Choosing the right legal structure is a pivotal step in shaping the success of any business deal. Whether you're launching a startup or securing funding, the legal framework you establish will influence everything from compliance to investor confidence. A well-documented structure not only protects your interests but also sets the stage for smoother negotiations.
For those unfamiliar with the finer details of deal terms, you may refer to term sheet basics, where foundational components of deal terms are explored in relation to the legal frameworks governing transactions. This article will delve into the significance of legal structures, the role of documentation, and how these elements create a solid foundation for business success. Let’s jump right in.
Comparing Business Structures for Effective Legal Foundations
Choosing the right business structure is a critical decision that impacts everything from liability protection to operational simplicity. This section explores common business structures, sole proprietorships, partnerships, corporations, and LLCs, offering a comparative analysis to help businesses weigh simplicity, cost, liability, and strategic trade-offs.
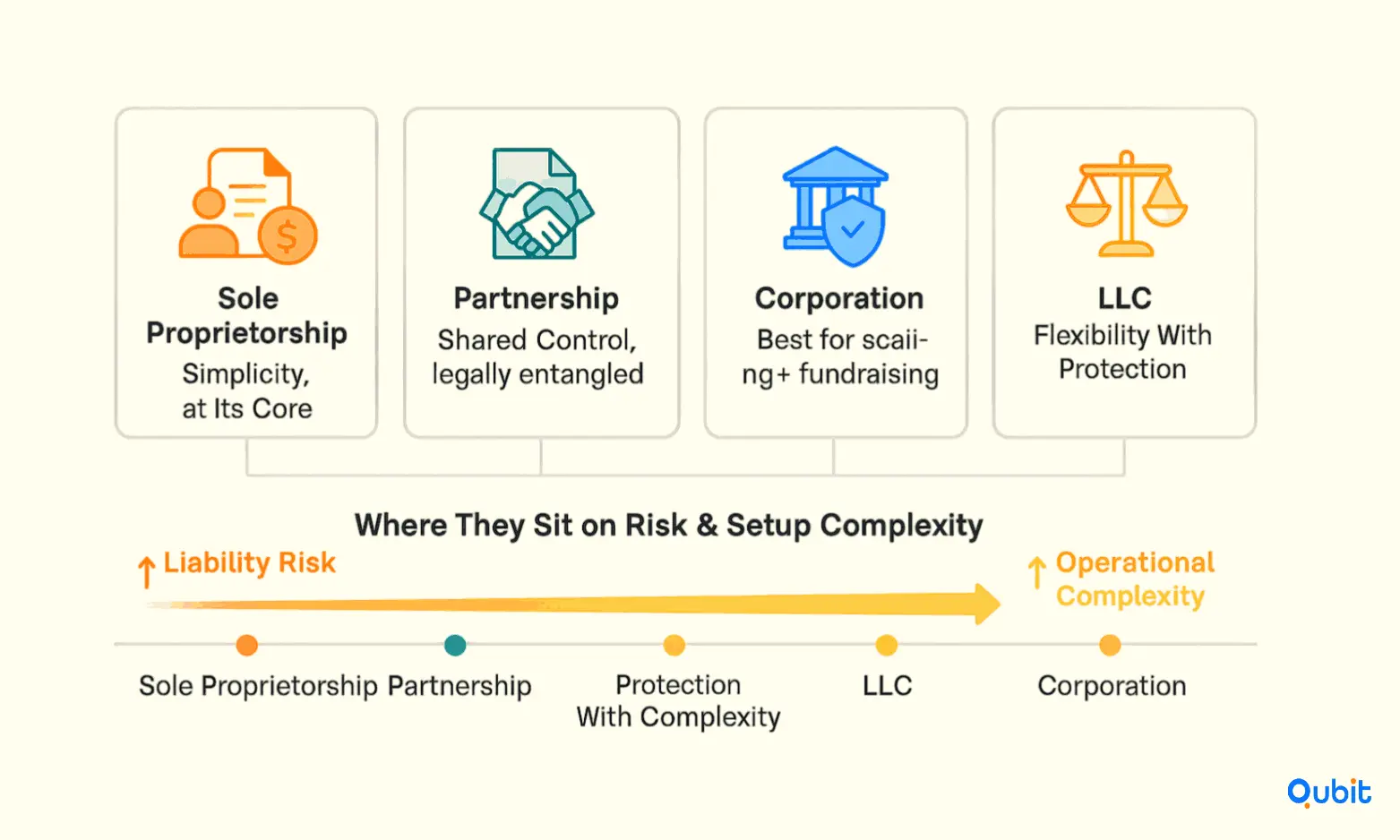
Sole Proprietorship: Simplicity at Its Core
A sole proprietorship is the simplest and most cost-effective business structure. It requires minimal paperwork and allows the owner to retain full control. However, this simplicity comes with a significant drawback: unlimited personal liability. If the business incurs debts or faces legal action, the owner's personal assets are at risk.
Partnerships: Shared Responsibility
Partnerships offer a collaborative approach to business ownership. General partnerships divide responsibilities and profits among partners, while limited partnerships allow some partners to limit their liability. While partnerships can foster innovation and shared expertise, they also expose partners to shared liabilities, which can complicate financial and legal matters.
Corporations: Robust Liability Protection
Corporations provide the highest level of liability protection, separating personal assets from business obligations. They are ideal for businesses seeking to scale or attract investors. However, corporations are more complex to establish and maintain, requiring compliance with strict regulations and incurring higher costs.
Limited Liability Companies (LLCs): A Balanced Approach
LLCs combine the liability protection of corporations with the operational flexibility of sole proprietorships and partnerships. They are particularly appealing for small to medium-sized businesses due to their tax advantages and straightforward management structure. While LLCs offer a balanced approach, they may involve higher initial setup costs compared to sole proprietorships.
Key Trade-Offs to Consider
When evaluating business structures, consider the following trade-offs:
- Simplicity vs. Liability Protection: Sole proprietorships and partnerships are easier to set up but offer less protection. Corporations and LLCs provide robust liability safeguards but require more effort to establish.
- Cost vs. Strategic Growth: Sole proprietorships and partnerships are cost-effective but may limit growth opportunities. Corporations and LLCs, while more expensive, offer scalability and investor appeal.
Understanding these distinctions is essential for building a legal foundation that aligns with your business goals.
Determining Who Should Incorporate and Who Should Not: Strategic Legal Decisions
Choosing whether to incorporate is a pivotal decision for any business. Incorporation offers distinct advantages, but it may not be the right path for every entrepreneur. By weighing the benefits and drawbacks, businesses can determine if this legal structure aligns with their goals for liability protection, growth, and funding.
Benefits of Incorporation
Incorporation provides a shield against personal liability, ensuring that business debts and legal claims do not impact the owner's personal assets. This is particularly valuable for businesses operating in industries with higher risks. Additionally, corporations often enjoy easier access to funding, as investors typically prefer the structured governance and transparency that comes with a corporate form.
Another advantage is the ability to scale. Corporations can issue shares, attract investors, and expand operations more seamlessly than sole proprietorships or partnerships. Tax benefits may also apply, as corporations can deduct expenses like health insurance and retirement contributions.
Drawbacks to Consider
Despite its advantages, incorporation is not without challenges. The process involves upfront costs and ongoing administrative requirements, such as filing annual reports and maintaining compliance with corporate laws. For small businesses or sole proprietors, these obligations may outweigh the benefits.
Taxation is another factor to consider. Corporations may face double taxation—once on profits and again on dividends distributed to shareholders. For businesses with limited revenue, this can be a significant disadvantage.
Who Should Incorporate?
Businesses seeking liability protection, external funding, or long-term scalability are prime candidates for incorporation. Startups aiming to attract investors often benefit from the structured governance of a corporate form. As you consider detailed negotiation strategies, negotiate startup investment terms offers an in-depth perspective designed for investors navigating complex agreements.
Who Should Not Incorporate?
Entrepreneurs running small-scale operations or those with minimal risk exposure may find incorporation unnecessary. Sole proprietors and partnerships often benefit from simpler tax structures and fewer compliance requirements.
Ultimately, the decision to incorporate depends on your business’s unique needs and goals. By evaluating liability concerns, growth potential, and funding strategies, you can determine whether incorporation is the right move for your venture.
Key Considerations for Optimal Legal Structure: Balancing Complexity and Compliance
Choosing the right legal structure for your startup is a pivotal decision that impacts liability, taxation, and scalability. Striking the right balance between operational simplicity and compliance is essential to ensure long-term success. This section explores the trade-offs involved and provides actionable insights to help you make informed decisions.
1. Balancing Simplicity with Liability Protection
While simpler structures like sole proprietorships or general partnerships may seem appealing due to their ease of setup, they often lack adequate liability protection. This means your personal assets could be at risk if the business faces legal or financial challenges. On the other hand, more complex structures like limited liability companies (LLCs) or corporations provide a shield for personal assets but come with additional compliance requirements.
For instance, S Corporations limit the number of shareholders to 100 or less, which can restrict fundraising opportunities. However, they offer the advantage of pass-through taxation, avoiding double taxation at both corporate and individual levels. Evaluating these trade-offs is crucial to align your legal structure with your business goals.
2. Tax Treatment and Compliance
Tax implications vary significantly across legal structures. Sole proprietorships and partnerships typically involve pass-through taxation, where profits are taxed as personal income. Corporations, however, face double taxation unless they qualify for S Corporation status. Understanding these nuances can help you optimize tax efficiency while maintaining compliance with regulatory requirements.
Effective legal documentation plays a key role in ensuring compliance. From operating agreements to shareholder agreements, having well-drafted documents not only safeguards your business but also instills confidence in potential investors.
3. Planning for Scalability
Your legal structure should also accommodate future growth. For startups aiming to attract investors or expand internationally, a corporate structure may be more suitable. It provides the flexibility to issue shares and raise capital. Conversely, simpler structures may hinder scalability due to limitations on ownership or fundraising.
Next Steps
To move forward, consult with legal and financial advisors to evaluate your specific needs. They can guide you in selecting a structure that balances complexity, compliance, and growth potential. Additionally, ensure that all necessary legal documentation is in place to support your strategic decisions.
By carefully weighing these considerations, you can set a strong foundation for your startup’s success.
Choosing the Right Jurisdiction: Incorporation Considerations for Global Success
Selecting the right jurisdiction for incorporation is a pivotal decision that can shape the trajectory of your business. Jurisdiction impacts everything from customer trust to operational efficiency, making it essential to evaluate factors like infrastructure, tax benefits, and regulatory frameworks.
Speed and Ease of Registration
The time it takes to incorporate or update records varies significantly across jurisdictions. For instance, UK share registry updates can be completed in a couple of days, ensuring minimal downtime for businesses. On the other hand, Estonia’s e-residence registration process, while innovative, typically takes several days to finalize. These differences highlight the importance of aligning your choice of jurisdiction with your operational timelines.
Banking and Financial Access
Access to banking services is another critical consideration. The UK’s thriving fintech ecosystem, marked by a growth in the number of UK fintech companies increasing access to e-banking services, provides startups with quick and digital-friendly banking solutions. This robust infrastructure can simplify financial operations and enhance investor confidence.
Tax and Intellectual Property Benefits
Taxation policies and intellectual property (IP) schemes also play a significant role in jurisdiction selection. Countries like Cyprus and Estonia are gaining attention for their attractive tax and IP schemes, offering businesses favorable tax rates and strong protections for intellectual assets. These benefits can significantly reduce operational costs while safeguarding innovation.
Regulatory Frameworks and Customer Trust
A jurisdiction’s regulatory environment influences both compliance requirements and customer perception. Transparent and business-friendly regulations can foster trust among customers and investors alike, while overly complex systems may hinder growth.
Understanding these factors enables businesses to make informed decisions that align with their goals. For more insights on evaluating legal structures and their impact on business valuation, explore startup valuation methods.
Post-Incorporation Strategies and Fundraising Considerations: Securing Your Next Deal
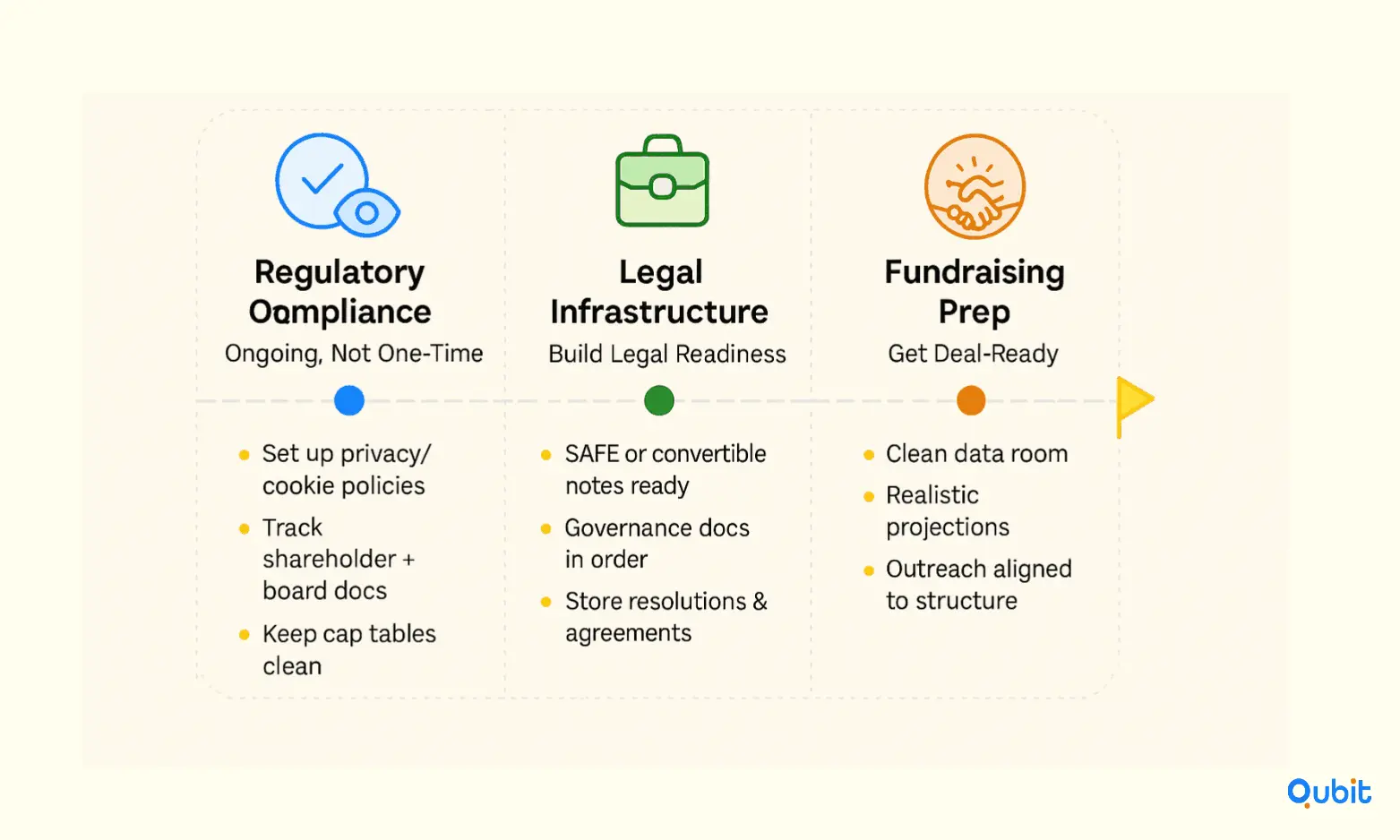
Establishing a solid foundation after incorporation is critical for long-term success. Ensuring post-incorporation compliance and preparing for fundraising requires attention to detail, strategic planning, and robust legal documentation. This section outlines actionable strategies to help founders finalize their legal structure and streamline investment opportunities.
Prioritize Regulatory Compliance
Compliance is not a one-time task but an ongoing commitment. Start by addressing essential legal requirements, such as drafting privacy and cookie policies to align with data regulations. For newly incorporated ventures, a privacy policy template can simplify this process and ensure adherence to legal standards.
Additionally, maintaining accurate records of shareholder agreements, board resolutions, and other corporate documents is vital. These records not only demonstrate professionalism but also reassure potential investors of your startup's operational integrity.
Build Robust Legal Documentation
Comprehensive legal documentation is the backbone of any successful fundraising effort. If convertible notes are part of your strategy, consult resources like safe convertible note agreements for structured guidelines. These agreements provide clarity on terms and conditions, helping founders and investors align expectations.
Prepare for Fundraising
Fundraising success hinges on preparation. Start by refining your pitch and ensuring your financial projections are realistic and well-documented. To close deals effectively, explore actionable tips from close startup investment deal, which connects transactional practices with nuanced legal documentation insights.
Equally important is understanding investor preferences and tailoring your outreach strategy. For broader insights, refer to how to do startup outreach for investors, which outlines strategies that complement your legal structure and fundraising goals.
Post-incorporation strategies are about more than ticking boxes—they’re about building a foundation for growth. By prioritizing compliance, strengthening legal documentation, and preparing for fundraising, founders can position their startups for success in securing their next deal.
Conclusion
Building a strong foundation for your startup begins with implementing the right strategies and ensuring your legal structure and documentation are airtight. Throughout this blog, we’ve explored key approaches to setting your business up for success, from securing compliance to creating a framework that supports growth and attracts investors. These steps are not just about avoiding pitfalls, they’re about positioning your startup for long-term sustainability and scalability.
A robust legal foundation is more than a necessity; it’s a strategic advantage. It reassures stakeholders, builds trust, and sets the stage for seamless fundraising efforts. If you’re ready to take the next step and present your business with clarity and confidence, we’re here to help.
Let us craft a compelling pitch deck that highlights your solid legal foundation. Get started with our Pitch Deck Creation service today!
Key takeaways
- Choosing the right legal structure is critical for managing liability and optimizing tax outcomes.
- Comparative analyses of business forms help inform strategic incorporation decisions.
- Jurisdiction plays a vital role in registration speed, investor perception, and regulatory compliance.
- Post-incorporation compliance and thorough legal documentation are essential for successful fundraising.
Frequently asked Questions
What is the best legal structure for a startup?
The best legal structure depends on factors such as liability, taxation, and growth plans. Many startups favor LLCs or corporations based on their specific needs and investor expectations.


 Back
Back



