The telecom sector is at the forefront of the digital revolution, powering everything from 5G networks and IoT connectivity to cloud infrastructure and smart city deployments. As the industry evolves, so too does the funding landscape for telecom startups. In 2025, with equity markets tightening and founders seeking to minimize dilution, venture debt has emerged as a strategic tool for telecom entrepreneurs looking to fuel growth, extend runway, and bridge to major milestones.
This comprehensive guide explores the venture debt landscape for telecom startups, including how it works, who’s lending, key trends, eligibility, pros and cons, and actionable strategies for founders.
What is Venture Debt and Why Is It Gaining Traction?
Venture debt is a form of debt financing tailored for venture-backed, high-growth startups. Unlike traditional bank loans, venture debt is typically provided by specialized lenders or venture debt funds that understand the unique risks and growth trajectories of startups. It’s most often structured as a term loan or revolving credit line, with repayment periods of 2–5 years and interest rates higher than traditional bank loans, but with far less dilution than equity rounds.
Why is venture debt booming in 2025?
- Equity markets are subdued: Venture capital funding for startups dropped by 45% last year. Startups are seeking alternative, less dilutive funding options.
- Runway extension: Telecom startups face long sales cycles and heavy capital expenditures. Debt provides a way to extend runway between equity rounds, fund growth, or bridge to IPO without giving up more ownership.
- Pre-IPO and growth-stage demand: Many telecom companies are using venture debt to finance asset-heavy business models, acquisitions, or pre-IPO expansion.
- Mainstream adoption: Venture debt has grown from a niche tool to a mainstream asset class, with global venture debt markets expanding at a 14% CAGR and India’s market alone reaching $1.23 billion in 2024.
How Venture Debt Works for Telecom Startups
Structure and Terms
- Term Loans or Credit Lines: Most venture debt is structured as a term loan (fixed amount, fixed term) or a revolving credit line (draw as needed).
- Interest Rates: Typically range from 10% to 18% per annum in India (and similar globally), reflecting higher risk.
- Warrants: Lenders may ask for warrants, rights to buy equity at a set price, so they can participate in future upside.
- Repayment: Interest-only periods (6–12 months) followed by principal plus interest payments over 2–5 years.
- Collateral: Usually does not require hard assets, but may be secured by company IP or assets.
- Covenants: May include financial performance targets, restrictions on further borrowing, or limits on major business changes.
Typical Use Cases
- Extending runway between equity rounds
- Funding capital expenditures (network buildout, equipment)
- Bridging to IPO or major acquisition
- Working capital for growth initiatives
- Refinancing existing debt
Venture Debt vs. Equity: Pros and Cons
| Aspect | Venture Debt | Equity Financing |
|---|---|---|
| Dilution | Minimal (warrants only) | High (gives up ownership) |
| Repayment | Required (interest + principal) | None |
| Cost of Capital | Lower (if startup grows as planned) | Higher (if company value increases) |
| Flexibility | More restrictive covenants | More operational freedom |
| Use Cases | Runway extension, asset purchase, bridge to IPO | Product development, scaling, hiring |
| Risk | Must repay regardless of business outcome | No repayment, but loss of control if underperform |
Key takeaway: Venture debt is ideal for startups with predictable revenue and a clear path to growth, who want to minimize dilution and retain control.
The 2025 Venture Debt Market: Telecom in Focus
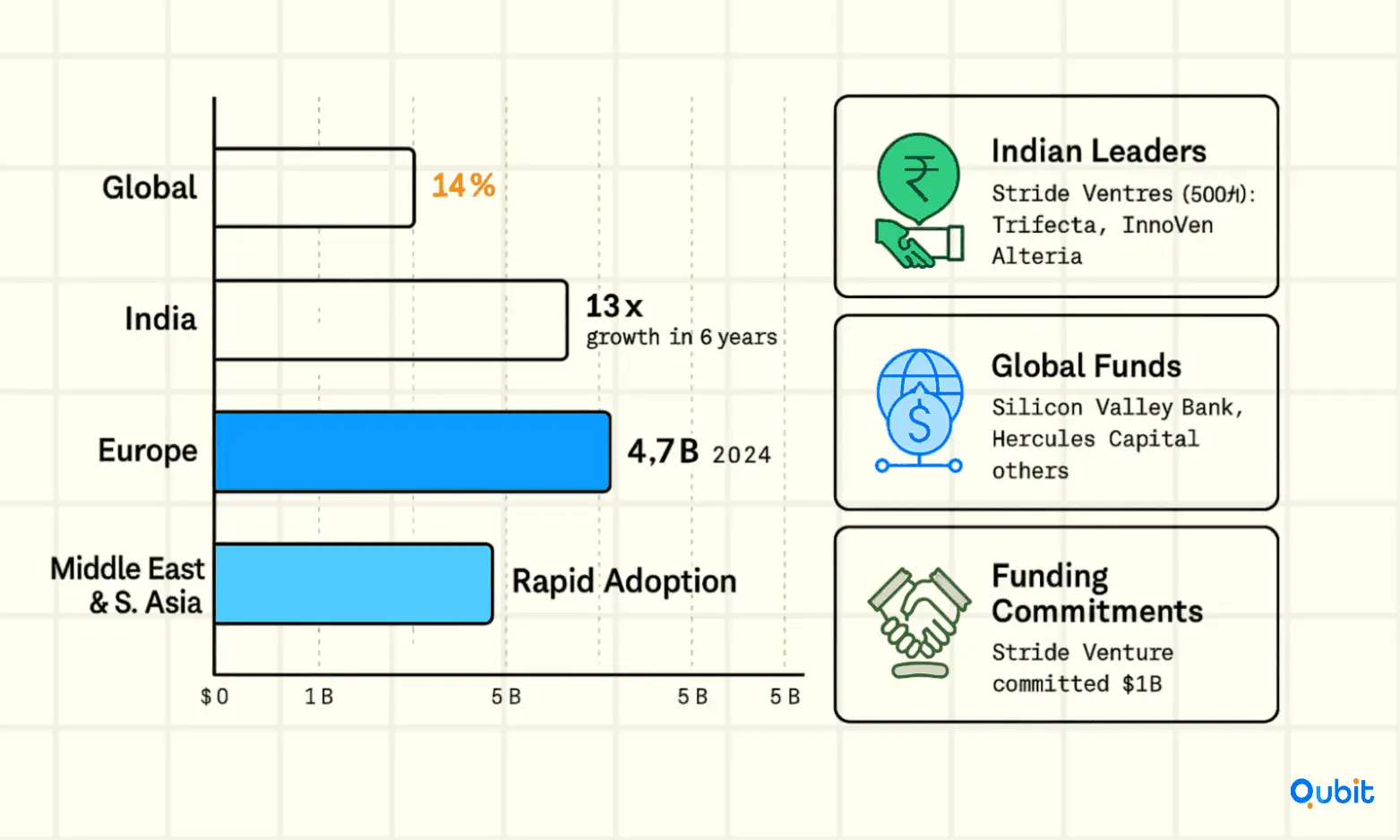
Global and Regional Growth
- Global venture debt market: Growing at 14% CAGR, now a mainstream asset class.
- India: Market reached $1.23 billion in 2024, up 13x in six years, with telecom, fintech, and deep tech among top sectors.
- Europe: Startups raised $4.7 billion in venture debt in 2024, with telecom infrastructure and IoT among the most active verticals.
- Middle East & Southeast Asia: Rapid adoption as VC markets mature and asset-heavy businesses seek capital.
Top Lenders and Funds
- Stride Ventures: Deployed $500M+ across 100+ companies, committed $1B for future investments.
- Trifecta Capital, InnoVen Capital, Alteria Capital: Leading Indian venture debt funds.
- Western lenders: Silicon Valley Bank, Hercules Capital, and others active in global telecom and tech.
Eligibility: Is Your Telecom Startup Ready for Venture Debt?
Typical criteria:
- Raised at least one round of institutional venture capital
- Demonstrable revenue growth and market traction
- Strong management team and scalable business model
- Clear path to profitability or next funding milestone
- Sufficient collateral or valuable IP (optional, but helps)
Venture debt is rarely available to pre-revenue or unproven startups, as lenders want to see evidence of growth and a solid investor base.
How Telecom Startups Are Using Venture Debt in 2025
1. Runway Extension and Working Capital
With longer gaps between equity rounds, 61% of Indian founders use venture debt to extend runway and manage working capital. This is especially vital in telecom, where sales cycles are long and capital needs are high.
2. Pre-IPO and Bridge Financing
40% of startups now use venture debt for pre-IPO bridge financing, helping scale operations and stabilize finances before going public. Companies like Ola Electric and Bluestone have leveraged this strategy to minimize dilution before their IPOs.
3. Asset Financing
Telecom is asset-heavy, network infrastructure, towers, and equipment require significant upfront investment. Venture debt allows startups to finance these assets without giving up equity.
4. Acquisitions and Expansion
Debt can fund acquisitions or rapid market expansion, especially when equity markets are slow or founders want to retain control.
5. Inventory and CapEx Management
37% of founders use venture debt to manage inventories and capital expenditures, smoothing cash flow and supporting scaling.
Key Trends Shaping Venture Debt for Telecom Startups
- Growth-stage focus: Most venture debt is flowing to startups with proven revenue and VC backing.
- Pre-IPO popularity: More companies are using debt to bridge to IPO, especially in India and Southeast Asia.
- Less dilution: Founders are increasingly choosing debt to avoid giving up more equity, especially as public markets reward higher founder ownership.
- Faster, streamlined process: Venture debt deals often close faster than equity rounds, with less exhaustive due diligence.
- Rise of specialized lenders: Dedicated venture debt funds and banks are offering tailored products for telecom and tech startups.
Investors are buzzing about virtualization and new spectrum deals, Top Telecom Trends Investors Are Watching in 2025 breaks down why these shifts are game-changers.
Risks and Challenges
1. Higher Cost of Capital
Interest rates for venture debt are higher than traditional bank loans, reflecting the greater risk. Startups must ensure that projected growth justifies the cost.
2. Repayment Pressure
Unlike equity, debt must be repaid regardless of business performance. Missed payments can trigger penalties or even force asset sales.
3. Restrictive Covenants
Lenders may impose covenants that restrict further borrowing, require certain financial performance, or limit operational flexibility.
4. Potential for Dilution
Warrants attached to venture debt can result in future equity dilution if exercised, though typically less than a full equity round.
5. Not for All Startups
Pre-revenue or unproven startups are unlikely to qualify. Venture debt is best for companies with predictable revenue and strong investor backing.
How to Secure Venture Debt: Actionable Steps
- Build a Track Record: Demonstrate revenue growth, customer traction, and a solid investor base.
- Prepare Financials: Lenders will scrutinize your cash flow, burn rate, and projections. Be ready with detailed data.
- Target the Right Lenders: Approach specialized venture debt funds or banks with experience in telecom and tech.
- Negotiate Terms: Focus on interest rates, repayment schedules, covenants, and warrant coverage. Seek flexibility where possible.
- Align with Equity Investors: Many lenders want to see strong VC backing; keep your investors in the loop.
- Plan for Repayment: Ensure your growth projections support timely repayment without straining operations.
Landing your next round often hinges on telling a solid story and showing real traction, How to Secure Funding for Telecom Startups walks through the tactics founders swear by.
Conclusion
Venture debt has become an essential tool in the telecom startup funding arsenal for 2025. As equity markets tighten and founders seek to minimize dilution, debt financing offers a flexible, strategic way to extend runway, finance growth, and bridge to major milestones, especially for asset-heavy, growth-stage companies.
While venture debt carries risks and requires careful planning, its role in the global telecom ecosystem will only grow as startups and investors look for smarter, more balanced funding strategies. Use our fundraising assistance to streamline your funding journey, connect confidently with investors.
Key Takeaways
- Venture debt is a fast-growing, less dilutive funding option for telecom startups with proven revenue and VC backing.
- It’s ideal for runway extension, asset financing, pre-IPO bridge rounds, and managing working capital or CapEx.
- Interest rates are higher than bank loans, and repayment is required regardless of business performance.
- Most venture debt is flowing to growth-stage and pre-IPO startups, especially in India, Europe, and Southeast Asia.
- Founders should carefully assess repayment capacity, negotiate terms, and use debt strategically alongside equity.
Frequently asked Questions
What is venture debt and how is it different from equity?
Venture debt is a loan for VC-backed startups, offering non-equity capital with minimal dilution. Unlike equity, it must be repaid with interest, and may include warrants for future equity.


 Back
Back



