Secondary sales can turn paper gains into real returns before an exit, but they are not a free win. The moment you sell early, you trade future upside for liquidity today, and you also signal something to the market, whether you mean to or not.
For early investors, secondaries usually show up when a company is raising a larger round, extending runway, or making room on the cap table for new institutions. Done well, a secondary sale helps you manage concentration risk, return capital to LPs, or rebalance your portfolio without hurting the company.
This guide is written for early-stage investors seeking strategies for secondary sales and enhanced portfolio liquidity. In the section below we will see when a secondary sale makes sense, how to evaluate pricing and timing, and how to sell responsibly while protecting your relationship with founders and future investors.
What is Secondary Sales in Private and Public Markets?
Secondary sales have become a cornerstone of modern financial ecosystems, offering critical liquidity solutions for early investors and stakeholders. Historical data highlights the market's growth trajectory. In 2022, secondary market volume reached $103 billion, rising to $114 billion in 2023 and $160 billion in 2024. This acceleration underlines investors' growing reliance on secondary transactions. Such context frames today's liquidity landscape.
Legal Controls in Secondary Sales
These transactions require careful navigation of company-imposed legal controls such as rights of first refusal and board approvals. Rights of first refusal allow the company or existing shareholders to match any third-party offer before a sale proceeds. Board approvals ensure that share transfers align with company interests and governance policies. Together, these mechanisms help maintain ownership stability and protect strategic interests during secondary sales.
These markets allow investors to buy and sell pre-existing assets. This enables portfolio diversification and reduces investment risks.
What began as niche mechanisms has evolved into sophisticated platforms that now play a pivotal role in global finance. Recent data reveals exceptional deal momentum. In Q1 2025, secondary deal execution totaled $45 billion, a 45% year-over-year gain. Significantly, $25 billion was GP-led, underscoring general partners' active role in market dynamics for institutional investors.
This remarkable growth underscores the increasing demand for liquidity solutions, as investors seek to optimize their portfolios and access capital more efficiently.
The secondary market's expansion is not just about numbers; it represents a shift in how investors approach long-term commitments. With the ability to trade assets more freely, stakeholders can better manage their financial strategies, ensuring flexibility without compromising returns.
This evolution highlights the growing importance of secondary market liquidity in addressing the dynamic needs of modern investors. As these platforms continue to mature, they are set to redefine how capital flows within the investment landscape.
Private Market Secondary Transactions
Private market secondary transactions, a form of secondary sales, offer a unique avenue for unlocking liquidity in an otherwise illiquid environment.
Types of Secondary Transactions
Secondary transactions in private markets typically fall into two categories: LP-led and GP-led deals.
LP-Led Transactions: LP-led transactions, which are deals initiated by Limited Partners seeking liquidity, often involve selling stakes in private funds.
GP-Led Transactions: GP-led transactions refer to deals initiated by General Partners, typically using continuation vehicles to extend asset life.
Valuation Challenges
Determining the value of private secondary transactions can be complex. Unlike public markets, private assets lack transparent pricing mechanisms, making it difficult to assess fair value. Investors often rely on metrics such as Net Asset Value (NAV) to gauge performance. However, discrepancies between NAV and trading percentages can arise due to market sentiment, asset quality, or liquidity constraints.
For instance, high-quality LP portfolios traded at an average of 89% of NAV in 2024, reflecting strong valuation dynamics. This figure underscores the importance of understanding market trends and asset quality when engaging in secondary transactions.
A landmark GP-led restructuring highlights practical execution. In 2018, Coller Capital and Goldman Sachs facilitated a €2.5 billion overhaul of Nordic Capital's 2008 vintage fund. This large-scale transaction involved restructuring legacy assets to extend investment horizons and optimize outcomes for both LPs and GPs, exemplifying the complexities and potential of modern secondary deals.
Performance Indicators
Performance in private secondary markets is often measured by trading percentages relative to NAV. These percentages provide insights into market sentiment and the perceived value of underlying assets. By examining these metrics, investors can make informed decisions about whether to buy or sell shares in private companies, ensuring alignment with their financial goals.
Private market secondary transactions continue to evolve, offering investors innovative ways to access liquidity and diversify their portfolios. Understanding transaction types, valuation challenges, and performance indicators is crucial for navigating this dynamic space effectively.
Despite deal activity, fundraising for commingled vehicles remains challenging, with a 24% decline year-over-year, marking the third straight year of slipping capital inflows. This trend complicates new private market strategies.
Public Market Secondary Transactions
Public market secondary transactions offer a unique blend of liquidity and transparency, making them a cornerstone of modern investing. Unlike private market transactions, which often involve lengthy negotiations and opaque pricing, public markets provide immediate liquidity through well-established exchanges. This accessibility ensures that investors can buy or sell shares quickly, with prices determined by clear and transparent mechanisms.
One of the defining characteristics of public secondary transactions is their reliance on transparent price discovery. Stock prices are influenced by real-time market dynamics, including supply and demand, economic indicators, and company performance. This clarity allows investors to make informed decisions based on readily available data, reducing the uncertainty often associated with private market deals.
However, significant insider sales in public markets can introduce complexities. When insiders, such as executives or major shareholders, sell large quantities of stock, it can signal potential concerns to the market. These transactions may lead to price fluctuations, as other investors interpret the sales as a lack of confidence in the company’s future performance. Careful analysis of the context surrounding insider sales is essential to avoid misjudging their implications.
For investors, understanding the mechanics of public market secondary transactions is crucial. The combination of liquidity and transparent pricing offers distinct advantages, but it also requires vigilance in interpreting market signals. By staying informed, investors can better navigate the opportunities and challenges presented by public channels.
Comparative Analysis: Private vs. Public Secondary Transactions
Private and public secondary sales each offer distinct advantages and challenges, making them suitable for different investment strategies. Private markets often attract investors with their potential for discounted valuations. However, this comes at the cost of limited liquidity, which can make exiting investments more complex and time-consuming.
On the other hand, public markets excel in transparency and ease of trading. With clear price discovery mechanisms and high liquidity, public secondary transactions allow investors to buy and sell assets with minimal friction. Yet, the trade-off lies in the comparatively lower upside potential, as public market valuations tend to be more efficient and less prone to significant discounts.
For investors, the choice between private and public secondary transactions often boils down to their risk tolerance, investment horizon, and liquidity needs. Those seeking higher returns and willing to accept longer holding periods may lean toward private markets. Conversely, investors prioritizing flexibility and transparency might find public markets more appealing.
Understanding these trade-offs is crucial for aligning investment decisions with financial goals. Whether you’re exploring discounted opportunities in private markets or the seamless trading experience of public markets, each path offers unique opportunities for growth.
Secondary Investment Strategies and Portfolio Management
Integrating secondary sales and investments into portfolio management can transform how investors approach risk and liquidity. These transactions, which involve purchasing existing equity from shareholders, offer strategic advantages that address common challenges in traditional investment cycles.
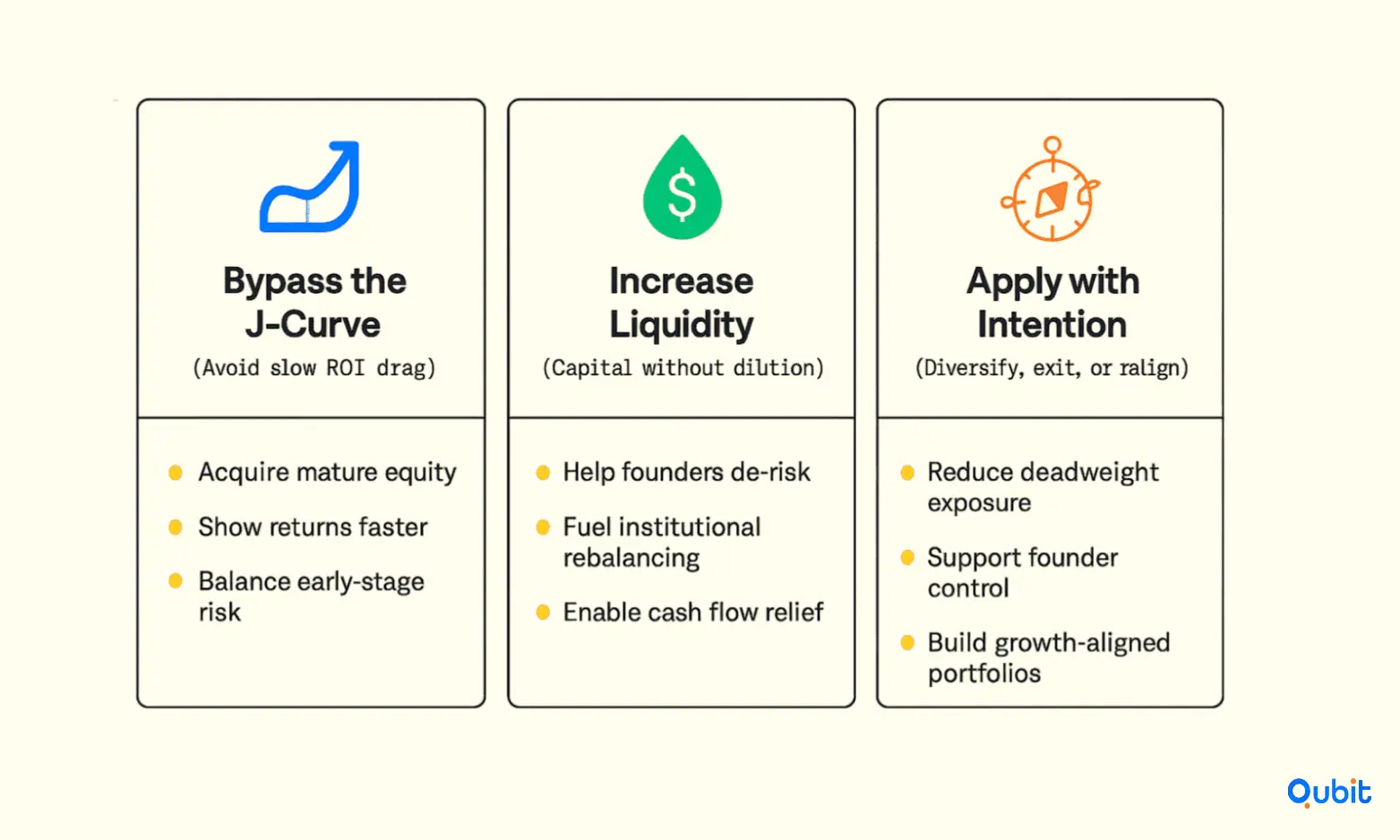
1. Mitigating the J-Curve Effect
Secondary investments are particularly effective in countering the J-Curve effect, a phenomenon where early-stage investments often experience negative returns before generating profits. By acquiring mature assets, investors can bypass the initial slow-growth phase, accelerating portfolio returns. This strategy is especially beneficial for institutional investors seeking to optimize performance metrics while maintaining a balanced risk profile.
2. Enhancing Liquidity
Liquidity is a critical concern for both founders and investors. Secondary transactions provide an avenue for founders to access immediate capital without diluting their ownership stakes. For institutional investors, these deals offer flexibility to rebalance portfolios, freeing up funds for new opportunities or addressing urgent cash flow needs.
3. Strategic Applications
For founders, secondary investments can serve as a tool to secure funding while retaining control over their ventures. Institutional investors, on the other hand, can use these transactions to diversify holdings, reduce exposure to underperforming assets, and align portfolios with long-term growth objectives. Insights on secondary sales are bolstered by exploring startup-portfolio-management, which illustrates approaches for growing your investment holdings while moderating risks.
Secondary investments are more than just a liquidity solution—they are a strategic tool for accelerating returns and optimizing portfolio performance. By understanding their applications, investors can unlock opportunities for both immediate gains and sustainable growth.
- Conduct due diligence
- Confirm valuation
- Complete legal transfer
- Use secure settlement
For example: An early investor used secondary sales to rebalance their startup portfolio when a primary fundraising round was delayed.
Coordinating Founder Secondary Sales with Equity Rounds
This approach involves aligning founder secondary sales with new priced equity rounds to streamline approvals and negotiations. By coordinating these events, companies can ensure that founder liquidity aligns with investor interests and current valuation benchmarks. This timing also helps maintain deal momentum and reinforces trust among all parties involved. It is a strategic way to balance personal liquidity with the company’s long-term goals.
Transaction Process and Operational Framework
Executing secondary transactions requires a structured approach to ensure accuracy, compliance, and efficiency. The process begins with rigorous due diligence, where the buyer and seller verify the authenticity of the asset, its ownership, and any associated risks. This step is crucial for identifying potential red flags and ensuring the transaction aligns with regulatory requirements.
Once due diligence is complete, the legal transfer procedures come into play. This involves drafting and signing agreements that formalize the transfer of ownership. These documents must be meticulously reviewed to avoid any ambiguities or disputes later.
Next, valuation confirmation ensures that the asset's price reflects its true market value. Independent appraisals or expert opinions are often sought to validate the agreed-upon price, providing transparency and fairness to both parties.
Finally, the transaction concludes with the settlement process, where funds are transferred, and ownership is officially recorded. This step often involves escrow services to safeguard the interests of both buyer and seller until all conditions are met.
Specialized brokers or platforms play a pivotal role throughout this process. They not only streamline operations but also ensure compliance with complex regulatory frameworks. For a deeper understanding of how secondary sales align with broader exit strategies, consider exploring the insights shared in startup-exit-strategies.
Best Practices for Secondary Sale Policies
- Draft comprehensive secondary sale policies that specify eligibility, approval steps, and any restrictions for all stakeholders involved.
- Communicate these policies clearly to employees and shareholders to set expectations and minimize misunderstandings before transactions occur.
- Review and update policies regularly to reflect changes in company structure, regulations, or market conditions impacting secondary sales.
Market Trends, Efficiency, and Regulatory Framework
For full-year perspective, secondary market volume hit $165 billion in 2024, marking a 40% rise over the prior year. This milestone solidifies 2024 as a peak performance period. This sustained upward trajectory highlights increasing investor confidence and the sector's strategic importance. As markets mature, more participants are drawn to the opportunities offered by secondary transactions, further fueling this expansion.
Recent deal activity reinforces this trajectory. During Q1 2025, private equity exit value reached $175.59 billion, nearly tripling the $65.4 billion recorded in Q1 2024. This surge represents the strongest quarter since Q2 2022 and highlights sustained investor engagement.
Technological advancements are playing a pivotal role in transforming the efficiency of these transactions. Automated platforms and enhanced data analytics are streamlining trade processes, reducing manual intervention, and improving overall accuracy. These innovations not only accelerate transaction speeds but also bolster compliance with regulatory standards, ensuring smoother operations for all stakeholders.
The combination of sustained market growth, technological efficiency gains, and regulatory transparency is reshaping the secondary transactions landscape. As these elements converge, they create a more robust and inclusive market environment, paving the way for continued expansion.
Additionally, integrating secondary investments with ESG considerations can enhance both financial outcomes and societal impact. Your exploration of early investment dynamics is deepened by the concepts presented in esg-startup-investments, highlighting ways that ESG considerations integrate with financial outcomes.
Conclusion
Effective management of secondary sales in both private and public markets requires a blend of strategic planning and operational precision. Prioritizing regulatory compliance ensures transactions are conducted transparently and within legal frameworks, while robust operational frameworks minimize risks and enhance efficiency. Strategic portfolio management further strengthens decision-making, enabling investors to optimize returns and mitigate potential challenges.
For those seeking to streamline their secondary transactions, professional guidance can make all the difference. At Qubit Capital, we specialize in connecting investors with tailored opportunities. Contact us to explore how our Investor Outreach service can support your goals and drive optimal outcomes.
Key takeaways
- Secondary markets are crucial for unlocking liquidity for early investors.
- There are distinct differences between private and public secondary transactions.
- Regulatory compliance, especially with SEC Rule 144, is essential for successful transactions.
- Strategic portfolio management can mitigate risks and optimize returns in secondary sales.
- Leveraging specialized platforms and advisory services, like those from Qubit Capital, can streamline the process.
Frequently asked Questions
How can early investors unlock liquidity through secondary sales?
Early investors can unlock liquidity by selling shares in secondary markets, accessing funds without waiting for IPOs or acquisitions.






