Insurance is a strategic lever that can shape a start-up’s growth, valuation, and appeal to investors. For emerging companies, securing the right coverage goes far beyond risk mitigation, it signals operational maturity and financial prudence, both of which are crucial in today’s competitive funding landscape.
This blog delves into the powerful link between insurance and a start-up’s funding prospects, drawing on industry data and real-world trends. We’ll examine how insurance influences investor decisions, impacts company valuation, and what practical steps founders can take to optimize their coverage for maximum fundraising success
Let’s jump right in!
Insurtech Overview: Unveiling Tech-Driven Insurance Innovations
The insurance industry is undergoing a remarkable transformation, fueled by cutting-edge technologies that are reshaping traditional practices. Insurtech, a fusion of insurance and technology, is driving efficiency, customization, and innovative service delivery across the sector.
The Role of Advanced Technologies
Artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), and blockchain are at the forefront of this evolution. AI enables insurers to analyze vast datasets, offering predictive insights that enhance risk assessment and fraud detection.
IoT devices, such as connected home sensors and wearable health trackers, provide real-time data, allowing insurers to tailor policies to individual needs. Blockchain technology ensures transparency and security in transactions, streamlining claims processing and reducing administrative overhead.
Transforming Legacy Models
Traditional insurance models, often criticized for their rigidity, are being revitalized through these innovations. Insurtech solutions empower companies to offer personalized experiences, automate processes, and improve customer satisfaction. For example, AI-driven chatbots can handle routine inquiries, freeing up human agents for complex cases. Similarly, IoT data enables dynamic pricing, where premiums adjust based on real-time behavior or conditions.
The integration of these technologies is not just about modernization; it’s about creating a more agile, customer-centric industry. As insurtech continues to evolve, it promises to redefine how insurance is delivered and experienced.
Insurtech Business Models & Trends: Market Dynamics and Resilience
The insurtech industry is evolving rapidly, showcasing a variety of innovative business models that cater to diverse consumer needs. From direct-to-consumer platforms to subscription-based and marketplace approaches, these models are reshaping how insurance is accessed and delivered. Despite a significant contraction in global funding, falling 45% year-over-year to $4.6 billion in 2023, the lowest level since 2017, the sector demonstrates remarkable resilience through strategic investments and acquisitions.
Diverse Business Models Driving Innovation
Insurtech companies are experimenting with multiple business models to address gaps in traditional insurance offerings:
- Direct-to-Consumer Platforms: These models simplify insurance purchasing by eliminating intermediaries, offering tailored policies directly to customers.
- Marketplace Models: Acting as aggregators, marketplaces allow users to compare policies from various providers, ensuring transparency and competitive pricing.
- Subscription-Based and Usage-Based Approaches: Subscription models provide predictable monthly costs, while usage-based schemes, often powered by IoT, adjust premiums based on real-time data, such as driving behavior or home security metrics.
Resilience Amid Funding Challenges
Despite the funding slump, early-stage deals remain stable, with a median investment of $3 million. Strategic acquisitions also underscore investor confidence. For instance, Next Insurance, a leading insurtech, secured backing from Allianz and Allstate, highlighting how established players continue to support promising startups even during downturns.
Emerging Trends in Insurtech
The adoption of AI-driven risk assessment tools is gaining traction, particularly in underwriting. Startups like Cytora are leveraging IoT and big data to refine risk evaluation, attracting higher valuations. Additionally, while Life & Health insurtechs experienced a sharper decline in funding (58%) compared to Property & Casualty (39%), the latter remains a focal point for innovation.
For startups aiming to enter this dynamic market, understanding consumer needs and competitive landscapes is crucial. Refer to How to do market research for a startup for actionable insights on analyzing new markets effectively.
Insurtech Valuation Multiples: Benchmarking with Financial Metrics
Valuation multiples are a cornerstone for comparing insurtech companies, offering a standardized framework that simplifies the analysis of financial performance and growth potential. Metrics like revenue and EBITDA multiples are particularly useful in this sector, where innovation and scalability drive investment decisions.
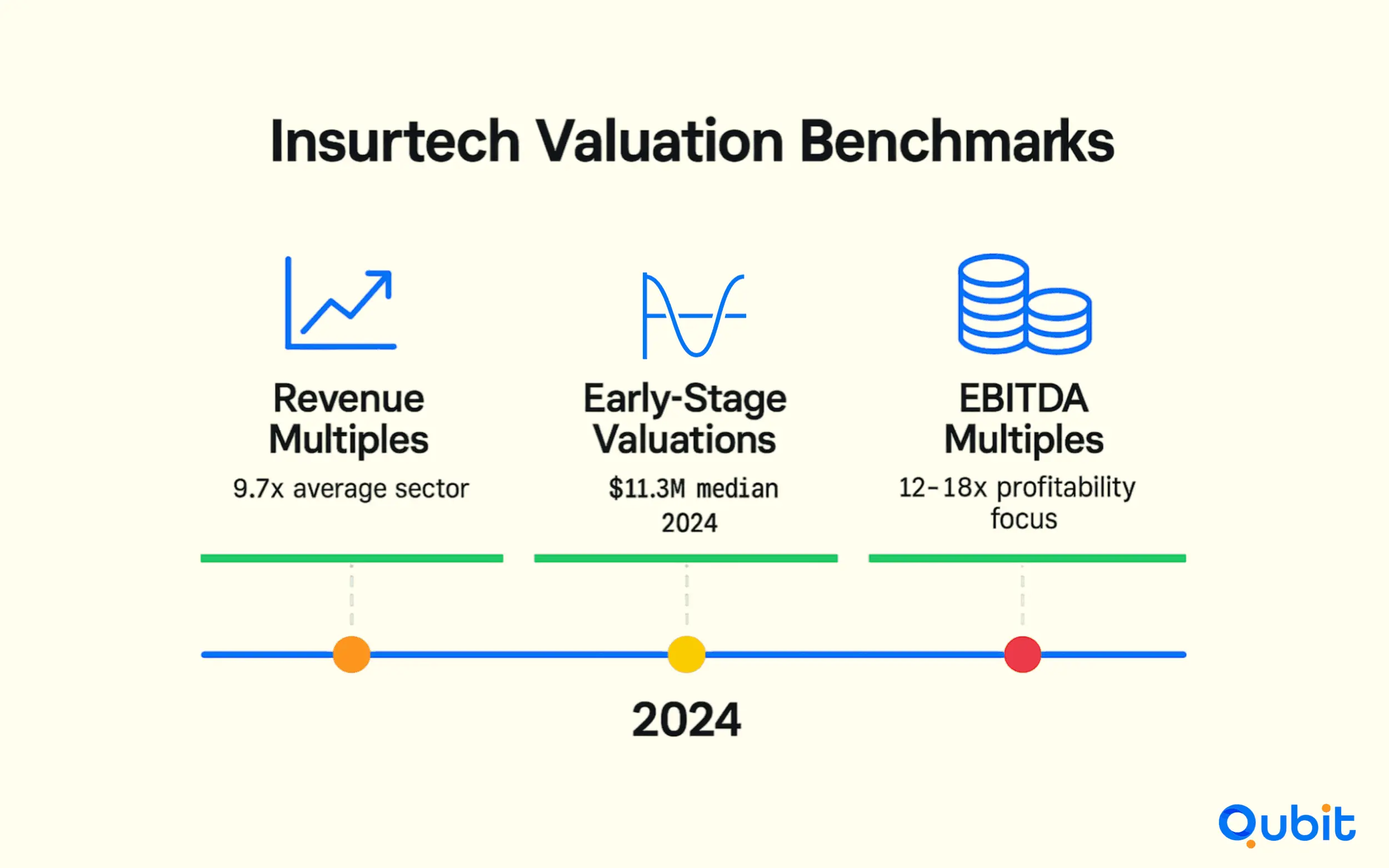
Revenue Multiples: A Snapshot of Growth
Revenue multiples are often aligned with the high-growth nature of insurtech businesses, making them a preferred metric for benchmarking. For instance, the average revenue multiple of 9.7x across 18 influential insurtech companies highlights the sector's robust valuation trends. This benchmark can help investors identify undervalued opportunities or validate premium valuations for companies with exceptional growth trajectories.
Early-stage insurtechs are also showing promising valuation growth. Pre-seed/seed median valuations rose 27.4% YoY to $11.3M in 2024, despite a decline in funding. This resilience underscores the optimism surrounding early-stage companies, even in challenging financial climates.
EBITDA Multiples: A Shift Toward Profitability
As insurtechs mature, investor focus often shifts to profitability metrics like EBITDA multiples. These metrics, which average between 12–18x, are gaining importance as companies transition from growth-focused strategies to sustainable profitability. This shift reflects evolving investor expectations and the need for insurtechs to demonstrate long-term financial stability.
Embedded Insurance: Unlocking Valuation Premiums
Embedded insurance models, such as those integrated with e-commerce or travel platforms, are driving higher valuation multiples. Companies like Cover Genius exemplify this trend, showcasing how synergy-driven growth can elevate market positioning and attract premium valuations.
Want investor-ready numbers and clearer storytelling? Try Qubit’s Financial Model Creation and get a model built for your stage.
Unique Challenges Faced by Insurance Startups
Insurance start-ups face a distinctive set of fundraising hurdles compared to other sectors.
- Regulatory Complexity: Insurance startups must comply with strict and often evolving regulatory requirements, which can vary by region and product. Licensing, solvency, and consumer protection regulations requires significant time and resources, making it harder to launch and scale.
- High Capital Requirements: Unlike many other startups, insurance businesses need to maintain substantial capital reserves to meet regulatory standards and ensure claims can be paid. This increases the initial funding burden and can deter investors seeking less capital-intensive opportunities.
- Investor Skepticism: Many investors are wary of the insurance sector due to its perceived complexity, long-term risk exposure, and the challenges of accurately assessing underwriting and claims risk. This skepticism can make it harder to attract funding, especially from generalist investors.
- Long Sales Cycles and Delayed Profitability: Insurance products often require lengthy customer acquisition processes and have slow revenue realization, making it difficult for startups to demonstrate early traction and rapid growth, key metrics for most investors.
- Integration with Legacy Systems: Many insurance startups must integrate with the outdated IT infrastructure of established carriers, which can be technically challenging, slow down product development, and increase operational costs.
- Building Trust with Customers: As new entrants, insurance startups often struggle to establish credibility and trust with potential customers, a critical factor in an industry built on reliability and security.
- Valuation Discrepancies: Founders and investors may have differing views on the startup’s value. Founders often focus on future potential, while investors emphasize current metrics and risks. This gap can complicate negotiations and lead to unfavorable terms or failed funding rounds.
- Limited Access to Debt Financing: Traditional loans typically require collateral, which most insurance startups lack, forcing them to rely on equity funding and face potential dilution.
- Competitive Fundraising Environment: The large number of new ventures in the market makes it difficult for insurance startups to capture investor attention and clearly communicate their unique value proposition.
- Resource Constraints: Gathering the extensive data and documentation required for due diligence is resource-intensive. Startups with limited staff and budget may struggle to meet investor demands efficiently.
- Unfamiliar Legal Terms: Many founders lack experience with complex legal and financial terminology in term sheets and investment agreements, which can lead to unfavorable deals or misunderstandings during negotiations.
- Economic and Market Uncertainty: Broader economic downturns or shifts in investor sentiment can further restrict access to capital and prolong fundraising timelines
Overview of Funding Stages (Seed, Series A, Series B and Beyond)
Fundraising for insurance start-ups typically progresses through defined stages:
- Seed Stage: Focuses on validating the business model and early product development, often funded by angel investors or seed funds.
- Series A: Targets scaling the team, acquiring initial customers, and refining technology. Venture capitalists look for evidence of product-market fit.
- Series B and Beyond: Supports market expansion, regulatory scaling, and operational maturity. Investors at this stage expect clear growth metrics and a path to profitability.
Understanding these stages, and tailoring your pitch and metrics accordingly, can improve your chances of securing the right capital at the right time.
Types of Investors in the Insurance Sector
Insurance start-ups attract a diverse investor base:
- Angel Investors:
- High-net-worth individuals who provide early-stage capital, often before a company has significant traction.
- Frequently bring industry experience, mentorship, and valuable connections.
- Typically invest in the concept or prototype phase and are willing to take higher risks for potentially higher returns.
- Venture Capitalists (VCs):
- Professional investors or firms that provide substantial funding in exchange for equity, usually at the growth or scaling stage.
- Seek high-growth potential, innovative business models, and a clear path to market leadership.
- Often offer strategic guidance, access to networks, and support with scaling operations.
- Private Equity (PE) Firms:
- Strategic Corporate Investors:
- Corporate Venture Arms:
- Institutional Investors:
- Family Offices:
- Crowdfunding and Retail Investors:
- Platforms that allow a broad base of individual investors to participate, typically in early-stage funding rounds
Regulatory and Compliance Readiness for Fundraising
Demonstrating readiness in these areas not only satisfies regulatory requirements but also builds credibility with investors, streamlines due diligence, and helps position the start-up for long-term success.
- Licensing and Registration:
- Obtain all necessary licenses and registrations from the relevant regulatory authority (such as IRDAI in India or NAIC in the US) before commencing operations.
- Licensing applications typically require detailed business plans, proof of capital adequacy, and information about the management team’s qualifications.
- Solvency Margin and Capital Adequacy:
- Product Approval:
- Corporate Governance and Management Disclosures:
- Provide comprehensive documentation on the company’s governance structure, including Articles of Incorporation, by-laws, and conflict-of-interest policies.
- Key executives and board members must undergo background checks and submit biographical affidavits to demonstrate ethical and professional standards.
- Operational Preparedness:
- Data Protection and Cybersecurity:
- Transparent Reporting and Recordkeeping:
- Consumer Protection and Fair Practices:
- Final Regulatory Approvals:
- Staying Updated:
- Continuously monitor regulatory changes and update compliance practices as needed to avoid penalties and maintain investor trust
Building Investor Trust and Overcoming Industry Skepticism
Trust is a major barrier for insurance start-ups, given the sector’s reputation for risk and regulatory hurdles. To overcome skepticism:
- Showcase a seasoned founding team with insurance and technology expertise.
- Highlight partnerships with established carriers or reinsurers.
- Provide transparent metrics on loss ratios, customer retention, and claims handling.
- Demonstrate robust risk management and compliance frameworks.
Building credibility early can differentiate your start-up in a crowded market.
Crafting a Compelling Pitch for Insurance Startups
A persuasive pitch for an insurance startup must do more than present an idea, it needs to instill confidence in investors about your ability to solve real problems, scale sustainably, and navigate a complex regulatory landscape. Here’s how to structure and strengthen your pitch:
1. Clearly Define the Market Gap
- Articulate the Problem: Start with a concise, data-backed description of the specific pain point or inefficiency in the insurance sector that your startup addresses. Use real-world examples or anecdotes to make the issue relatable.
- Quantify the Opportunity: Support your problem statement with market data, such as the size of the underserved segment, inefficiencies in claims processing, or gaps in existing coverage, to demonstrate the scale and urgency of the opportunity.
2. Present a Distinctive Solution
- Showcase Your Product or Model: Explain how your technology, platform, or business model uniquely addresses the identified market gap. Highlight key features, such as automation, AI-driven underwriting, or seamless customer experiences, that differentiate you from incumbents and competitors.
- Demonstrate Value: Clearly link your solution to tangible benefits, cost savings, improved efficiency, faster claims, or better risk assessment.
3. Demonstrate Traction and Validation
- Show Early Results: Present evidence of traction, such as successful pilot programs, signed partnerships with carriers or brokers, regulatory milestones (like obtaining licenses), or initial customer acquisition metrics.
- Highlight Testimonials and Endorsements: If available, include positive feedback from early users or endorsements from industry experts to strengthen credibility.
4. Explain the Business Model and Revenue Strategy
- Clarify How You Make Money: Outline your revenue streams—premiums, commissions, SaaS fees, or other monetization models.
- Show Scalability: Explain how your business model can grow efficiently, referencing market expansion plans or technology that supports scale.
5. Address Regulatory and Compliance Readiness
- Show Preparedness: Emphasize your understanding of regulatory requirements and demonstrate steps taken to secure necessary licenses, meet solvency margins, and implement robust compliance protocols. This is especially important in insurance, where investor confidence hinges on regulatory risk management.
6. Map Out the Path to Profitability and Growth
- Project Financials and Milestones: Share realistic financial projections, including customer growth, revenue targets, and break-even timelines. Outline major upcoming milestones, such as new product launches or expansion into new markets.
- Discuss Regulatory Scalability: Explain how your compliance framework supports future growth, making it easier to enter new regions or launch additional products.
7. Anticipate and Address Investor Concerns
- Mitigate Perceived Risks: Proactively address common investor concerns around underwriting risk, claims management, and long-term viability. Highlight your risk controls, reinsurance partnerships, or advanced analytics that reduce exposure.
- Showcase Team Expertise: Present a founding team with deep industry and technical experience, and, if possible, advisors or board members with strong insurance backgrounds.
8. Craft a Compelling Narrative
- Tell a Story: Weave your pitch into a coherent narrative that connects the problem, your solution, your team, and your vision for the future. Use clear, jargon-free language and visuals to make your story memorable and persuasive
Using Reinsurance and Strategic Partnerships for Capital Efficiency
Reinsurance arrangements and strategic partnerships can help insurance start-ups manage risk and conserve capital. By transferring portions of risk to established reinsurers, start-ups can limit their exposure and meet regulatory requirements with less capital. Partnering with established carriers can also provide access to underwriting expertise, distribution channels, and credibility, making your start-up more attractive to investors.
Case Studies: Successful Fundraising Stories in Insurtech
Highlighting real-world examples can inspire confidence and provide practical lessons. For instance:
- Next Insurance secured major funding rounds by partnering with industry giants like Allianz and Allstate, leveraging these relationships to validate their model and accelerate growth.
- Lemonade attracted significant VC interest by pioneering AI-driven underwriting and transparent claims processing, addressing both scalability and trust.
These stories underscore the importance of innovation, regulatory readiness, and strategic alliances in successful fundraising.
Step-by-Step Guide to Preparing for Due Diligence in Insurance Fundraising
- Organize Regulatory Documentation: Ensure all licenses, filings, and compliance records are up-to-date.
- Prepare Financial Statements: Provide audited or reviewed financials, including loss ratios and reserves.
- Detail Risk Management Processes: Document underwriting guidelines, claims procedures, and reinsurance agreements.
- Showcase Technology and Data Security: Demonstrate robust IT infrastructure and data protection measures.
- Compile Key Metrics: Present customer acquisition, retention, and growth data.
- Anticipate Investor Questions: Prepare clear, honest answers about challenges and future plans.
Thorough preparation can expedite the fundraising process and build investor confidence.
Conclusion
Throughout this blog, we’ve explored how insurance coverage plays a pivotal role in shaping startup valuations. From data-driven insights to real-world case studies, the evidence underscores the importance of integrating robust insurance strategies into your business model. A well-structured insurtech approach not only mitigates risks but also enhances investor confidence, positioning your startup for sustainable growth.
As you consider the actionable steps outlined here, remember that the right insurance strategy can be a game-changer for your valuation and fundraising efforts. Ready to raise smarter? Explore our insurance fundraising services. Let’s work together to unlock your startup’s full potential.
Key Takeaways
- Securing funding requires addressing both financial metrics and trust deficits in the insurance sector.
- A clear, structured business plan from seed to Series A is essential for investor confidence.
- Incorporating insurtech trends and AI-driven analysis can unlock new investor avenues.
- Adaptive insurance coverage and risk management strategies protect startups during growth.
- Sustained innovation and a strong internal culture are critical to long-term success.
Frequently asked Questions
How does insurance coverage impact my startup’s valuation?
A well-structured insurance strategy signals proactive risk management to investors, often translating into a higher valuation. Think of insurance as your startup’s “safety seatbelt”—it shows you’re ready for bumps, making investors more confident in backing you.






