friction and a clear “fix or replace” recommendation for each.
3. Using Competitive Positioning Maps
Building on customer journey mapping, competitive positioning maps help visualize where your offering stands relative to others. These maps plot competitors along key dimensions, such as price versus features or customer satisfaction versus market presence. This visualization quickly reveals crowded spaces, underserved segments, and potential areas for differentiation. Positioning maps support clearer communication of your unique value to stakeholders.
4. Surveys, Focus Groups, Ethnographic Research
Combining these research methods yields rich data:
- Quantitative validation of known issues.
- Qualitative discovery of latent needs.
- Real-world observation of behavior that people may be unaware of or reluctant to report.
5. Data Analytics and Market Reports
Use product analytics to find gaps customers may never articulate, like drop-offs, low adoption, repeated support themes, churn reasons, and slow time-to-value. Then layer market reports and competitor tracking to understand where rivals are investing and what the category expects next. The magnitude of modern analytics cannot be understated.
Global AI investment is forecasted to reach €1.9 trillion by 2030. Such figures underscore the importance of leveraging advanced tools to compete effectively. The output should be a short set of data-backed hypotheses you can test in product and positioning.
How Startups Can Use Competitive-Gap Analysis to Find Opportunities
A practical view of the most common opportunity types this analysis reveals, and how to turn them into product and fundraising advantages.
1. Discovering Untapped Customer Segments
Competitive-gap analysis helps you spot customer groups that competitors ignore or serve poorly. Start by mapping who current products are built for, then look for people with the same core need but different constraints, budgets, workflows, or compliance requirements. These segments often show up in niche forums, support tickets, “workaround” behavior, and low-satisfaction review patterns.
The opportunity for new market entrants is significant. 1,123 blended finance transactions, totaling $213 billion, have been recorded to date. Investors are actively pursuing untapped segments through innovative deal structures. Startups that identify unique niches can position themselves for substantial funding.
2. Identifying Product/Service Feature Gaps
Feature gaps are easiest to find, but the goal is not to copy competitors. The goal is to identify which missing or weak capabilities block adoption or retention. Look for repeated requests in reviews, sales calls, and support data, then map them to the customer journey stage where they matter most.
The strongest gaps are tied to outcomes, not “nice-to-have” features, such as saving time, reducing errors, improving compliance, or improving collaboration. Addressing unmet needs through user feedback can lead to rapid adoption and increased customer satisfaction.
3. Spotting Customer Experience and Service Deficiencies
Many markets are “good enough” on product, but weak on experience. Competitive-gap analysis surfaces where users feel friction, confusion, or abandonment, especially in onboarding, support response times, setup complexity, and usability. These are high-leverage gaps because better experience often increases activation and retention without requiring a huge feature roadmap.
Track where customers drop off, what they complain about repeatedly, and which steps feel manual or stressful. Poor onboarding, slow customer support, or inconvenient interfaces are common pain points ripe for disruption.
4. Operational Efficiencies and Scalability Gaps
Some startups win by delivering the same value more efficiently. Competitive-gap analysis can reveal where incumbents are slow, expensive, or operationally bloated, creating room for a leaner model. Look for long turnaround times, high service overhead, rigid processes, or pricing that does not match the value delivered.
If you can reduce cost, time, or complexity while maintaining quality, you can win on unit economics and scale earlier. Startups can also succeed by delivering similar products but more efficiently or scaling more effectively, reducing costs or turnaround times for customers.
5. Presenting Competitive-Gap Insights to Investors
Gap insights become powerful when you translate them into a clean investment narrative. Show the gap, prove it exists, show your wedge, then show why you can defend it. Use simple visuals like matrices, positioning charts, and customer-journey snapshots, supported by data and direct customer evidence.
Highlight what you will win on, why competitors cannot easily copy it, and what milestones validate the strategy. Integrate these insights across multiple slides with concise commentary so investors can quickly see strategic awareness, market understanding, and a credible path to differentiation.
Case Studies of Startups Finding Unmet Needs via Competitive-Gap Analysis
Slack identified unmet needs in workplace communication and addressed them with an innovative platform.
1. Slack: Solving Workplace Communication Gaps
Before Slack launched in 2013, workplace communication relied heavily on email chains that buried important threads, lacked searchability, and failed to support real-time collaboration or tool integrations. Teams juggled multiple apps like email, chat clients, and project tools, leading to fragmented workflows and lost productivity.
Slack conducted deep competitive analysis of tools like IRC, Campfire, and early Microsoft offerings, identifying the core gap: no platform combined threaded conversations, channel-based organization, rich integrations (over 2,000 apps at launch), and mobile-first accessibility in one intuitive interface.
By prioritizing these unmet needs, Slack achieved product-market fit rapidly, growing from zero to 15,000 daily active users in months and hitting 500,000 by 2015 without traditional sales teams. This gap-focused approach not only disrupted email dominance but also attracted enterprise adoption, culminating in a 27.7 billion USD acquisition by Salesforce in 2021.
2. HubSpot: Integrating Marketing and Sales Tools
In the mid-2000s, marketing and sales teams operated with siloed software—Marketo for leads, Salesforce for CRM, Google Analytics for tracking—creating data silos, manual handoffs, and up to 30% lead leakage from poor alignment. HubSpot's founders analyzed this ecosystem and pinpointed the unmet need for an all-in-one inbound platform that unified content marketing, SEO, email automation, CRM, and sales enablement without requiring technical expertise or high costs.
Launched in 2006, HubSpot filled this gap by offering free CRM tools as a gateway, scaling to paid tiers with seamless integration, which resonated with SMBs underserved by enterprise-heavy competitors. The result: over 100,000 customers by 2020, public listing in 2014, and annual recurring revenue exceeding 2 billion USD today, validating how gap analysis in cross-functional tools drives sticky adoption.
3. Zoom: Improving Video Conferencing Usability
Pre-2011, video tools like WebEx, GoToMeeting, and Skype for Business suffered from clunky interfaces, download requirements, long join times (often 60+ seconds), poor mobile support, and frequent crashes under load. Zoom's analysis revealed the competitive gap in "frictionless" conferencing: users needed one-click joins, HD quality at scale, gallery views for 49+ participants, and reliability for 1,000-user meetings without enterprise pricing premiums.
By engineering for these pain points, using adaptive bitrate streaming and browser-based access, Zoom launched with superior UX, enabling viral growth from 0 to 10 million daily participants pre-pandemic. This led to 300 million daily meeting users by 2020, a market cap peak over 180 billion USD, and dominance in both consumer and enterprise segments, showing how usability gaps in legacy tech create massive openings for agile challengers.
Challenges and Common Pitfalls in Competitive-Gap Analysis
A quick checklist of what commonly breaks competitive-gap work, and how to avoid it.
- Data reliability and bias: Limited, outdated, or unvalidated data can push you toward the wrong conclusions. Use multiple sources, cross-check findings, and separate facts from opinions.
- Overlooking indirect competitors: The real threat is often not a lookalike product. It can be a new technology, a different workflow, or a behavior shift that replaces the need entirely. Scan broadly and revisit the landscape regularly.
- Misinterpreting customer needs: What customers say is not always what they mean. Pair interviews with behavior data, observation, and quick prototypes to confirm what actually drives decisions.
- Failing to act: A gap only matters if you execute on it. Assign owners, set timelines, fund the work, and ship in small iterations so insights turn into real advantages.
Continuous Improvement and Monitoring
Competitive-gap analysis is not a one-time activity. The market evolves continuously, so your startup must iterate, refine, and monitor progress actively.
Regularly update your analysis:
- Schedule quarterly or semi-annual reviews.
- Use customer feedback and KPIs aligned with your gap-closing initiatives.
- Stay attuned to emerging trends and technological shifts.
Iteration maintains competitive relevance and sustains growth momentum.
Conclusion
Competitive-gap analysis provides startups with a strategic roadmap for uncovering unmet needs and achieving differentiation. Ultimately, the startups that thrive are those that not only identify what isn’t working in existing solutions but also move quickly and creatively to close those gaps, delighting customers, building loyalty, and establishing new market standards.
With rigorous, repeated competitive-gap analysis at the core of your strategy, your venture stands the greatest chance of solving meaningful problems and fulfilling untapped market potential. Take your competitive-gap analysis and start building your product roadmap today.
Our Investor Discovery and Mapping service is designed to empower startups with tailored insights that enhance outreach performance. Explore how we can help you uncover opportunities and build meaningful connections.
Key Takeaways
- Competitive-gap analysis helps startups identify where current market solutions fall short, revealing opportunities to meet unmet customer needs.
- Understanding unmet needs is critical to creating differentiated products that solve real problems and resonate with customers.
- The analysis compares products, services, and experiences across competitors to find feature gaps, operational inefficiencies, or underserved customer segments.
- Setting SMART goals, thorough market research, competitor analysis, and benchmarking are foundational steps in the process.
- Combining qualitative research (interviews, focus groups) with quantitative data (surveys, analytics) strengthens insights.
- Startups use the findings to prioritize high-impact opportunities, improve user experience, and build innovative solutions that address real pain points.
Frequently asked Questions
What is competitive-gap analysis?
Competitive-gap analysis compares a startup’s offerings to competitors to find unmet customer needs.