The intersection of impact investing and sustainable FoodTech is reshaping the future of agriculture and food systems. As investors increasingly prioritize environmental and social outcomes alongside financial returns, sustainable FoodTech innovations are gaining momentum. These advancements address critical challenges such as food security, climate change, and resource efficiency.
Your exploration of diverse funding models gains additional context with the discussion on how to secure funding for agritech startups, which outlines various capital acquisition pathways within the broader AgriTech and FoodTech landscape.
This blog delves into the transformative role of impact investing in driving sustainable agriculture financing, highlighting emerging trends, alternative funding models, and the generational shift in investor priorities.
Why Impact Investing Matters for FoodTech
The food industry faces unprecedented challenges: climate change, resource constraints, population growth, and persistent issues of nutrition and food security. To address these, sustainable FoodTech must:
- Reduce emissions and waste across the entire value chain
- Advance climate resilience and regenerative agriculture
- Deliver nutritious, safe, and traceable food to a growing population
- Support the livelihoods of producers while strengthening food systems’ equity and resilience
Impact investors—those prioritizing quantifiable positive outcomes alongside financial returns—play a critical role in enabling these goals by directing capital to companies with mission-driven business models, rigorous measurement, and scalable technologies
Core Trends Shaping Impact Investing in FoodTech
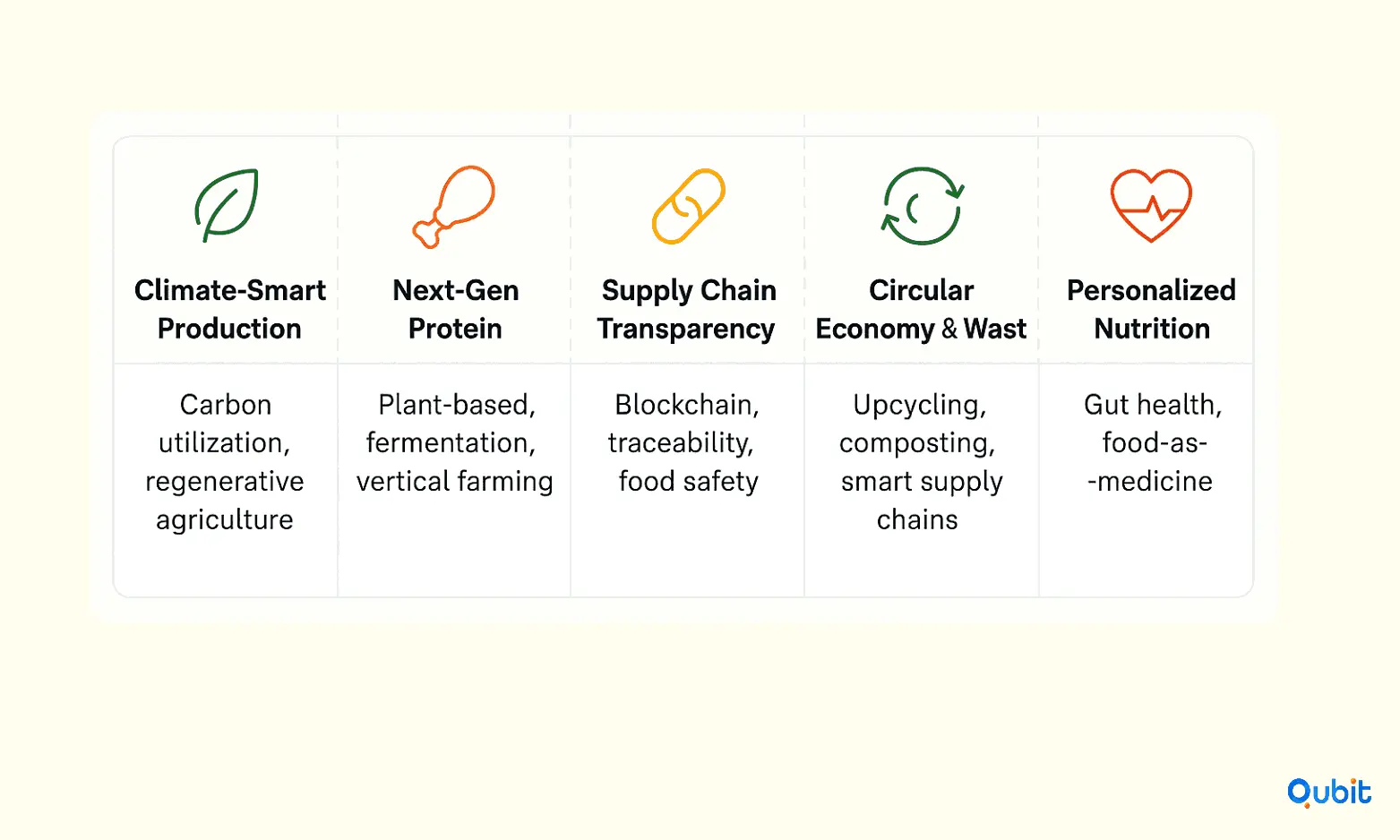
1. Climate-Smart and Regenerative Food Production
A growing share of impact capital is flowing to technologies that transform agriculture into a climate solution:
- Carbon Utilization: Startups like Arkeon are pioneering the conversion of CO₂ into proteins and essential nutrients, using microbes to radically reduce land, water, and input needs.
- Regenerative Agriculture: Platforms rewarding carbon sequestration, soil health, and biodiversity restoration are gaining ground. These approaches are designed to go beyond “do less harm” and create net-positive environmental impacts.
2. Next-Generation Protein and Sustainable Ingredients
Investment in alternatives to conventional animal proteins—plant-based, fermentation-derived, and cultivated meats—is driven by both environmental and animal welfare mandates. These technologies focus on producing protein with a fraction of the emissions, water, and land requirements of traditional livestock.
- Precision Fermentation: Enables the sustainable production of key food ingredients—proteins, fats, vitamins—without industrial agriculture’s footprint.
- Vertical Farming & Drought-Resistant Crops: Crop science and controlled-environment agriculture expand food production while reducing resource use.
3. Supply Chain Transparency and Traceability
Sustainability in FoodTech requires trust and verification, leading to heavy investments in supply chain transparency, blockchain-enabled traceability, and digital food safety tools.
- The food traceability market is expected to grow at 10.4% CAGR through 2029 as companies like Carrefour and Walmart set new standards for tracking products “from seed to shelf” and disclosing sustainability credentials.
- IoT sensors, RFID tagging, and DNA-based traceability solutions are now integral to tracking emissions, provenance, and fair trade claims.
4. Circular Economy and Food Waste Solutions
Reducing food loss at all stages—from farm to fork—not only conserves resources but creates investable opportunities. Impact investors increasingly fund startups in:
- Food waste analytics and upcycling
- Composting and biomaterials from food byproducts
- Energy-efficient kitchen and storage technologies for consumers and restaurants
- Smart supply chain platforms to optimize distribution and reduce spoilage
5. Personalized Nutrition and Health
Investments are also accelerating in personalized nutrition, gut health, and food-as-medicine platforms that combine advanced bioscience with machine learning to help individuals and communities achieve better health while reducing chronic disease burdens
SAFSF Farm and Food Systems Lenders and Investors Group
The SAFSF Farm and Food Systems Lenders and Investors Group represents a dynamic coalition of 18 active lenders and investors committed to advancing sustainable agriculture financing. Established in August 2020, this group has emerged as a vital force in deploying capital to improve farm and food systems, particularly during periods of market disruption like the COVID-19 pandemic.
A Decade of Expertise Driving Impact
With over ten years of industry experience, SAFSF has cultivated a unique approach to financing that bridges philanthropic grants and private investment dollars. This integration, often referred to as "Philanthropic-Impact Capital Fusion," enables the group to scale ventures in local farm economies while addressing systemic challenges in food systems. By combining these funding streams, SAFSF ensures that both immediate needs and long-term sustainability goals are met.
Responding to Market Disruptions
The COVID-19 pandemic underscored the fragility of global food systems, creating unprecedented challenges for farmers, distributors, and consumers. SAFSF's strategic response highlighted the importance of aligning capital with sustainability objectives. The group’s ability to adapt and deploy resources effectively during this crisis demonstrated the power of collaborative financing models in stabilizing and transforming food systems.
A Commitment to Equity and Climate
SAFSF’s work is deeply rooted in addressing climate, health, and equity concerns within agriculture. Their efforts align with tools like A Funder Toolkit on Climate, Health and Equity, which explores how comprehensive philanthropic strategies can complement impact investments in farm and food systems. By prioritizing equity and environmental sustainability, SAFSF ensures that its investments create lasting value for communities and ecosystems alike.
Impact Investing Moves from Niche to Norm in Agtech & Foodtech
Impact investing in sustainable FoodTech has evolved from a specialized strategy into a mainstream financial movement, reshaping the agtech and foodtech sectors. This transformation is driven by the growing emphasis on Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) objectives, mission-driven investment strategies, and supportive governmental policies. Investors are increasingly aligning their portfolios with sustainability goals, creating a ripple effect across industries that prioritize ethical and environmental responsibility.
The Rise of ESG Strategies
The adoption of ESG-focused investment strategies has surged, with approximately $17.1 trillion in assets under ESG strategies now representing one-third of total assets under management. This significant share underscores the mainstream acceptance of ESG principles, as investors recognize their potential to drive both financial returns and measurable impact. Companies in agtech and foodtech are leveraging these funds to innovate solutions that address pressing global challenges, such as food security and climate change.
Mission-Driven Investing Gains Momentum
Mission-driven investing has become a cornerstone of sustainable finance, particularly in agtech and foodtech. Investors are increasingly allocating capital to businesses that align with their values, fostering trust and long-term partnerships. For example, startups focusing on alternative proteins or regenerative agriculture are attracting attention for their ability to address sustainability challenges while meeting consumer demand for ethical products. This alignment of purpose and profitability is reshaping the investment landscape, making mission-centricity a key driver of growth.
AI-Driven Impact Optimization
Technology is playing a pivotal role in enhancing the efficiency and transparency of impact investments. AI-driven tools are being integrated into production processes, predictive analytics, and supply chain management to optimize ESG performance. These innovations enable companies to measure their sustainability outcomes more accurately, providing real-time insights that guide strategic decisions. For instance, AI can help agtech firms predict crop yields or monitor soil health, ensuring that investments deliver tangible benefits for both the environment and stakeholders.
Government Policies and Global Frameworks
Supportive policies and frameworks, such as the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), are accelerating the shift toward impact investing. These global benchmarks provide a standardized approach to measuring and reporting sustainability outcomes, helping investors track progress and align their objectives with broader societal goals. By linking investment strategies to specific SDGs, companies can quantify their impact and attract capital from socially conscious investors.
Innovative Financing Models
The rise of innovative financing models, such as revenue-based financing agritech, is further fueling the growth of impact investing in agtech and foodtech. This flexible funding approach correlates returns with revenue milestones, allowing startups to scale sustainably while aligning investor interests with long-term success. By exploring alternative funding solutions, businesses can access capital without compromising their mission-driven objectives.
Impact investing in sustainable FoodTech is no longer a niche practice, it’s a powerful force shaping the future of agriculture and food technology. As ESG strategies, mission-driven approaches, and technological innovations continue to gain traction, the sector is poised for transformative growth.
What Impact-Driven Investors Look for in FoodTech
Impact-oriented VCs and funds evaluate not only financial potential but also measurable contributions to sustainability, nutrition, and social value. Key criteria include:
- Scalability and Replicability: Can the technology or solution be deployed widely, across global food systems, or tailored to multiple local contexts?
- Quantifiable Outcomes: Emphasis on third-party validation and transparent reporting for carbon, water, land use, or social metrics.
- Unit Economics and Affordability: Solutions need to be accessible—not just to wealthy consumers, but to large and underserved populations.
- Alignment with Key Megatrends: Impact investors align portfolios with climate resilience, healthier diets, and circular economy mandates identified as critical for the food transition.
Funding Structures and Collaborations
1. Direct VC & Growth Equity
Specialized impact VCs and multi-stage funds are writing larger checks into growth-ready FoodTech with proven product-market fit, especially those with strong, validated impact metrics.
2. Blended Finance and Philanthropic-Backed Funds
Some catalytic investors use first-loss or patient capital structures, enhancing overall risk-return profiles and crowding in commercial investors.
3. Corporate Collaborations
Large food and consumer goods companies are co-investing via CVC arms and partnership programs aligned to their sustainability goals. These can catalyze scaling through procurement, distribution, and R&D support.
4. Government and Public-Private Programs
Many governments offer subsidies, co-investments, or risk-sharing vehicles to de-risk investment in high-impact FoodTech, especially in agritech, food safety, and public health initiatives.
Challenges and Watchpoints
Despite accelerating interest, FoodTech impact investing faces hurdles:
- Scaling Beyond Niche: Many sustainable, ethical, or healthy foods face high costs and limited market penetration; bridging the gap to mass adoption remains a challenge.
- Cost and Integration Barriers: Digital transformation is seen as essential but costly, with nearly 70% of food companies reporting cost as a barrier to tech investment.
- Measurement Rigor: The field still strives for robust, standardized measurement and verification of climate, nutrition, and community impacts.
- Investor Discipline: With capital overall tightening, investors are rewarding sustainable FoodTech firms that combine impact with proven operational and commercial excellence.
Outlook 2025: Sustainable FoodTech as Core to the Food Revolution
All evidence suggests sustainable FoodTech will be at the center of the next food revolution, offering multi-trillion dollar opportunities for investors who can combine financial acumen with environmental and social vision.
- VCs and corporates are sharpening focus on mature, scalable solutions rather than purely “feel-good” or unproven technologies.
- AI, precision fermentation, digital traceability, and alternative proteins remain hotspots for both tech and impact funds.
- Impact measurement, consumer adoption, regulatory adaptation, and value-chain integration will define winners in the space.
As industry professionals report, investment in AI (50%), supply chain traceability (48%), big data analytics, robotics, and energy conservation is rapidly increasing among food companies in 2025, driven by equal measures of productivity, risk management, and sustainability.
Success Stories and Emerging Leaders
Innovators such as Arkeon (CO₂-to-protein), Natural Trace (DNA-based supply chain), and precision fermentation platform companies illustrate how breakthrough science, transparent measurement, and sustainable vision can attract impact investors and corporate collaborators alike.
Meanwhile, mainstream players are not left behind: global food retailers and CPG leaders are:
- Rapidly increasing investments in tech-enabled traceability, carbon footprint monitoring, and low-impact ingredient sourcing.
- Developing public-private partnerships that accelerate the scaling—and impact—of new sustainable food technologies.
Conclusion
Impact investing is not a peripheral trend but a driving force in the sustainable transformation of food systems globally. As investors, startups, and corporates align around measurable sustainability and health outcomes, FoodTech is uniquely positioned to deliver both resilient financial returns and planetary benefit in 2025 and beyond.
Your sustainable FoodTech startup deserves investors who value impact as much as returns. Don’t settle for generic pitches or shotgun outreach. Our Investor Discovery and Mapping service helps you strategically identify mission-aligned VCs and impact funds, craft tailored engagement plans, and confidently secure the capital that truly supports your vision of a greener, more equitable food system.
Key takeaways:
- Impact investing in FoodTech prioritizes scalable climate-smart solutions, health innovation, and supply chain integrity.
- Transparency, rigorous measurement, and collaborative partnerships are critical for attracting capital and driving real change.
- The sector’s leaders will be those who navigate cost, integration, and market adoption challenges while proving robust economic and sustainability gains.
Frequently asked Questions
What is impact investing in foodtech?
Impact investing in foodtech refers to investment strategies that aim to generate financial returns while creating measurable social and environmental benefits within the food technology sector. This approach focuses on supporting innovations that address global challenges such as food security, sustainability, and waste reduction.


 Back
Back



