Understanding the details of venture capital (VC) and private equity (PE) is essential for anyone exploring the capital market. These two funding models are crucial in shaping businesses. However, they differ significantly in their approach, investment strategies, and target companies. While venture capital focuses on high-growth startups, private equity typically invests in established businesses seeking operational improvements or expansion.
The comparison of venture capital and private equity gains depth when you consider the broader analysis of types of startup funding. This blog aims to break down the fundamental differences between VC and PE. It offers actionable insights for startups and finance professionals alike. Let’s jump right in!
VC vs. PE: Key Terms and Core Differences
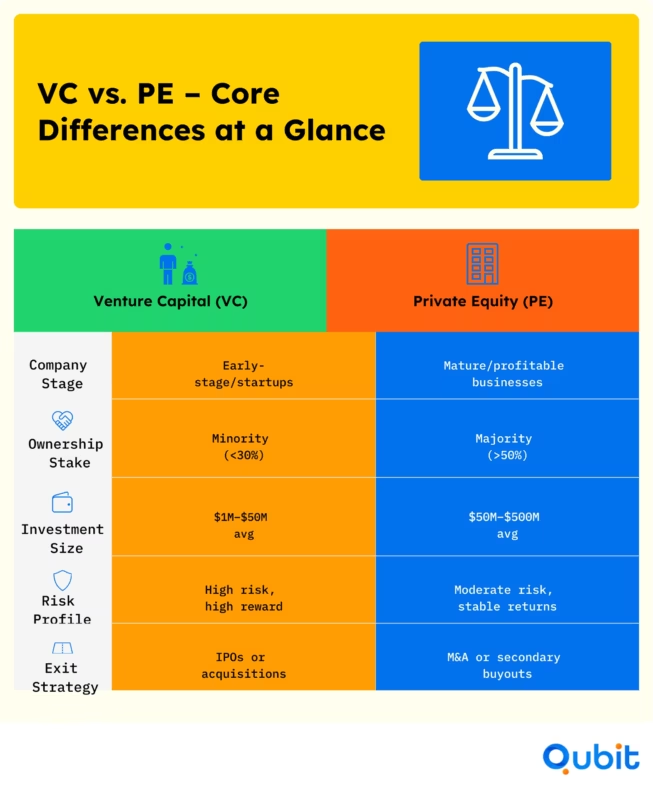
To understand the capital market, you need clarity on the distinctions between venture capital (VC) and private equity (PE). While both focus on investing in businesses, their approaches differ significantly.
Private equity firms typically target mature companies, acquiring majority stakes to implement operational improvements. These investments often span 4–7 years, aiming to enhance profitability and prepare businesses for resale or public offerings.
Venture capital firms prioritize early-stage companies, often taking minority positions to fuel rapid growth. Although traditionally focused on startups yet to achieve profitability, recent trends reveal some overlap between VC and PE strategies.
As the EQT Group Investment Team explains: “VC focuses on startups yet to achieve profitability, while PE targets established companies with stable financials.” This distinction highlights the varying risk profiles and structural nuances that define each investment strategy.
Which Companies Fit VC vs. PE Investments?
Investment strategies differ significantly between venture capital (VC) and private equity (PE) firms, largely based on the maturity and growth potential of the companies they target. VC firms typically focus on startups and emerging businesses in industries like technology, healthcare, and fintech, seeking high-growth opportunities with scalable models. In contrast, PE firms prioritize established companies with stable cash flows and proven market performance, often in sectors such as manufacturing, retail, and infrastructure.
In 2024, [U.S. buyout funds raised $325 billion, underscoring the substantial capital available for established companies seeking PE investment.
Market insights become clearer when referencing top private equity firms 2024, which offers a current snapshot of leading players in the industry. Exceptions exist, but the core distinction lies in VC’s appetite for innovation versus PE’s preference for stability.
VC Size vs. PE Size: Ownership Stakes and Deal Sizes Compared
Ownership stakes and deal sizes vary significantly between venture capital (VC) and private equity (PE) investments, reflecting their distinct approaches to equity markets. PE transactions typically involve acquiring larger ownership percentages, often exceeding 50%, as firms aim for controlling stakes in established companies. In contrast, VC rounds usually result in smaller stakes, averaging around 20–30%, as they focus on funding early-stage startups.
Deal sizes also differ markedly. PE deals frequently fall into the higher range, with transactions often exceeding $100 million. Meanwhile, VC investments are more common in the $25–$100 million range, with approximately 25% of deals occurring in this bracket, according to PitchBook Stats, which highlights the prevalence of mid-sized transactions in the market.
This comparison underscores how PE and VC cater to different segments of the equity markets, shaping their investment strategies accordingly.
Understanding Risk and Structures in VC vs. PE
The contrasting approaches to risk management in venture capital (VC) and private equity (PE) reveal fundamental differences in their investment structures. PE firms prioritize stability by implementing rigorous structural controls and risk mitigation strategies, often focusing on established companies with predictable cash flows. In contrast, VC embraces higher risks, targeting early-stage startups with significant growth potential but uncertain outcomes.
These differences extend to financing models and deal structuring. PE transactions often involve complex mechanisms like buyouts, which rely heavily on debt financing and operational restructuring. On the other hand, VC deals typically revolve around cash equity injections, enabling startups to scale rapidly while accepting the inherent risks of unproven business models.
How to Drive Returns with Value Creation Strategies
Private equity (PE) and venture capital (VC) firms employ distinct approaches to create value and maximize returns. PE firms often focus on operational improvements, enhancing EBITDA, and utilizing financial engineering to unlock growth potential. By refining processes and optimizing performance, they aim to achieve multiple expansion, which increases the valuation of the businesses they acquire.
On the other hand, VC firms prioritize innovation and rapid revenue growth. Their strategies revolve around supporting early-stage companies, fostering groundbreaking ideas, and scaling businesses quickly to generate outsized returns. This approach is particularly effective for startups aiming to disrupt industries and capture market share.
For readers interested in a deeper dive into private equity mechanics, this lbo return attribution explainer walks through how PE firms break down returns in leveraged buyouts, shedding light on the financial engineering behind PE performance.
Hands-On Management Tactics in VC and PE for Success
Private equity (PE) firms often prioritize operational involvement to enhance portfolio performance. Many deploy dedicated operational teams, focusing on restructuring, efficiency improvements, and growth strategies. For example, the KKR Fund demonstrates this approach by utilizing specialized teams for operational overhauls, as highlighted in this press release.
In contrast, venture capital (VC) firms typically adopt a less hands-on strategy. Their involvement centers around strategic advisory, offering guidance on scaling, market positioning, and fundraising rather than direct operational management. This distinction underscores the differing priorities between PE and VC firms in driving portfolio success.
How HR Strategies Differ in VC and PE
Recruiting and team-building approaches in venture capital (VC) and private equity (PE) reflect their distinct operational goals. VC firms often prioritize agility, seeking professionals with diverse skill sets to adapt to fast-paced startup environments.
Conversely, PE firms focus on structured expertise, valuing candidates with deep financial and operational backgrounds to drive portfolio company performance. These differences highlight how each sector tailors its HR strategies to align with its investment philosophy and organizational needs, emphasizing unique professional attributes in hiring practices.
VC vs. PE Recruiting: Streamlined vs. Adaptive – Which Works Best?
Recruiting strategies in Private Equity (PE) and Venture Capital (VC) differ significantly, shaping both talent acquisition and career trajectories. PE firms often rely on a structured recruiting process, emphasizing predefined roles and clear pathways. This approach aligns with the private equity investment process, which highlights structured pathways that impact recruitment requirements on the PE side.
On the other hand, VC firms adopt a more flexible and adaptive hiring model, prioritizing dynamic skill sets to match the fast-paced nature of startups. These contrasting methods influence the skills demanded in each industry, with PE favoring specialization and VC valuing versatility.
The discussion gains further context with working with private equity pros and cons, which examines both the benefits and challenges associated with such partnerships. Understanding these strategies can help businesses align with the right investment model to achieve their growth objectives.
How VC and PE Work Environments Differ
The contrasting work cultures of Venture Capital (VC) and Private Equity (PE) create distinct professional experiences. VC thrives on rapid decision-making and a dynamic environment, often requiring swift evaluations of startups and emerging technologies. In contrast, PE adopts a methodical approach, emphasizing detailed portfolio monitoring and structured processes. Work-life balance also varies significantly: VC professionals often juggle unpredictable schedules, while PE teams operate within more defined routines. These differences highlight the unique demands and rewards of each investment sector.
What Pays More: VC vs. PE Compensation Insights
Compensation in venture capital (VC) and private equity (PE) varies significantly, with PE associates often commanding higher salaries. First-year PE associates typically earn between $250K and $350K annually, a figure that surpasses the compensation packages commonly seen in VC roles. This disparity highlights the lucrative nature of PE positions, especially for professionals entering the field early in their careers.
In 2025, [PE associates earn $250,000-$400,000+ total compensation](https://www.joinleland.com/library/a/private-equity-associate-salary), highlighting the lucrative nature of private equity roles compared to venture capital.
When comparing total compensation packages in both fields, the PE Salary range of $250K–$350K serves as a benchmark for understanding the financial advantages of private equity roles. These figures underscore the competitive edge PE offers in terms of earning potential.
Your Guide to Exit Strategies and Opportunities
Exit strategies in venture capital (VC) and private equity (PE) differ significantly, reflecting their distinct investment approaches. While PE professionals often favor structured acquisitions as their primary exit route, VC investors typically rely on initial public offerings (IPOs) or secondary sales to achieve returns. These contrasting methods highlight the tailored strategies each sector employs to align with their investment goals.
For businesses aiming to attract PE investments, structuring your operations to meet investor expectations is crucial. The preparedness of your venture can be better understood with insights from preparing startup for private equity, which details strategies to align your business with investor expectations.
Understanding these exit pathways not only clarifies the endgame for investors but also helps businesses shape their growth strategies effectively.
Building a career in venture capital (VC) or private equity (PE) requires thoughtful planning and a clear understanding of industry demands. These fields are highly competitive, often requiring candidates to possess strong analytical skills, financial acumen, and a knack for identifying growth opportunities. Professionals should evaluate their personal strengths and align them with the unique challenges of each sector.
Choosing between VC and PE involves considering factors like work environment, deal structures, and long-term career goals. While VC focuses on early-stage investments and innovation, PE emphasizes mature businesses and operational improvements. Understanding these distinctions can help aspiring professionals make informed decisions about their career paths.
Both sectors offer rewarding trajectories, but success hinges on preparation and adaptability.
What’s Trending in VC and PE Right Now
Fresh perspectives are shaping the VC and PE sectors, with influential posts spotlighting emerging trends. From innovative investment strategies to insights on market dynamics, these resources offer a window into the evolving landscape. Stay ahead by exploring curated content that deepens your understanding of the industry’s pulse. Whether it’s a groundbreaking analysis or a thought-provoking discussion, these trending topics provide valuable knowledge for professionals seeking to refine their approach.
Smart Tactics for VC and PE Investments
Venture Capital (VC) and Private Equity (PE) investments operate on distinct principles, each tailored to different stages of business growth. VC focuses on early-stage startups, providing innovative funding methods to fuel their development and scalability. On the other hand, PE targets mature companies with established revenue streams, aiming to optimize operations and unlock higher value.
Emerging trends in both sectors highlight the importance of deal size in shaping returns. VC investments often involve smaller amounts spread across multiple startups, while PE deals are typically larger, concentrated on fewer companies. This divergence in strategy reflects their unique risk profiles and growth objectives.
What the Power Law Means for VC Success
Venture capital success often hinges on a phenomenon known as the power law. A small fraction of investments generates the majority of returns, creating a highly skewed performance curve. For example, in 2024, only 3.6% of VC exits accounted for an astonishing 78.9% of total returns. This underscores the critical importance of identifying and backing high-potential startups early. While most investments may yield modest outcomes, the few that succeed can redefine portfolios and drive exponential growth. Understanding this dynamic is essential for venture capitalists aiming to maximize their impact and achieve long-term success in a competitive market.
How Value Creation Works in VC and PE
Venture Capital (VC) and Private Equity (PE) firms employ distinct strategies to create value for their portfolio companies. VC firms prioritize early-stage growth by offering strategic advisory services and connecting startups with influential networks. This approach helps young companies scale quickly and secure additional funding.
On the other hand, PE firms focus on operational transformation. By applying sector-specific expertise, they optimize processes, reduce inefficiencies, and implement large-scale changes that drive profitability. PE firms often target mature businesses, aiming to unlock hidden potential through restructuring and innovation.
Understanding these contrasting methods highlights how VC and PE firms tailor their approaches to meet the unique needs of their investments, ultimately fostering growth and maximizing returns.
Your Guide to the Investment Lifecycle and Exits
The journey of an investment begins with fundraising, progresses through active management, and culminates in an exit strategy. Venture Capital (VC) and Private Equity (PE) firms both adhere to structured investment cycles, but their approaches to exits differ significantly. VC firms often aim for high-growth exits via IPOs or acquisitions, capitalizing on innovation and scalability. On the other hand, PE firms typically focus on acquisitions or secondary market sales, prioritizing stable returns and operational efficiency. Understanding these pathways is essential for investors seeking to align their strategies with the dynamics of the investment lifecycle.
Where to Learn More: Case Studies and Resources
For those eager to deepen their understanding of venture capital (VC) and private equity (PE), exploring real-world examples and curated resources can be invaluable. One standout is the Growth Case, which highlights how a scaling startup secured growth equity, effectively bridging the gap between late-stage VC rounds and smaller PE transactions. This case study provides practical insights into how these funding strategies overlap in real-world scenarios.
Dive into these resources to uncover actionable strategies and broaden your perspective on VC and PE dynamics.
Conclusion
Choosing between venture capital (VC) and private equity (PE) requires a clear understanding of their distinct approaches to value creation, risk profiles, and exit strategies. Throughout this blog, we’ve explored how VC focuses on early-stage growth and innovation, while PE emphasizes mature businesses and operational efficiency.
Recognizing these differences is crucial for aligning your funding strategy with your business goals. Whether you’re seeking rapid expansion or stable growth, evaluating your risk tolerance and long-term aspirations will guide you toward the right path.
If you’re ready to secure the funding that matches your vision, we at Qubit Capital are here to assist. We designed our Fundraising Assistance service to help you navigate the complexities of financing and take the next step confidently. Get in touch today to start your journey toward success.
Key Takeaways
Venture capital (VC) typically targets early-stage startups with high growth potential, while private equity (PE) focuses on mature businesses with established operations and cash flow.
Key deal dynamics, including investment size (PE deals often exceed $100 M versus VC rounds more commonly ranging from $25 M to $100 M), ownership stake, and risk appetite — differ substantially between VC and PE, influencing both investor expectations and company decision-making.
When it comes to value creation, VC firms often support scalable innovation and lean experimentation, while PE firms emphasize operational optimization, HR restructuring, and recruiting leadership talent.
Career paths in VC and PE diverge, with PE roles generally commanding higher compensation (first-year associates earning $250 K–$350 K compared to lower ranges in VC), differing workload intensity, and exit timelines, offering distinct professional trajectories for aspiring finance professionals.
Startups seeking funding, investors building portfolios, or professionals choosing between career tracks must understand these nuanced differences to make informed, strategic decisions.
Frequently asked Questions
What is the difference between venture capital and private equity?
Venture capital (VC) targets early-stage startups with high growth potential, offering funding for minority equity stakes, while private equity (PE) focuses on mature companies, often acquiring controlling interests to improve operations. VC involves higher risk for potential exponential returns, whereas PE uses structured strategies to mitigate risk and optimize profitability.


 Back
Back



